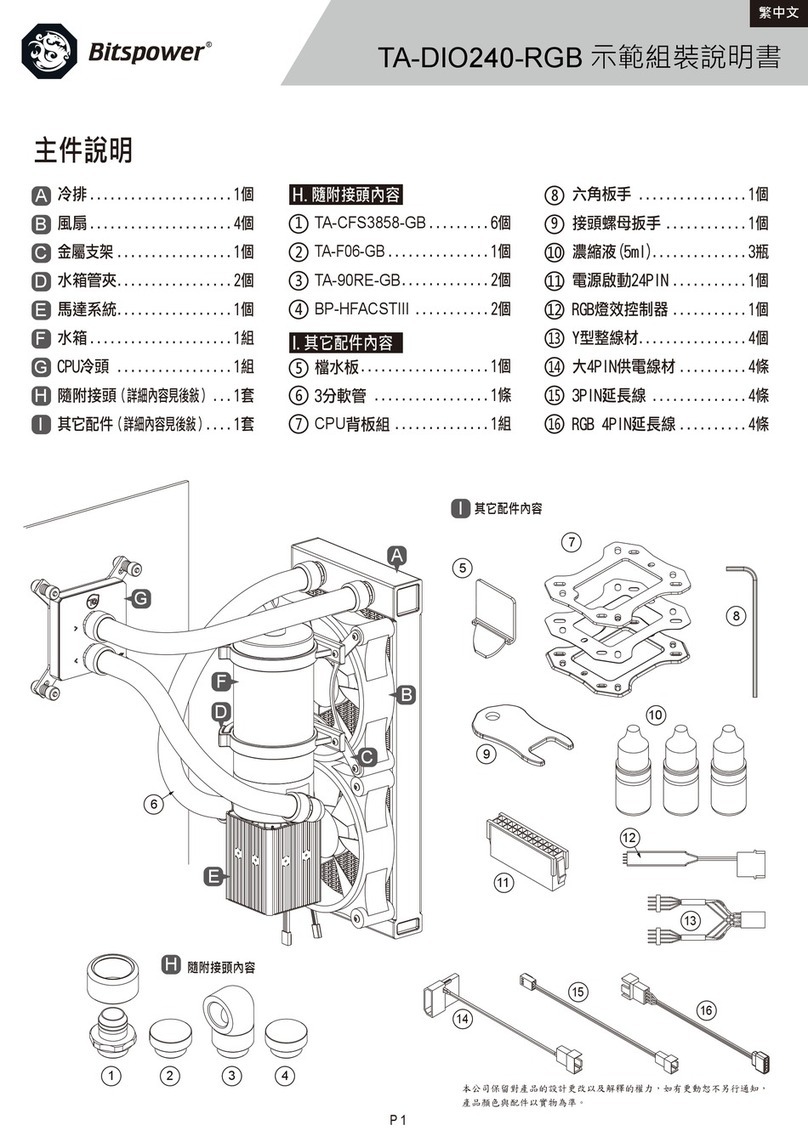
Lauterbach ICE Emulator User manual

ICE Emulator for 8051 1
©1989-2019 Lauterbach GmbH
ICE Emulator for 8051
TRACE32 Online Help
TRACE32 Directory
TRACE32 Index
TRACE32 Documents ......................................................................................................................
ICE In-Circuit Emulator .................................................................................................................
ICE Target Guides ......................................................................................................................
ICE Emulator for 8051 ............................................................................................................. 1
WARNING .............................................................................................................................. 3
Quick Start ............................................................................................................................ 4
Troubleshooting ................................................................................................................... 7
FAQ ........................................................................................................................................ 8
Configuration ........................................................................................................................ 12
8051 12
80152 13
80C152JA DIL 13
80C152JA-PLCC 13
80C152JB-PLCC 13
C515C 13
C505C 14
Basics .................................................................................................................................... 15
Emulation Modes 15
SYStem.Clock Clock generation 16
SYStem.CPU CPU modes 17
SYStem.Access Dualport access 17
General SYStem Settings and Restrictions ....................................................................... 18
General Restrictions 18
Special I/O-Register Module M582 18
Special I/O-Register Module MCL580 21
Special I/O-register Module 517E 22
Internal Memory 23
SYStem.Line Bus configuration 24
SYStem.Line CPU signals 25
SYStem.Option DUMMY DUMMY cycles 25
SYStem.Options ................................................................................................................... 26
SYStem.Option IOSTOP Stop peripherals 26

