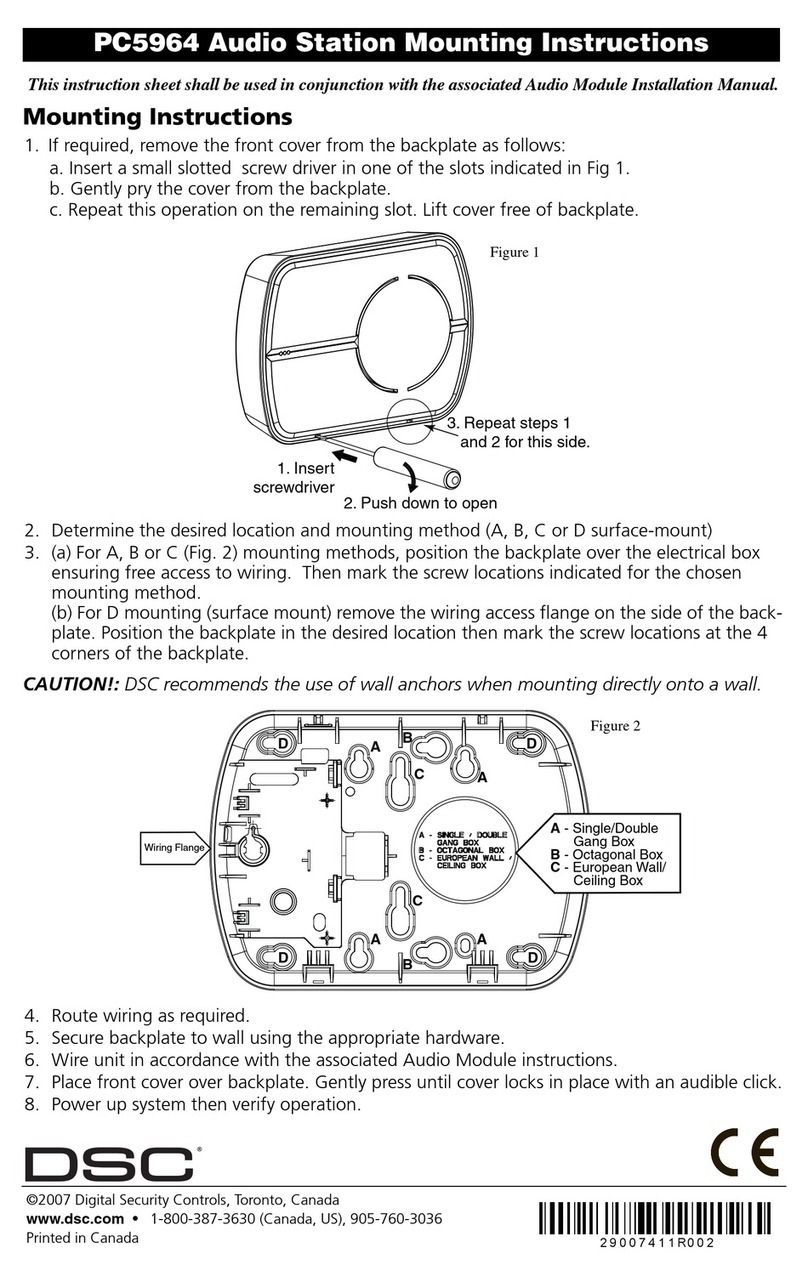
Helios Installation Guide
© 2012 MicroPower Technologies, Inc. 7
quality site survey, please refer to the MicroPower documentation titled “Site Survey
Guidelines”.
With unobstructed line-of-sight between the hub and camera antennas, the system can
reliably transmit video up to 1/2 mile in distance. However, obstacles such as trees,
buildings, fences, etc. will impact the wireless performance in terms of maximum
transmission distance and data rate speeds. Once a video link is established, if
obstructions are present, or the distance between the antennas is too great, then the
video streams may experience dropouts and/or reduced camera frame rates. A wall or
tree may not cause any significant performance impact at short ranges, yet can
completely block a signal at long distances. Additionally, for best extremely short range
performance, the minimum distance between the video hub antenna and the wireless
Camera antenna should be 25 feet (unless signal attenuators are installed).
For further education and guidelines on RF effects, refer to MicroPower document “A
Guide to Optimizing Your RF Setup”.
Since the wireless camera is powered by solar energy, the critical impact of sun direction
and shadows on the panels cannot be overstated. It is advisable that the camera be
positioned in such a way that two or more of the built-in solar panels receive adequate
direct sunlight during the peak charging hours from 11 a.m. to 3 p.m.
When selecting a location for the wireless camera that will be installed in the Northern
Hemisphere, the auxiliary solar panel must be mounted on the SOUTH side of a pole or
structure, facing SOUTH.With the camera’s built-in solar panels, it is also preferable to
mount the camera on the South side of the pole, to minimize shadows created by the
pole, and to ensure good light coverage across all of the panels as the sun moves across
the sky. For East or West facing cameras, try to mount the camera on the South side of
the pole, and point the camera in the desired direction. For optimum solar
performance, always try to avoid the North side of the pole.
(In the Southern Hemisphere below the equator, the directional considerations are
reversed)
Areas with insufficient direct sunlight will eventually produce camera outages, such
areas include, but are not limited to:
•Solar panels shaded under a roof eave
•Underneath a tree canopy or foliage which does not receive adequate sunlight
•Next to a tall building that casts a shadow over the camera during peak charge
times. (Particularly during the important mid-day charging period)
•A camera mounted such that the pole that it is attached to, or other area objects
(wires, cables, etc.) cast shadows across multiple solar panels during peak charge
times.