Table o Contents
1 Welcome............................................................................................................................................................................. 5
1.1 his guide................................................................................................................................................................... 5
1.2 Why RS-232 FPGA boards?....................................................................................................................................... 5
1.3 he Pluto boards........................................................................................................................................................ 5
1.4 Boards characteristics................................................................................................................................................ 5
2 Software tools..................................................................................................................................................................... 6
2.1 Important downloads.................................................................................................................................................. 6
2.2 FPGA software........................................................................................................................................................... 6
2.3 C/C++ compiler........................................................................................................................................................... 6
3 FPGAconf........................................................................................................................................................................... 7
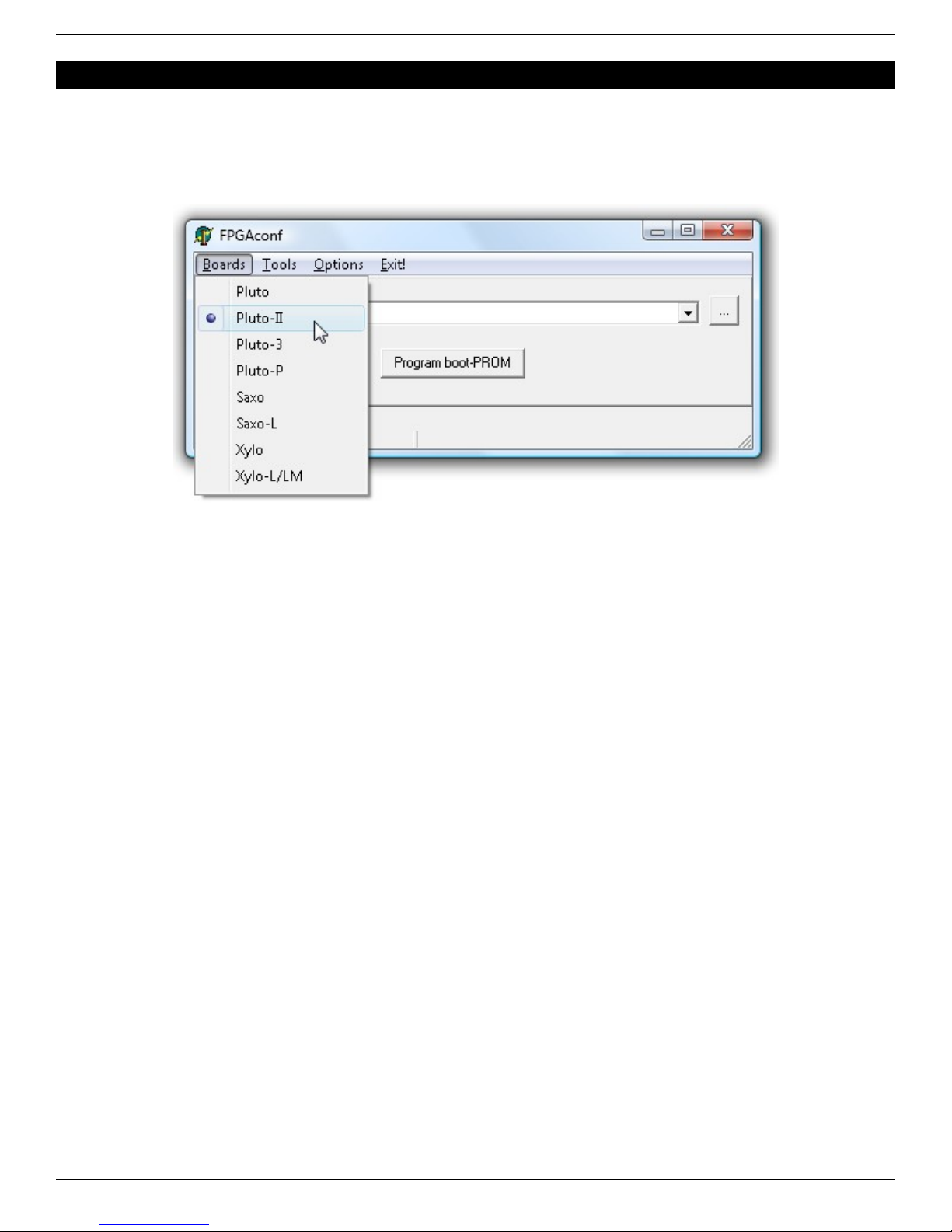
3.1 Board selection........................................................................................................................................................... 7
3.2 Configuring the FPGA................................................................................................................................................ 7
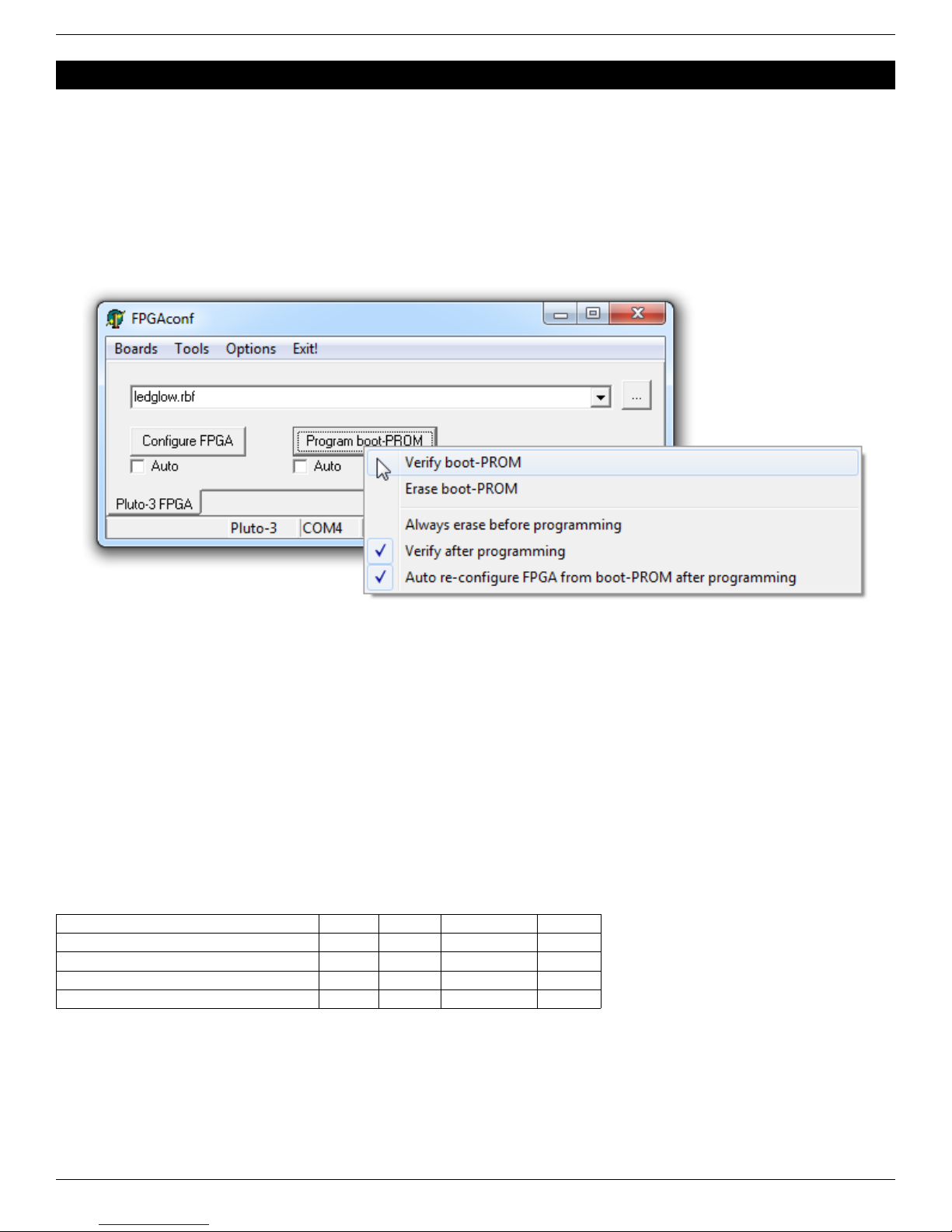
3.3 FPGAconf options...................................................................................................................................................... 7
4 FPGA boot-PROM (Pluto-II/-IIx/-IIx HDMI/-3)..................................................................................................................... 8
4.1 What's the boot-PROM?............................................................................................................................................. 8
