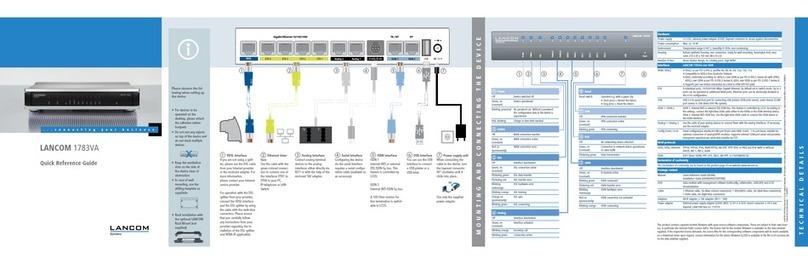
LANCOM 3850 UMTS
Preface
3
EN
Preface
Thank you for placing your trust in this LANCOM product.
The combination of UMTS/HSDPA, WLAN, DSL and VPN opens up a completely
new range of possibilities in enterprise connectivity—for example, mobile
conference rooms that are connected via UMTS/HSDPA and offer Internet
access over WLAN or access to the company network via VPN.
As a back-up connection for site coupling, UMTS/HSDPA is cheaper and faster
than the conventional alternative, ISDN. Furthermore, it is significantly less
prone to failure as there are no cables which are at risk from construction
works. Using VRRP with the LANCOM 3850 UMTS offers fully vendor-inde-
pendent high availability and a completely transparent, automatic switch of
media in the event of backup.
Apart from that, UMTS/HSDPA is able to bridge the “last mile” for customers
who do not have access to an equivalent broadband connection. The UMTS/
HSDPA card is simply operated in the CardBus expansion slot of the LANCOM
3850 UMTS. The device automatically switches Internet access between
HSDPA, UMTS and GPRS depending on availability.
Security settings
To maximize the security available from your product, we recommend that you
undertake all of the security settings (e.g. firewall, encryption, access protec-
tion) that were not already activated when you purchased the product. The
LANconfig Wizard 'Security Settings' will help you with this task. Further infor-
mation is also available in the chapter 'Security settings'.
We would additionally like to ask you to refer to our Internet site
www.lancom.eu for the latest information about your product and technical
developments, and also to download our latest software versions.
User manual and reference manual
The documentation of your device consists of the following parts:
Installation guide
User manual
Reference manual
You are now reading the user manual. It contains all information you need to
put your device into operation. It also contains all of the important technical
specifications.