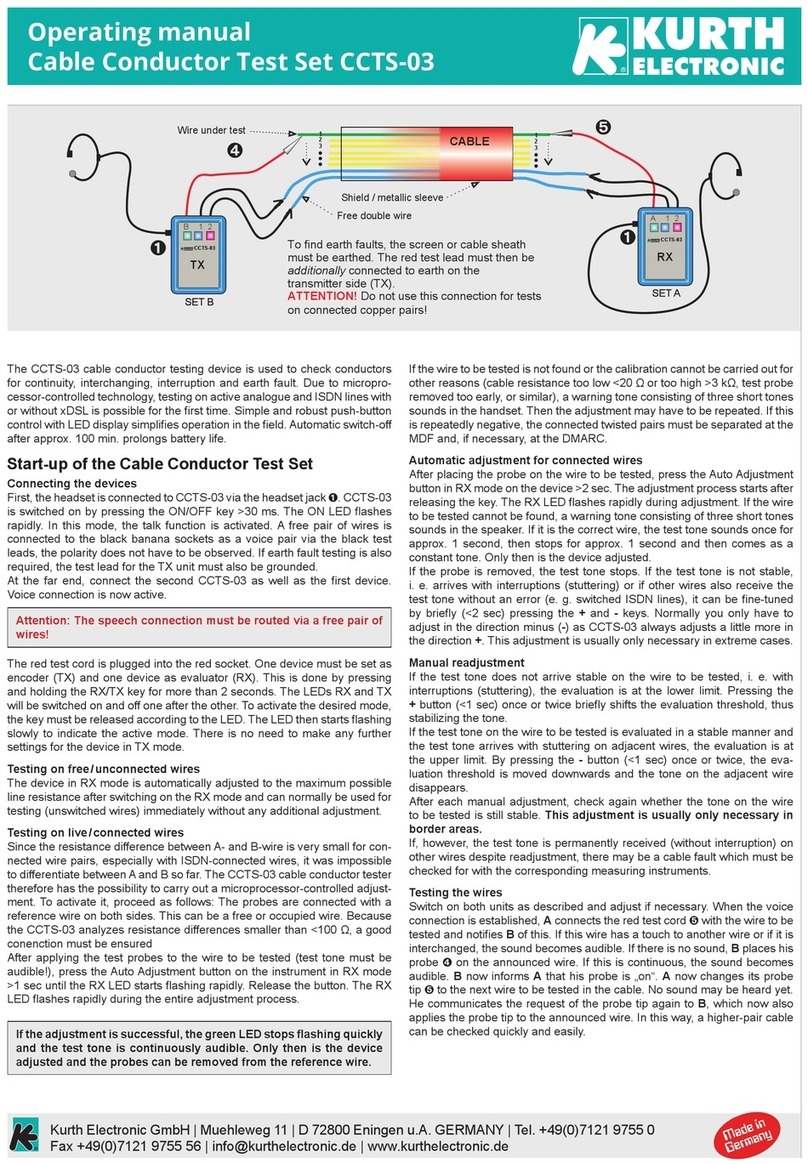
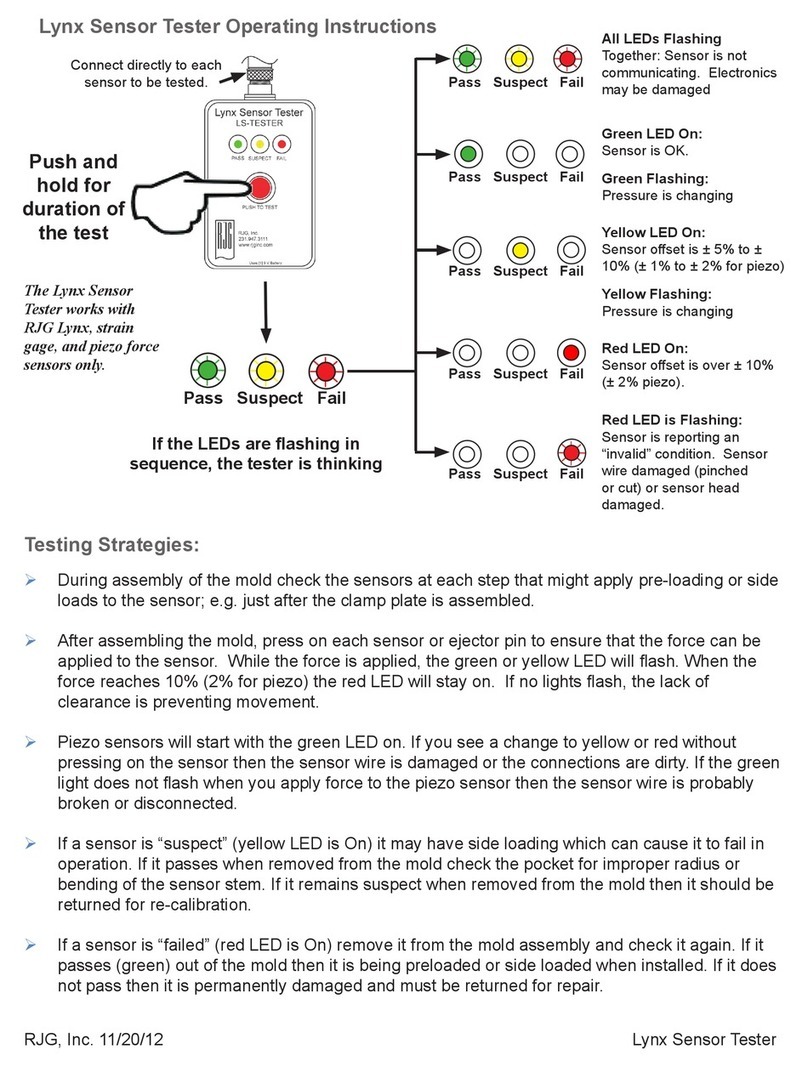
Table of Contents OX-TRAN Model 2/22 Operator’s Manual
vi Revision R MOCON, Inc.
Chapter 5: Testing Flat Film Samples .......................................................................................................5-1
Testing Suggestions.............................................................................................................................5-1
Preparing for a Film Test......................................................................................................................5-2
Sample Size.........................................................................................................................................5-2
Using Masks ........................................................................................................................................5-2
Orienting the Sample ...........................................................................................................................5-3
Humidified Testing ...............................................................................................................................5-4
Filling the Humidifiers...........................................................................................................................5-4
Filling the Humidifiers during a Test .....................................................................................................5-4
Mounting a Sample in the Test Cell......................................................................................................5-6
Loading and Unloading the Test Cell....................................................................................................5-7
Setting Up and Starting a Film Test......................................................................................................5-8
Monitoring and Controlling a Film Test .................................................................................................5-8
Chapter 6: Testing Packages....................................................................................................................6-1
Testing Suggestions.............................................................................................................................6-1
Preparing the Instrument for a Package Test .......................................................................................6-2
Package Testing Methods....................................................................................................................6-3
Testing using Ambient Conditions ..................................................................................................6-3
Package Conditioning.....................................................................................................................6-3
Testing using an Environmental Chamber......................................................................................6-3
Package Mounting Methods.................................................................................................................6-4
Mounting Bottles, Cups and Trays using a Package Plate..............................................................6-4
Mounting Pouches and Bags..........................................................................................................6-5
Supplying a Test Gas...........................................................................................................................6-6
Using Ambient Air for the Test Gas ................................................................................................6-6