4.2 Boot-PROM actions.................................................................................................................................................... 8
4.3 Boot-PROM requirements.......................................................................................................................................... 8
4.4 Boot-PROM and J AG............................................................................................................................................... 8
4.5 Boot-PROM on-demand FPGA configuration............................................................................................................. 8
5 FPGAconf extras................................................................................................................................................................ 9
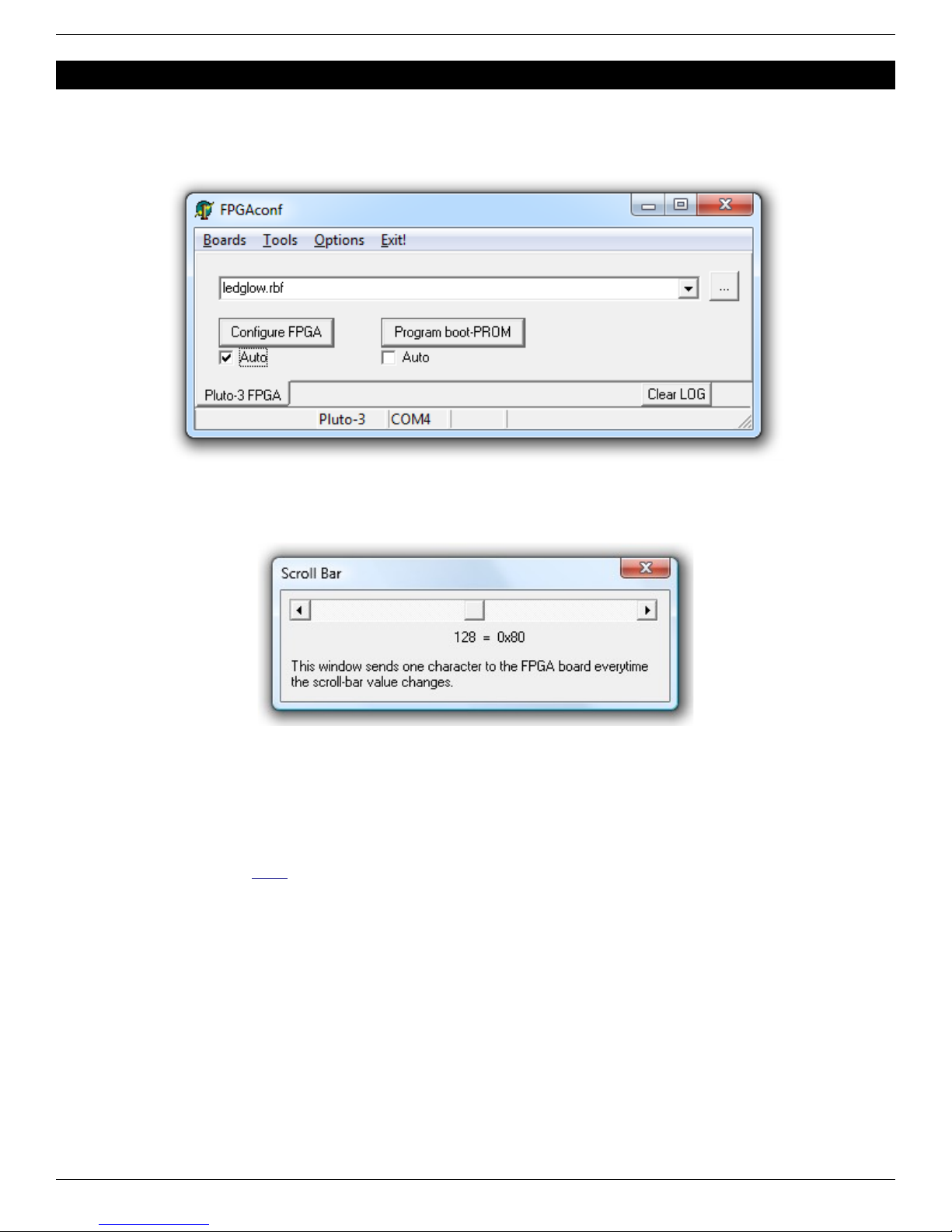
5.1 Auto configuration mode............................................................................................................................................. 9
5.2 Scrollbar..................................................................................................................................................................... 9
5.3 erminal...................................................................................................................................................................... 9
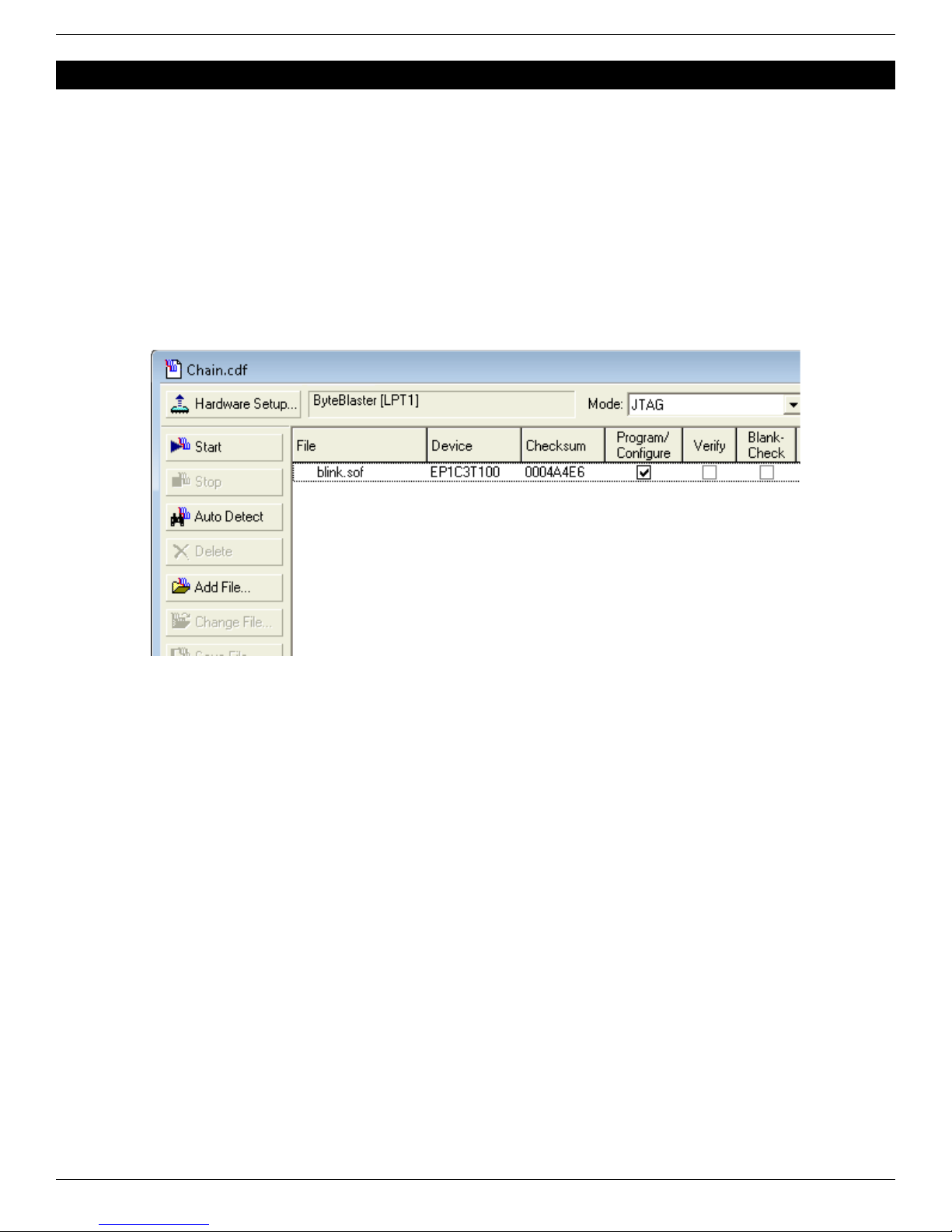
6 FPGA configuration using Quartus-II J AG support (Pluto-II/-3)......................................................................................10
6.1 J AG requirements................................................................................................................................................... 10
6.2 J AG configuration................................................................................................................................................... 10
7 FPGA project using Quartus-II (Pluto/-II/-3)...................................................................................................................... 11
7.1 Create a new project................................................................................................................................................. 11
7.2 A simple start............................................................................................................................................................ 11
8 FPGA projects with Xilinx's ISE (Pluto-IIx/HDMI).............................................................................................................. 12