ICE Emulator for 8051 2
©1989-2019 Lauterbach GmbH
SYStem.Option DMA DMA operation 27
SYStem.Option TestClock Clock error check 28
Exception Control ................................................................................................................ 29
eXception.Activate Force exception 29
eXception.Enable Enable exception 29
eXception.Trigger Trigger on exception 30
eXception.Pulse Stimulate exception 31
Banked Target Systems ....................................................................................................... 32
Internal 32
External 33
Memory Access Routines 36
Memory Classes ................................................................................................................... 37
State Analyzer ....................................................................................................................... 38
Keywords for the Trigger Unit 38
General 8051 Keywords for the Trigger Unit 38
80152 Keywords for the Trigger Unit 39
Keywords for the Display 40
Dequeueing 40
Port Analyzer ........................................................................................................................ 41
Keywords for the Port Analyzer 41
Additional Trace Channels 42
Module 8051 42
Module M582 42
Adapter M582-C562 42
Adapter M582-C552 42
Module M592 43
Module S517-C535 43
Module 80152 43
Module MCL580 44
Support .................................................................................................................................. 45
Compilers 45
3rd-Party Tool integrations 45
Realtime Operation Systems 46
Emulation Frequency ........................................................................................................... 47
Emulation Modules .............................................................................................................. 49
Module Overview 49
Order Information 53
Physical Dimensions ........................................................................................................... 54
Adapter .................................................................................................................................. 79

ICE Emulator for 8051 3
©1989-2019 Lauterbach GmbH
ICE Emulator for 8051
Version 06-Nov-2019
For general informations about the In-Circuit Debugger refer to the “ICE User’s Guide” (ice_user.pdf). All
general commands are described in “PowerView Command Reference” (ide_ref.pdf) and “General
Commands and Functions”.
WARNING
NOTE: Do not connect or remove probe from target while target power is ON.
Power up: Switch on emulator first, then target
Power down: Switch off target first, then emulator
P:000072 \\KEILS\KEILS\sieve+6F ........... MIX AI
E::w.d.l
addr/line code label mnemonic comment
P:00006E 351D addc a,1D ; a,primz
P:000070 F51F mov 1F,a ; k,a
32 while ( k <= SIZE )
P:000072 C3 clr c
P:000073 E520 mov a,20
P:000075 9413 subb a,#13
P:000077 E51F mov a,1F ; a,k
P:000079 9400 subb a,#0
P:00007B 30D202 jnb ov,80
P:00007E B2E7 cpl acc.7
E::w.v.f /l /c E::w.r
while ( TRUE ) Cy _ R0 8 A 0 SP >00
{ AC _ R1 0 B 0 -01 B2
sieve(); F0 0 R2 0 IE 0 -02 00
-000 sieve() RS 0 R3 0 DPTR 0 -03 00
i = 0 Ov _ R4 0 PSW 0 -04 03
primz = 3 F1 0 R5 0 PC 72 -05 00
k = 3 P _ R6 0 SP 24 -06 03
anzahl = 0 Tsk R7 0 XSP 0 -07 00

