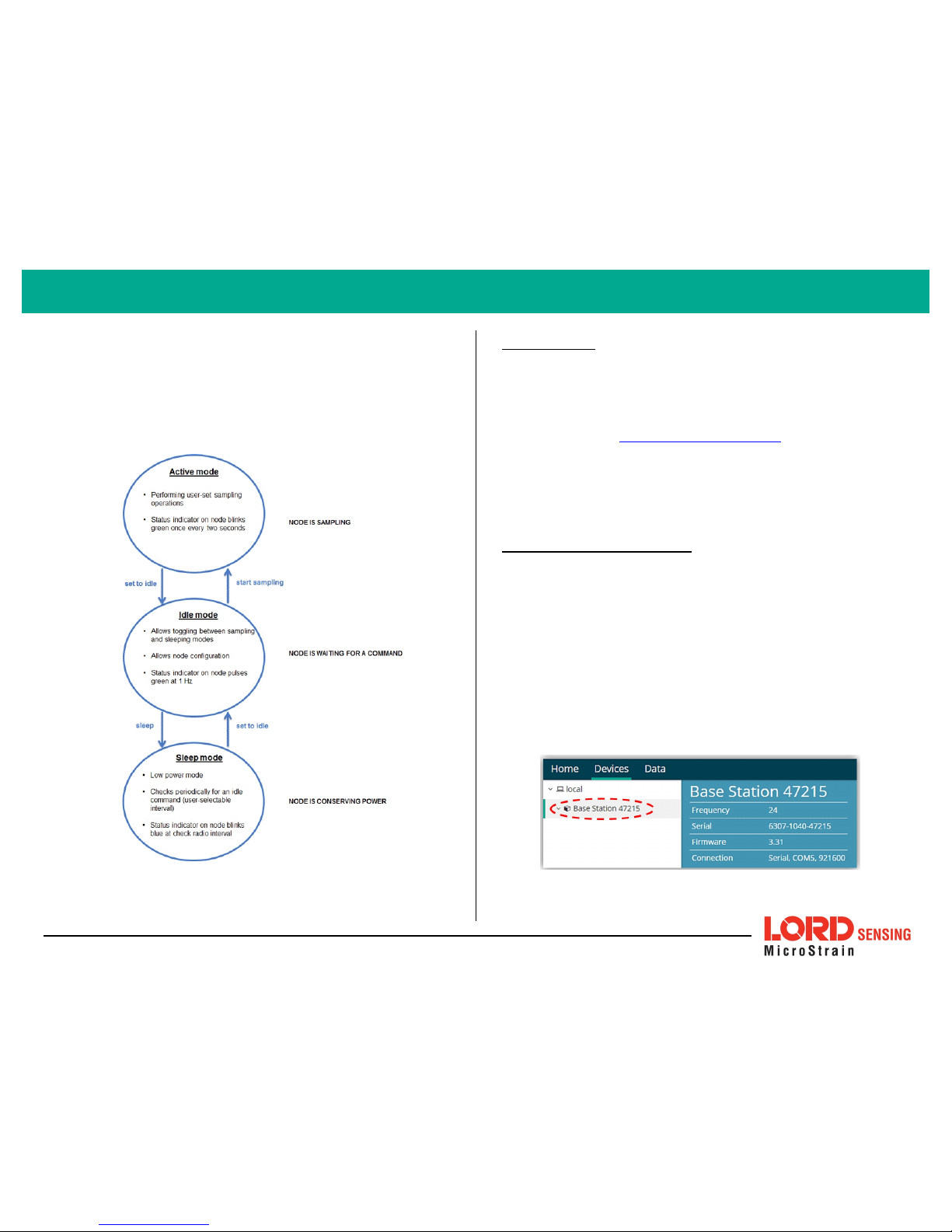
SYSTEM OPERATION
Sensor nodes have three operational modes:
active
,
sleep
, and
idle
. When the
node is sampling, it is in active mode. When sampling stops, the node is switched
into idle mode, which is used for configuring node settings, and allows toggling
between sampling and sleeping modes. The node will automatically go into the
ultra low-power sleep mode after a user-determined period of inactivity. The
node will not go into sleep mode while sampling.
Figure 1 - Node Operational Modes
1. Install Software
Install the SensorConnect software on the host computer before connecting any
hardware. The SensorCloud web platform is also available for data visualization
and analysis, and it is accessed by logging onto the SensorCloud website. The
SensorConnect software is available on the LORD Sensing website for free
download:
http://www.microstrain.com/software
SensorCloud is an optional data collection, visualization, analysis, and remote
management tool. It is based on cloud computing technology and is accessed
directly from a web connection. Automatic, real-time data collection is available
through Ethernet gateways, such as the WSDA- 1500. Data files can also be
uploaded. . For more information, see Connect toSensorCloud on page 1.
2. Establish Gateway Communication
Drivers for the USB gateways are included the SensorConnect software
installation. With the software installed, the USB gateway will be detected
automatically whenever the gateway is plugged in.
1. Power is applied to the gateway through the USB connection. Verify
the gateway status indicator is illuminated, showing the gateway is
connected and powered on.
2. Open the SensorConnect software.
3. The gateway should appear in the Controller window automatically
with a communication port assignment. If the gateway is not
automatically discovered, verify the port is active on the host
computer, and then remove and re-insert the USB connector.
Figure 2 - USB Gateway Communication
2
G-Link®-200 Wireless Accelerometer Node Quick Start Guide