8.1 Create a new project................................................................................................................................................ 12
8.2 A simple start............................................................................................................................................................ 12
9 FPGA connections............................................................................................................................................................ 13
9.1 FPGA pins................................................................................................................................................................ 13
9.2 IO headers................................................................................................................................................................ 13
9.3 Boot-PROM connection (Pluto-II/-IIx/HDMI/-3).........................................................................................................13
9.4 HDMI (Pluto-IIx/HDMI).............................................................................................................................................. 13
9.5 Power header........................................................................................................................................................... 13
9.6 XDI connector......................................................................................................................................................... 14
9.7 Secondary connector................................................................................................................................................ 14
10 J AG connection............................................................................................................................................................ 15
10.1 J AG on Pluto........................................................................................................................................................ 15
10.2 J AG on Pluto-II..................................................................................................................................................... 15
10.3 J AG on Pluto-IIx/HDMI......................................................................................................................................... 15
10.4 J AG on Pluto-3..................................................................................................................................................... 15
11 Flashy boards................................................................................................................................................................. 16
11.1 FlashyMini design................................................................................................................................................... 16
11.2 FlashyDemo design................................................................................................................................................ 16
12 FPGA configuration through RS-232.............................................................................................................................. 17
12.1 Pluto/-II/-IIx FPGA configuration............................................................................................................................. 17
With a UAR .............................................................................................................................................................. 17
Without a UAR ......................................................................................................................................................... 17
12.2 Pluto-3 FPGA configuration.................................................................................................................................... 17
13 Quartus-II J AG indirect mode (Pluto-II/-3).................................................................................................................... 18
13.1 What is it?............................................................................................................................................................... 18
13.2 Create a “J AG indirect configuration” file.............................................................................................................. 18
13.3 Program the boot-PROM........................................................................................................................................ 18
14 Power requirements....................................................................................................................................................... 19
14.1 Wall adapter........................................................................................................................................................... 19
14.2 USB to power jack cable......................................................................................................................................... 19
FPGA RS-232 development boards Page 2