ICE Emulator for 8051 4
©1989-2019 Lauterbach GmbH
Quick Start
Before debugging can be started, the emulator must be configured by software:
Ready to run setup files for most standard compilers can be found on the software CD in the directory
…/Demo/I51/Compiler. All setup files are designed to run the emulator stand alone without target
hardware.
The following description should make the initial setup (to run the emulator together with the target
hardware) easier. It describes a typical setup with frequently used settings. It is recommended to use the
programming language PRACTICE to create a batch file, which includes all necessary setup commands.
PRACTICE files (*.cmm) can be created with the PRACTICE editor pedit (Command: PEDIT <file name>)
or with any other text editor.
A basic setup file includes the following parts:
1. Set cpu-type and -mode
2. Set system options
3. Select dualport mode (optional)
4. Set mapper (optional)
5. Select frequency (optional)
6. Activate the emulator
7. Load application file (optional)
8. Set breakpoints (optional)
9. Start application
10. Stop application (optional)

ICE Emulator for 8051 5
©1989-2019 Lauterbach GmbH
Here a typical example, how to setup the system:
1. Set cpu-type
The command sys.cpu is used to select one derivative within a cpu-family and to set its operation
mode.
2. Set system options
The system window controls the CPU specific setup. Please check this window very carefully and set
the appropriate options. Use the button in the main tool bar and click to the option check box
(Command: HELP.PICK) to get online help in a pop up window.
3. Select dualport mode (optional)
Dualport allows access to emulation RAM, while emulation is running. This is necessary to display
variables, set breakpoints or display the flag listings while the emulation is running. System.Access
selects how dualport access is done.
4. Set mapper (optional)
The mapper controls the memory access of the CPU. This means the use of internal or external
memory, the protection of a memory bank etc. Address ranges must be defined by using memory
classes.
5. Select frequency (optional)
The CPU can be clocked by an internal (emulator) or external (target) clock source. If the internal
clock is used, the clock is provides by the VCO of the emulator. The setting of the internal clock is
done by the “vco” command.
The current CPU frequency can be displayed in the counter window.
system.down
system.cpu I8051
; switch the system down
; select derivative Intel 8051
system.option IOSTOP on ; switch IOSTOPE mode on
system.access denied ; denied: dualport is disabled
map.reset
map.ram P:0x0--0x07fff
map.ram X:0--0x0FFFF
map.intern P:0x0--0x07fff
map.extern X:
; reset mapper (all external)
; emulation RAM: 32KB (e.g. for
; program)
; emulation RAM: 64 KB (e.g. for data)
; map program memory internal
; map data memory external
vco.clock 20. ; input clock to the EXTAL pin of the cpu is set
; to 20 MHz (only necessary if internal clock is
; used)
?

ICE Emulator for 8051 6
©1989-2019 Lauterbach GmbH
6. Activate the emulator
When the emulator is activated a debug-monitor program is loaded into a hidden emulator memory.
Afterwards, a bondout reset-signal is inactivated and the monitor program starts. This program allows
access to user memory (data.dump, data.list) and cpu-registers, and gives control to start and stop
the emulation.
7. Load application file (optional)
Application can be loaded by various file formats. UBROF format is often used to load code and
symbol information. For information about the load command for your compiler see Compiler.
8. Set breakpoints (optional)
There are several ways to set breakpoints (Command: Break.Set). Breakpoints can be displayed
using the Break.List command.
9. Start application
Application can be started with giving a break address. For example ”go main” starts the application
and stops at symbol main.
10. Stop application (optional)
Application can be breaked manually by using th BREAK command.
system.mode emulint ; system works with internal target
; clock
data.load.ih test.hex ; load application file
breakpoint.set main /program
breakpoint.set flags /write
; set program break on function
; main
; set write break on variable
; ’flags’
go ; run application
break ;break application manually

ICE Emulator for 8051 7
©1989-2019 Lauterbach GmbH
Troubleshooting
No Information available.

