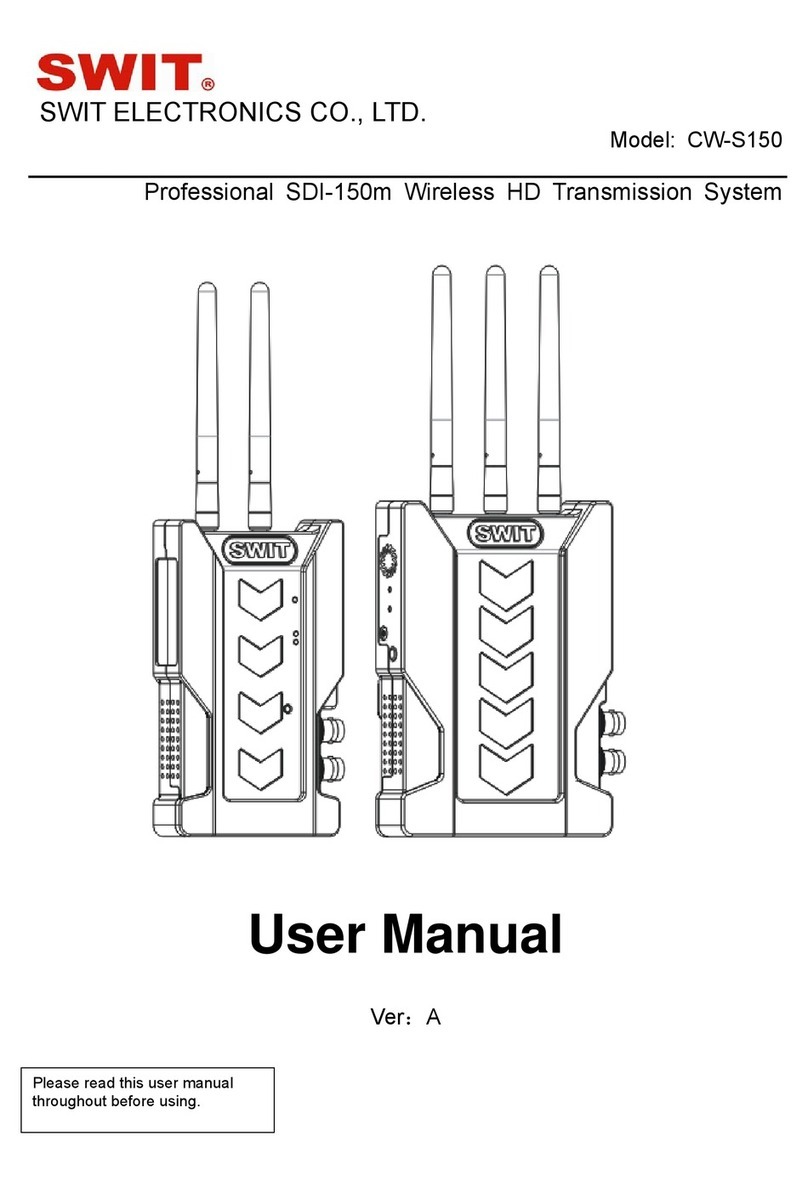
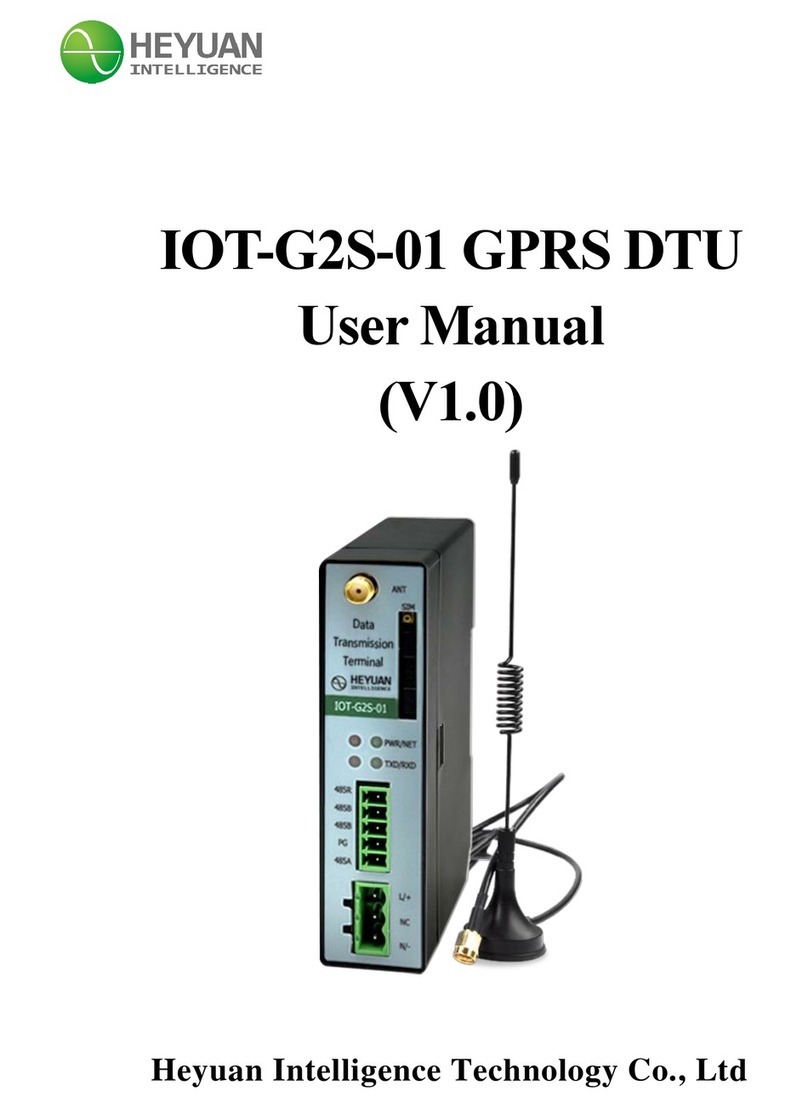
FCC Notice
According to FCC 15.407(e), the device is intended to operate in the frequency band of 5.15GHz
to 5.25GHz under all conditions of normal operation. Normal operation of this device is
restricted to indoor used only to reduce any potential for harmful interference to co-channel MSS
operations.
Reminder:
To comply with FCC part 15 rules, this WLAN Radio must only be used as a system as FCC
certified. The system must also be professionally installed to ensure compliance with the Part 15
certification and end users are not allowed to install by themselves. It is the responsibility of the
operator and professional installer to ensure that only certified systems are deployed in where
FCC rules apply.
Notice :
The changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance
could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
1. To comply with the FCC RF exposure compliance requirements, no change to the antenna or
the device is permitted. Any change to the antenna or the device could result in the device
exceeding the RF exposure requirements and void user’s authority to operate the device.
2. The Radio and Antenna must be professionally installed.
FCC RF Radiation Exposure Statement:
1. This Transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna
or transmitter.
2. This equipment complies with FCC RF radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with a minimum distance of
20 centimeters between the radiator and your body.