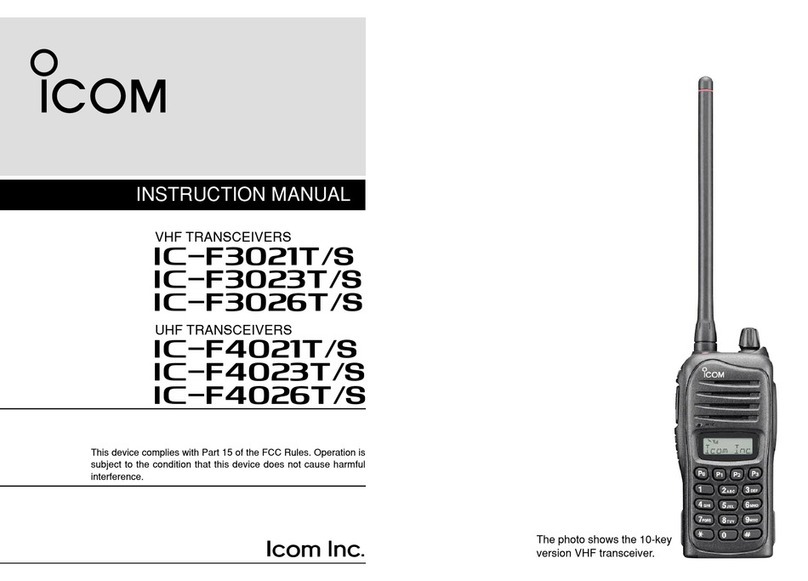
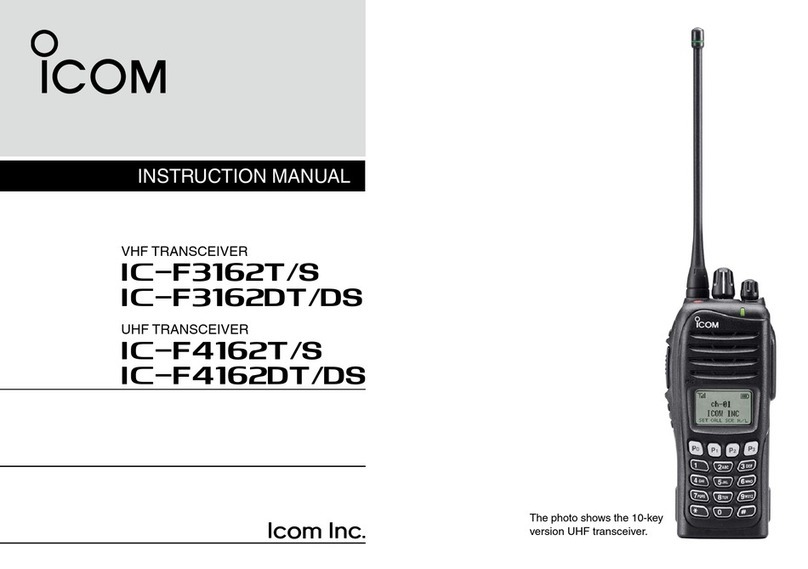
5 - 2
• While receiving 350–470 MHz
The 350–470 MHz band signals are passed through the LPF (L1–
L3, C1–C6), HPF (L4, C7–C9) and attenuator (D7), then applied
to the RF amplifier (Q600) via the band switch (D600) and HPF
(L600, L601, L608, L611, C600–C602, C630, C631, C633).
The amplified signals are applied to the tuned RF amplifiers for
A_BAND (Q601, D601, D602, D604, D605) and B_BAND (Q651,
D650, D651, D653, D654).
The amplified signals by Q601 are then applied to the A_BAND
1st mixer (IC900, pin 1) via the band switch (D606).
The amplified signals by Q651 are then applied to the B_BAND
1st mixer (MAIN UNIT; IC50, pin 1) via the band switch (D655) and
J1001 (pin 15).
- 350–470 MHz -
• While receiving 600–999 MHz
The 600–999 MHz band signals are passed through the HPF
(L8, L9, C16–C18) and band switch (D700), then applied to the
tuned RF amplifier (Q700, Q701, D702–D704) via the attenuator
(D701).
The amplified signals are applied to the A_BAND 1st mixer (IC900,
pin 1) via the band switch (D706).
- 600–999 MHz -
5-1-2 1ST IF CIRCUITS (RF AND MAIN UNITS)
The 1st IF circuits contain the 1st mixer, 1st IF amplifier and the
1st IF filter. The 1st IF mixer converts the received signals into a
fixed frequency of the 1st Intermediate Frequency (IF) signal. The
converted 1st IF signal is filtered at the 1st IF filters and amplified
at the IF amplifier.