ICE Emulator for 8051 8
©1989-2019 Lauterbach GmbH
FAQ
Debugging via
VPN
Ref: 0307
The debugger is accessed via Internet/VPN and the performance is very
slow. What can be done to improve debug performance?
The main cause for bad debug performance via Internet or VPN are low data
throughput and high latency. The ways to improve performance by the debugger
are limited:
In PRACTICE scripts, use "SCREEN.OFF" at the beginning of the script
and "SCREEN.ON" at the end. "SCREEN.OFF" will turn off screen
updates. Please note that if your program stops (e.g. on error) without exe-
cuting "SCREEN.OFF", some windows will not be updated.
"SYStem.POLLING SLOW" will set a lower frequency for target state
checks (e.g. power, reset, jtag state). It will take longer for the debugger to
recognize that the core stopped on a breakpoint.
"SETUP.URATE 1.s" will set the default update frequency of
Data.List/Data.dump/Variable windows to 1 second (the slowest possible
setting).
Prevent unneeded memory accesses using "MAP.UPDATEONCE
<address_range>" for RAM and "MAP.CONST <address_range>" for
ROM/FLASH. Address ranged with "MAP.UPDATEONCE" will read the
specified address range only once after the core stopped at a breakpoint or
manual break. "MAP.CONST" will read the specified address range only
once per SYStem.Mode command (e.g. SYStem.Up).

ICE Emulator for 8051 9
©1989-2019 Lauterbach GmbH
Ta r g e t Po w e r
Supply Switch
Ref: 0103
Is there a simple way to control target power supply via the ICE to prevent
problems after the ICE has been powered off?
Follow the sequence below.
If you own an output probe COUT8, connect it to the STROBE output con-
nector.
Type PULSE2. and press F1. You will get the pin out of the output probe
COUT8. Pin 13 (OUT6) delivers +5 V after the emulator has finished its ini-
tialization and 0 V if the emulator is powered off. This can be used to drive
a relay via a transistor to switch the target power on and off automatically if
the Pulse Generator is not used for other purposes. The schematic of the
switching unit can be found in the file TARGETC.CMM.
Additionally Pin 13 (OUT6) can be controlled by ICE commands.
Target power supply off. "PULSE2.P +"
Target power supply on. "PULSE2.P -"
The following PRACTICE command file creates 3 buttons in the Toolbox for:
Target power on
Target power off
Target power off and QUIT.
To show the buttons automatically after starting the TRACE32 software, call the
script with the DO command from system-settings.cmm in your TRACE32
system directory (create system-settings.cmm if it does not exist).
https://www.lauterbach.com/faq/targetc.cmm
Wrong
Location after
Break
Ref: 0030
Why is the location after break wrong?
Most emulators use some bytes of user stack for the break system. Therefore it
is necessary to have valid stack, if single step or breakpoints are used.
Bank Number
for Bank File
(*.bnk)
Ref: 0114
Which number contains R6 if the bank file is called?
The parameter value in R6 of the bank file contains the number of the requested
bank. However, it depends on the used bank logic if R6 contains value 1 for the
bank 1. A better description is, that R6 contains the same value as the value of
the bank probe input lines for the appropriate bank number. If there is a address
translation by the MMU command, R6 could contain 3 for bank 1 depending on
the address translation.
8051
Banking using
8051 Ports
Ref: 0049
I have some problems using 8051 ports as a bank register. Do you know
reasons for that behavior?
If port pins are used as additional address lines for banking purposes, the
address lines must be synchronized to the regular addresses. In other case,
nobody can predict when the port pins are valid. Refer to the manufactures 8051
manual.

