90‐90‐885 (Rev.B)
TOGA*3‐1
Section3TECHNICALDESCRIPTION
3‐1PRINCIPLESORTHEORYOFOPERATION
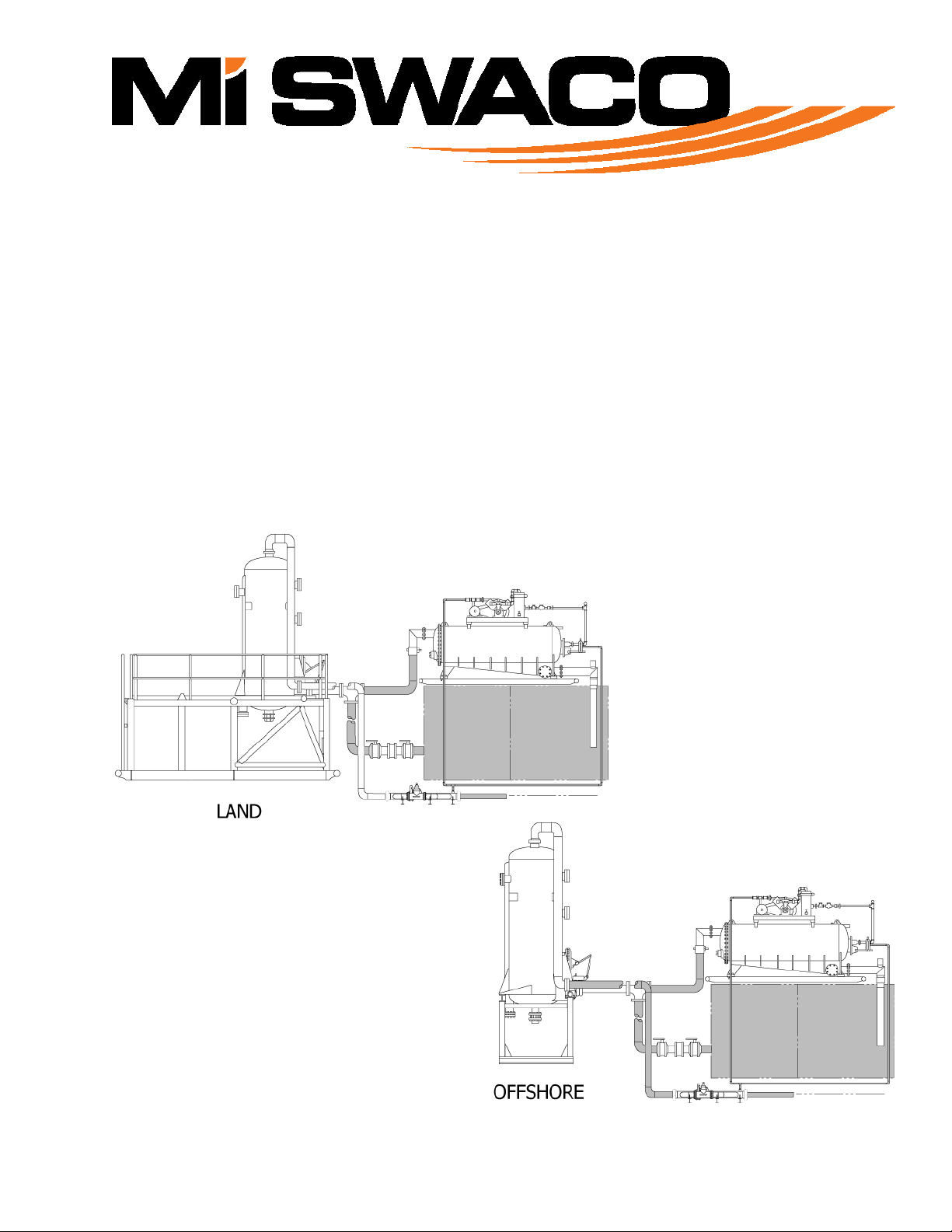
Thedrillingfluidcirculatedfromawellmayincludegasand/orformationliquidswhichhaveenteredthewell
bore.Asthefluidapproachesthesurfacethehydrostaticpressureisreduced,andthegasbubblesinthefluid
expandandformheadsormassivepocketsofgas.Theseheadsofgasorgascutmudarecirculatedfromthewell
borethroughtheflowlineorchokemanifoldintoasixinchinletlineontheMUD/GASSEPARATOR*.Thefree
gasisseparatedfromthefluidbyaseriesofbafflesinthevesselandventedintotheflarelinethroughaneight
inchlineonthetopoftheMUD/GASSEPARATOR*Vessel.
3‐1.1MUD/GASSEPARATOR*FloatValve
TheFloatoperatedcontrolvalveinsidetheMUD/GASSEPARATOR*vesselopenstopreventoverfillingofthe
VesselandclosestomaintainaliquidsealontheeightinchMudReturnLine.Theliquidsealpreventsthe
separatedgasfrombeingdischargedintothemudreturnline.
3‐1.2BackPressureManifold
TheBackPressureManifoldisinstalledintheMUD/GASSEPARATOR*VentLinetodampenthesurgeeffects
fromtheexpandinggasandpreventtheblowingofmudintotheVentLine.Abackpressuresettingof15‐50psi
(1.1–3.5kg/cmsquared)isrecommendedontheMUD/GASSEPARATOR*Vessel.
3‐1.3D‐GASSER*
ThegascutmuddischargedfromtheMUD/GASSEPARATOR*isdrawnintotheD‐GASSER*Vesselbya
vacuumforcecreatedbythedischargepipelowpressurejetassembly.Thefluidisdistributedoverabaffleina
thinevenlydispersedlayer.Thisthinlayeroffluidisexposedtoavacuumofatleasteightinchesofmercury
createdbythevacuumpump.Thevacuumforceremovestheentrainedgasesfromthefluidandthedegassed
fluidisdischargedintotheactivesystem.TheentrainedgasremovedfromthefluidbytheD‐GASSER*isvented
intotheclosedflaresystem,down‐streamoftheMUD/GASSEPARATOR*BackPressureManifold.
TheTOGA*systemutilizesM‐ISWACO’sstandardMUD/GASSEPARATOR*andD‐GASSER*whichhavebeen
specificallymodifiedtoassuretotalcontainmentandcontrolofthetoxicgascutmud.ThemodifiedD‐GASSER*
includestwocompletevacuumpumpsystems.Thevacuumpumpexhaustlinesareconnectedthrougha
manifoldcontainingaseriesofcheckvalvestopreventthepossibilityofblowbackfromtheflarelines.Plug
valveslocatedoneithersideofthecheckvalvesareusedtoprovideameanstoisolateandsafelyrepairorreplace
eithervacuumpumpsystemwhiletheotherisstilloperationalaswellastoconfigurethevacuumpumpsystems
foralternativemethodsofoperation.Thefirstalternativeistorunbothvacuumpumpsystemssimultaneouslyto
assuremaximumdegassingefficiencywhenlargevolumesofgasareencountered.Thesecondalternativeisto
provideameansforredundancyintheeventtheprimaryvacuumpumpsystemfailsduringkickconditions.