• A_BAND (0.495–999 MHz)
The received signals from the RF circuits are applied to the A_
BAND 1st IF mixer (RF UNIT; IC900, pin 1), and converted into
the 61.65 MHz (FM/AM)/59.25 MHz (WFM) 1st IF signal by being
mixed with 1st Local Oscillator (LO) signals from the VCOs (VCO
UNIT).
While receiving 0.495–76 MHz band signals, the 1st LO signals
are generated at BC BAND VCO (VCO UNIT; Q1, D1, D3, D5, D6),
and for receiving 76–260 MHz band signals, the 1st LO signals are
generated at VHF BAND VCO (VCO UNIT; Q51, D51, D54).
Tuned RF amplifier
D604, D605 Q601 D601, D602
D606
to the A_BAND
1st mixer
(IC900, pin 1)
Tuned RF amplifier
D653, D654 Q651 D650, D651
D600
D655
to the
B_BAND 1st mixer
(MAIN UNIT; IC50, pin 1)
ATT
D7
from the
antenna
HPF
Q600 350
-
470 MHz
RF
amp.
HPF LPF
from the
antenna
Tuned RF amplifier
600
-
999 MHz
D703, D704
D701
HPFATT
Q700 D702Q701
D706
to the A_BAND
1st mixer
(IC900, pin 1)
D700
While receiving 260–999 MHz band signals, the 1st LO signals are
generated at UHF BAND VCO (VCO UNIT; Q101, D101, D104).
If the receiving frequency is 600 MHz or higher, the VCO output
signal is doubled at the doubler circuit (RF UNIT; Q850) before
being applied to the 1st mixer (RF UNIT; IC900, pin 3).
In FM/AM mode, the converted IF signal is applied to the 1st IF
filter (MAIN UNIT; FI1) via the mode switch (D2) to filter out the
unwanted signals, then applied to the IF amplifier (MAIN UNIT;
Q100).
In WFM mode, the converted IF signal is applied to the 1st IF
amplifier (MAIN UNIT; Q1) via the mode switch (D2).The amplified
1st IF signal is applied to the 2nd IF mixer (MAIN UNIT; Q2), and
converted into the 13.35 MHz IF signal by being mixed with the
45.95 MHz Lo signal. The converted IF signal is passed through
the IF filter (MAIN UNIT; FI2) to filter out the unwanted signal, then
applied to the IF amplifier (MAIN UNIT; Q100).
The amplified 1st or 2nd IF signal from the IF amplifier (MAIN
UNIT; Q100) is then applied to the A_BAND IF IC (MAIN UNIT;
IC100, pin 16).
• A_BAND 1st IF CIRCUIT
• B_BAND (118–174 MHz, 350–470 MHz.)
The received signals from the RF circuits are applied to the
B_BAND 1st IF mixer (MAIN UNIT; IC50, pin 1), and converted
into the 46.35 MHz 1st IF signal by being mixed with 1st Local
Oscillator (LO) signals from the VCOs.
While receiving 118–174 MHz band signals, the 1st LO signals are
generated at B_BAND VBVCO (MAIN UNIT; Q301, D300, D301),
and for receiving 350–470 MHz band signals, the 1st LO signals
are generated at B_BAND UBVCO (MAIN UNIT; Q351, D350,
D352).
The converted 1st IF signal is passed through the 1st IF filter
(MAIN UNIT; FI50) to filter out the unwanted signal, then applied to
the 1st IF amplifier (MAIN UNIT; Q200). The amplified 1st IF signal
is then applied to the B_BAND IF IC (MAIN UNIT; IC200, pin 16).
• B_BAND 1st IF CIRCUIT
IF
amp.
D3 D2
1st/2nd IF
signal to
the IF IC
(IC100, pin 16)
BPF
FI1
LO signal
from the TCXO (X450)
via Q450, Q451
61.65 MHz
(FM/AM)
BPF
FI2
13.35 MHz
(WFM)
Q100
Q1Q2
IF
amp.
LO signals
from the VCOs
Received signals
from the
RF circuits
1st mixer
IC900
MAIN UNIT
RF UNIT
1st IF signal
to the IF IC
(IC200, pin 16)
BPF
46.35 MHz
Q200
IF
amp.
LO signals
from the VCOs
Received signals
from the
RF circuits
1st mixer
IC50
MAIN UNIT
FI50