ICE Emulator for 8051 1 0
©1989-2019 Lauterbach GmbH
8051
CPU Internal
Memory
Externally
Ref: 0010
Can I map the CPU internal memory externally?
No, not recommended.
The CPU internal programm area must be mapped internally because this
memory is an on-chip memory. If the 8051 is in microcontroller mode (EA=1),
the program area can never be substituted with a memory on the target. The
CPU internal data area can not be mapped externally as well, because there is
no access to the internal address and data bus in any case.
But what is the difference between memory which is mapped internally or
externally? Only off-chip memory (program or/and data area) can be mapped
internally (within the emulator provided emulation memory) or mapped
externally (to the user provided memory on the target, external the emulator).
8051
Differences
Bond-out vs.
non Bond-out
Ref: 0008
What is the difference between a bond-out and a non bond-out emulator?
A bond-out chip provides a lot of additional signals and features which simplify
the control of a CPU, like the user program stop, entry to the user program and
exit from the user program. Basically however, the bond-out chip provides the
addresses, data and the control lines of a CPU internal program area (EPROM,
PROM, EE_PROM, FLASH_ROM). As an option, all internal peripherals and
interrupt sources can be stopped while the user program has been stopped.
Additional registers contain information about pending interrupts etc. Some
bond-out chips are "Combi-CPUs" which can emulate more than a derivative of
the 8051 family.
A non bond-out emulator uses the original chip, which is readily available their
local distributor. There are no additional lines and information available about
the internal memory area and there is no direct way to stop internal peripherials
or to prevent internal interrupt requests during an user program stop. Special
workarounds (provided by the emulator) cater for nearly the same comfort as a
bond-out solution. Please bear mind that the program area must be external
(EA=0).
Conclusion: If you use a 8051 derivative in microcontroller mode (EA=1) and
have not got program memory on the target, then you must choose the bond-out
solution. This solution supports both methods of operation EA=0 and EA=1. In
the other case, if you use only the microprocessor mode (EA=0) with EPROM
on the target, you may choose the non bond-out version.
8051
Reset while
Real Time
Program
Execution
Ref: 0064
What can cause error messages while real time program execution, if the
RESET line is activated or released?
There is a difference in behavior of the original CPU and the emulator. The
emulator does not have a Schmitt-Trigger input like the CPU has. In case of
problems, it is recommended to check the RESET line: Are there spikes, heavy
noise or is the falling or rising slope of RESET slower than 10 us.

ICE Emulator for 8051 1 1
©1989-2019 Lauterbach GmbH
8051
Stop Internal
Watch-dog
Timer
Ref: 0011
How can I stop the internal watch-dog timer after break?
There are two different ways to stop or to service the internal watch-dog timer for
the case, that the watch-dog cannot be disabled by software. It depends on the
emulation technique which is used.
If a bond-out chip is used, the customer may choose the IOSTOP option in the
SYSTEM control window. After break, all internal peripherals including the
watch-dog timer are stopped or inhibited if the option is on.
In a non bond-out system, the watch-dog timer must be serviced after break to
prevent a reset. The TRACE32 is able to support any software routines in the
background while the emulator has stopped the user programm execution. To
achieve that behavior, follow the instruction you will get if you type HELP TASK
or on the appropriate pages in the user guide.
This procedure can also be used to keep the emulator active for any interrupt
requests after an user programm break.
8051
Trace Internal
Registers
Ref: 0009
How do I trace a chip internal data transfer from one register to an other?
Neither a bond-out based nor a non bond-out emulator has access to the
internal busses between the registers. Also it is impossible to see any access to
or from an internal auxiliary memory area, except the CPU provides special
modes. During real time program execution there is no chance to trace these
accesses or make decisions depending on the content. During program
emulation (not a real time program execution) there are a lot of emulator
instructions to verify register or internal memory. As a combination of both, so-
called spot breakpoints are available.
Nevertheless the emulator and the analyzer are able to trigger and trace on the
access type (e.g. read bit direct) and on the internal addresses of byte direct and
bit direct accesses.
https://www.lauterbach.com/faq/8051tir.txt

ICE Emulator for 8051 1 2
©1989-2019 Lauterbach GmbH
Configuration
The configuration between the derivatives of the 8051 family is done by changing the probe or connector
modules. The software is configured automatically.
8051
To emulate the 8051 ROM version (no external memory) without bondout chip, a piggy-back version of the
8051 chip is used on the 8051 adapter. The OKI 85C154VS and the MHS 80C31P8/P16 are such piggy-
back versions of 8051. They require an additional small adapter cable between the EPROM socket and the
26-pin connector on the module.
:: C
:: .
:: ::
:: ::
:: ::
:: ::
:: ::
::
::
AB
Con A Con B Jumper C
no Piggy-Back not used not used closed
OKI-85C154VS connected open closed
MHS-80C51P32 open connected open

