Always tighten the bolts at the specified torque. If the torque is
insufficient or excessive, the bolt will break, which is dangerous as the
chuck or work will fly out. Use the bolts attached to the chuck, and do not
use bolts other than these.
・If the torque is insufficient or
excessive, the bolt will break, which
is dangerous as the chuck or work
will fly out.
・Fix the lathe spindle or the chuck
when you tighten bolts. Your hand
could slip and get injury when you
work without fixing the spindle.
・You cannot control the torque by a
hex key. You must use a torque
wrench for torque control.
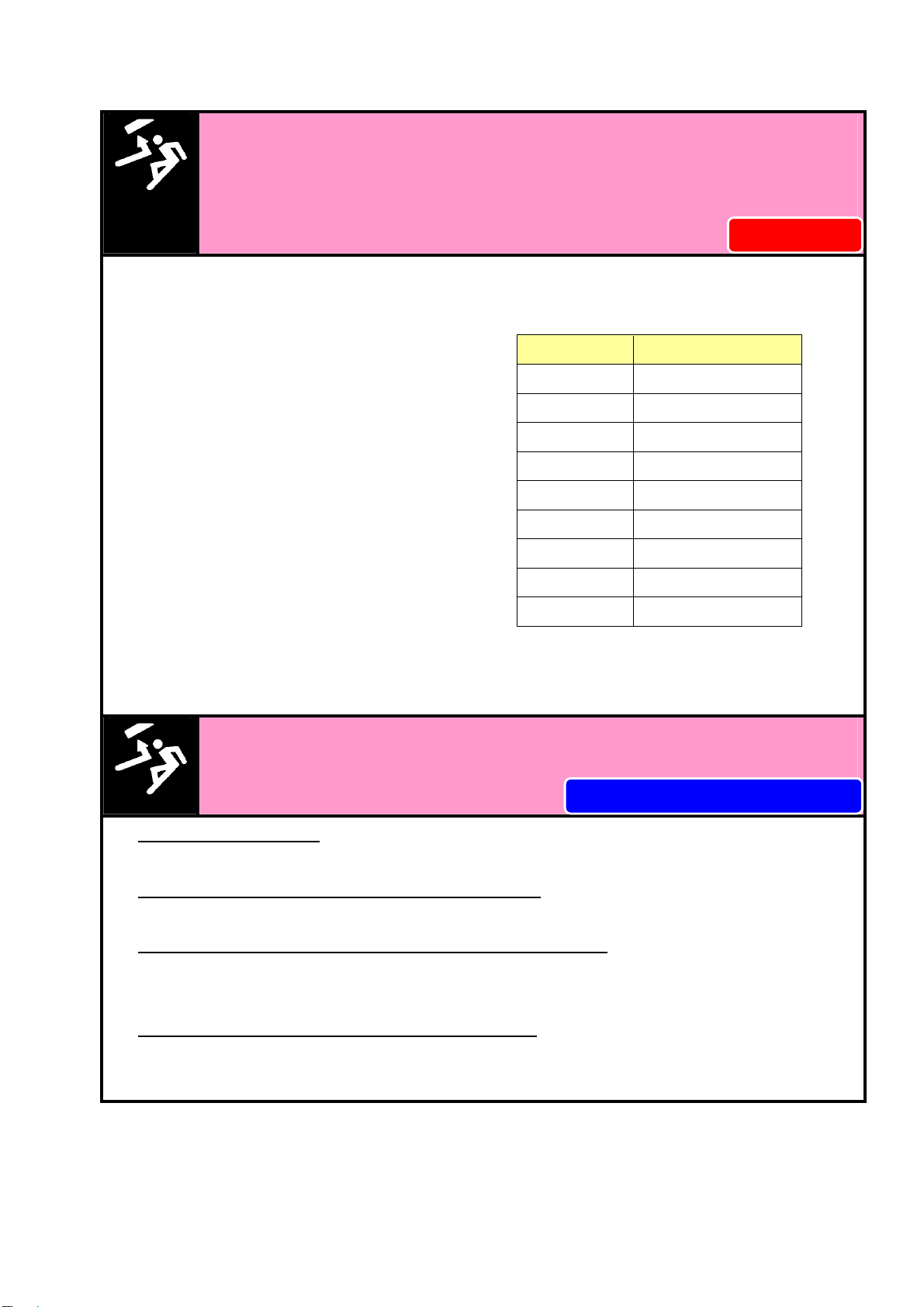
・Tighteningtorqueismomentofforcewhenyoutightenabolt.Tighteningtorque=F×L.
Provide sufficient strength for the draw pipe.
Provide sufficient screw depth for the draw pipe.
Firmly tighten the draw pipe.
・If the draw pipe break, the gripping force is instantly lost and this is dangerous as work
will fly out.
・If the screw depth of the draw pipe is insufficient, the screw will break and the gripping
force will be lost instantly, and this is dangerous as work will fly out.
・If the engagement of the screw of the draw pipe is loose, vibration may occur resulting
in breakage of the screw. If the screw breaks, the gripping force will be lost instantly,
which is dangerous as the work will fly out.
・If the draw pipe is unbalanced, vibration occurs, the screw is broken and the gripping
force will be lost instantly, which is dangerous as the work will fly out.
Specified torque for
socket head cap screw
Bolt size Tightening torque
M4 3.8 N・m
M5 7.5 N・m
M6 13 N・m
M8 33 N・m
M10 73 N・m
M12 107 N・m
M14 171 N・m
M16 250 N・m
M20 402 N・m
For Machine Tool Manufactures
For All Users