Using a Compressed Gas for the Test Gas ....................................................................................6-6
Setting Up and Starting a Package Test...............................................................................................6-8
Monitoring and Controlling a Package Test ..........................................................................................6-8
Chapter 7: Maintenance............................................................................................................................7-1
Cleaning the Instrument .......................................................................................................................7-1
Cleaning the Air Filters.........................................................................................................................7-2
Cleaning the Test Cells ........................................................................................................................7-3
Maintaining the Test Cells ....................................................................................................................7-3
Drying Out the Humidifiers ...................................................................................................................7-3
Test Cell Components and Part Numbers ............................................................................................7-4
Maintaining the Oxygen (Coulox) Sensor .............................................................................................7-5
Verifying Oxygen Sensor (Coulox) Performance ............................................................................7-5
Replacing the Coulox Sensor .........................................................................................................7-5
Maximizing Coulox Sensor Life ......................................................................................................7-5
System Standby...................................................................................................................................7-6
System Shutdown for Storage or Repair ..............................................................................................7-6
Chapter 8: Troubleshooting.......................................................................................................................8-1
Error Messages and Warnings .............................................................................................................8-1
Troubleshooting Testing Problems .......................................................................................................8-1
Recovering from a Sensor Over-Range Condition................................................................................8-2
Recovering from a Power Failure .........................................................................................................8-2
Chapter 9: Specifications ..........................................................................................................................9-1
Physical Specifications.........................................................................................................................9-1
Environmental Requirements ...............................................................................................................9-1
Electrical Requirements .......................................................................................................................9-1
Gas Supply Requirements ...................................................................................................................9-2