ICE Emulator for 8051 1 3
©1989-2019 Lauterbach GmbH
80152
80C152JA DIL
Mount adapter 80152JA-DIL and connect bridge array in position A for 83C152JA emulation or in position B
for romless version and for DMA. The correct CPU type is set automatically in the system window.
80C152JA-PLCC
Mount adapter 80152JB-PLCC and select CPU-type 80C152JA in system window. Set bridge array in
position A for 83C152JA emulation or position B for romless version and for DMA.
80C152JB-PLCC
Mount adapter 80152JB-PLCC and select CPU-type 80C152JB in system window. Depending on the used
bus mode set the bridge array as shown in position A or B.
C515C
For proper operation all switches of DIPSWITCH S101 must be closed and all switch of DIPSWITCH S100
must be open.
B .xx A
.xx
.xx
.xx
.xx
.xx
Pos A: 80C152JA,80C152JB, Opfetch via P5/P6, P5/P6 of target open
Pos B: 80C152JB, Opfetch via P0/P2, P5/P6 connected to target

ICE Emulator for 8051 1 4
©1989-2019 Lauterbach GmbH
C505C
The C505C is a subset of the C515C with some differences.
The A/D input lines are normally connected at Port1. Due to the C515C as emulation CPU, the A/D input
lines are connected at Port6. For redirection of the A/D lines to Port6 from target Port1, the DIPSWITCH
S101 and S100 must be set correctly.
Only for A/D operation, the appropriate pin of S101 must be closed and the equivalent pin of S100 must be
open.
For digital functions the appropriate pin of S101 must be open and the equivalent pin of S100 must be
closed.
Never close or open equivalent pins of S101 and S100 simultaneously.
For emulation the A/D unit of the C515C must be supplied.
S100: pin 1: C505C Port10
pin 2: C505C Port11
pin 3: C505C Port12
pin 4: C505C Port13
pin 5: C505C Port14
pin 6: C505C Port15
pin 7: C505C Port16
pin 8: C505C Port17
S101: pin 1: C505C A/D0 (Port60)
pin 2: C505C A/D1 (Port61)
pin 3: C505C A/D2 (Port62)
pin 4: C505C A/D3 (Port63)
pin 5: C505C A/D4 (Port64)
pin 6: C505C A/D5 (Port65)
pin 7: C505C A/D6 (Port66)
pin 8: C505C A/D7 (Port67)

ICE Emulator for 8051 1 5
©1989-2019 Lauterbach GmbH
Basics
Emulation Modes
The emulation head can stay in 6 modes. The modes are selected by the SYStem.Up or the SYStem.Mode
command.
Format: SYStem.Mode <mode>
<mode>: ResetDown
ResetUp
AloneInt
AloneExt
EmulInt
EmulExt
E::SYS
system Mode Clock TimeReq Line EW CPU
Down RESet VCO 1.000ms OFF I8051
Up Analyzer Low TimeOut Running I8051GB
Monitor Mid 50.000us ON I80152JA
RESet ResetDown High ALways I80152JB
ResetUp Line EA O80154
cpu-type NoProbe Access OFF Line EOW S80515A
I8051 AloneInt Slow ON OFF S80517A
- AloneExt Fast ALways Running S80535
EmulInt Advanced ON S80537
BankMode EmulExt Denied Option ALways V80552
OFF DUMMY V80562
INTern BankFile IOSTOP Line EBEN V80592
EXTern DMA OFF V80652
TestClock ON V80654
ALways V80662
V80851
Line V80528
HWPD H8051
C501
C502
C503

ICE Emulator for 8051 1 6
©1989-2019 Lauterbach GmbH
In active mode, the power of the target is sensed and by switching down the target the emulator changes to
RESET mode. The probe is not supplied by the target. When running without target, the target voltage is
simulated by an internal pull-up resistor.
SYStem.Clock Clock generation
Reset Down Target is down, all drivers are in tristate mode.
Reset Up Target has power, drivers are logically in inactive state, but not
tristate.
Alone Internal Probe is running with internal clock, driver inactive. This mode is used
for 'standalone' operation.
Alone External Probe is running with external clock, driver inactive.
Emulation Internal Probe is running with internal clock, strobes to target are generated.
Emulation External Probe is running with external clock, strobes to target are activated.
Format: SYStem.Clock <option>
<option>: VCO
High
Mid
Low
VCO Variable frequency 1…35 MHz.
Low, Mid,
High
2.5, 5.0 or 10.0 MHz.

ICE Emulator for 8051 1 7
©1989-2019 Lauterbach GmbH
SYStem.CPU CPU modes
Selects the emulated processor type. This function is only required to distinguish pin compatible processors
in the same emulation module.
SYStem.Access Dualport access
The mode can be changed only if the system is “down”.
If DUMMY Cycle is active and the access mode FAST or ADVANCED is selected, sometimes wrong data
values can appear in the trace of DUMMY cycles.
Format: SYStem.CPU <type>
<mode>: I8031 … V80851
Format: SYStem.Access [ Slow | Fast | Advanced | Denied ]
Slow Dualport access while ALE is active, for slow clock.
Fast Dualport access while DUMMY-Cycle, for medium clock.
Advanced Forced Dualport access while DUMMY-Cycle, for high speed emulation.
Denied No Dualport access, when user program is running.

ICE Emulator for 8051 1 8
©1989-2019 Lauterbach GmbH
General SYStem Settings and Restrictions
General Restrictions
Special I/O-Register Module M582
Internal Memory Program accesses to internal memory cannot be traced by the
analyzer. Data selective breakpoints are not possible. Address read
or write breakpoints on direct accessed or bit accessed memory are
possible.
MOVX addressed by Ri
(all bondout versions)
MOVX accesses to the emulation memory addressed by Ri causes
wrong results. The upper byte of the address is wrong. The analyzer
can not record and qualify these accesses. It is recommended to
map such areas external for a correct program execution. But keep
in mind that the analyzer doesn't work correctly.
Stack Usage The probe for 80152 needs a valid stack at breakpoints. It uses
2 bytes of stack. All other derivatives need no stack.
Target Program Memory It’s not possible to load or modify the target program memory area,
except the program area and the data area are not separated. The
internal program memory area of a microcontroller (EA="1") should
always mapped internal, because it’s not possible to load a program
into this area.
Power Down Mode On boards till rev. 5 there is no support for power down mode
because the CPU oscillator stops immediately and therefore several
errors can appear. Newer boards support power down modes while
the emulation is running. The dualport access mode must be set to
Denied in this case.
Slow Down Mode Slow down mode is only supported in Slow dualport access mode.
Idle Mode The Emulator supports idle mode while a user program is running,
but only without dualport access. Do not switch on the idle and
power down bits in the peripheral window, or the system will go
down immediately. Switch the dualport access mode to Denied. If
idle mode was terminated by a reset, the analyzer records wrong
INTACK cycles between last fetch before idle mode and restart from
P:0000, but in reality there was no interrupt acknowledge.
PCON (only 80C517/537) It is not possible to modify the bits PDE and PDS by an emulator
command while the emulation is stopped. A modification is only
possible in a user program using two special commands following
immediately after each other.

ICE Emulator for 8051 1 9
©1989-2019 Lauterbach GmbH
Reset The duration of target-reset and other reset signals from exception
window must exceed 24 clock periods + 3 us. For Reset with high
repetition rate it’s recommended to switch the dualport access mode
to Denied to avoid dualport errors.
Watchdog Reset (only
552/562)
Different from the original CPU, the Emulator generates no RESET
pulse for the external units in a watchdog reset cycle. The internal
RESET is executed.
ADC (only 552 and 562) There is an incompatibility between the 552 and the 562 concerning
the ADC resolution and the conversion time. The resolution is
always 10 bit resp. 50 clock cycles conversion time. For use without
a target, the AVREF+ and AVREF- have 10 kand AVSS and
AVDD 10 in series.
Operation Mode (only
M517E)
Don't use command SYStem.Up for emulation without target
system. Use always SYStem.Mode AloneInt. Otherwise errors can
appear, because the CPU will start up with external clock from a
slow auxiliary oscillator of the 80517 and will not use the internal
clock of the emulator.
Additional SFRs (only
80C515/80C535)
The special function registers of the 80C517 are also available when
emulating the 80C515. For correct emulation of the 80C515/80C535
don’t use the following SFR's: 0ECH, 0EDH, 0EEH, 0EFH, 0F6H,
0F7H, 0FAH.
XRAM Access (only
515A/517A)
When the XRAM is enabled, the XMAP1 SFR must be set,
otherwise the breakpoints and analyzer trace will not work in this
address range.
DMA cycles The trigger unit can't distinguish between a DMA-READ and a DMA-
WRITE cycle. The readflag and the write flag are set correctly. All
DMA accesses are displayed in the trace as 'RW-DMA'. The
address, the DATA and the timestamp of a DMA record is not correct
when memory to memory DMA transfers are made in the internal
RAM.
Emulation break during
DMA transfer (80152)
If a break appears while a DMA-channel is transferring data, the
DMA stops and can’t be restarted automatically. Normally the last
executed cycles of the DMA transfer are running in the emulation
monitor program, and therefore they are not sampled by the
analyzer. If a DMA cycle is in progress, the transfer will be finished
(including burst mode), before the break sequence takes place.
Interrupts during Single
Step
To prevent the execution of interrupts from internal sources during
assembler and HLL single stepping, the commands
SETUP.IMASKASM and SETUP.IMASKHLL must be used.

ICE Emulator for 8051 2 0
©1989-2019 Lauterbach GmbH
This additional register is only available if IOSTOP is active. The register concerns the current interrupts in
progress and it is called Interrupt Status Register ISR (at location D:9E). The original CPU does not
incorporate this register. The ISR is invisible while the user program is running. A RESET sets the ISR to
0FFH. When an interrupt of level 0 or level 1 occurs, the corresponding level code appears as defined below.
Depending on the selected CPU, some of the interrupt sources may be inhibited.
*) Within the 83C581 mode, check flags RI, TI and IFE to decide weather a SIO 0 or E2PROM interrupt has
occurred.
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
<Level 1 Code> <Level 0 Code>
Internal Source Level Code 51 851 662 652 562 552
external0 0000 xxxxxx
timer0 0001 xxxxxx
external1 0010 xxxxxx
timer1 0011 xxxxxx
SIO0*) 0100 xxxxxx
E2PROM*) 0 1 0 0 x
SIO 1 0 1 0 1 x x
T2 capt. 0 0 1 1 0 x x
T2 capt. 1 0 1 1 1 x x
T2 capt. 2 1 0 0 0 x x
T2 capt. 3 1 0 0 1 x x
ADC complete 1 0 1 0 x x
T2 compare 0 1 0 1 1 x x
T2 compare 1 1 1 0 0 x x
T2 compare 2 1 1 0 1 x x
T2 overflow 1 1 1 0 x x
Table of contents
Other Lauterbach Computer Hardware manuals
Popular Computer Hardware manuals by other brands

Connect Tech
Connect Tech Sentry-X user guide
Alphacool
Alphacool GPX-N 1080-M17 instruction manual

Sony
Sony SMO-D501 Specification and operating instructions
TouchNetix
TouchNetix aXiom AX80A EVK quick start guide

American Megatrends
American Megatrends MegaRAC 780 Series Quick install guide

NexxTech
NexxTech 8021910 owner's manual