Quick Start Guide
MIP Soft & Hard Iron Calibration
3DM-GX3-25 (fw version 2.0.00 and above)
3DM-GX3-35
3DM-GX3-45
Overview
Most models of the 3DM-GX3®series contain a magnetometer. The magnetometer values are
available as fully calibrated outputs and are also used to correct heading drift in the Orientation
Matrix, Euler Angles and Quaternion outputs. The 3DM-GX3®has been carefully designed to
eliminate as many ferro-magnetic components as possible to prevent distortions in the readings
of the earth’s magnetic field which can cause errors in the magnetometer output. In addition, the
magnetometer is factory calibrated on non-magnetic stages in order to compensate for any
remaining internal sources of error. However, these measures can only compensate for error
sources that are internal to the device; they cannot compensate for errors that may be introduced
externally by mounting structures or adjacent devices. Careful mounting of the 3DM-GX3®can
avoid external magnetic anomalies caused by sources such as coils, magnets, and ferrous metal
structures and mounting components (steel nuts and bolts). Often these sources are hard to avoid
or are hidden and so a field calibration of the magnetometer after final installation is highly
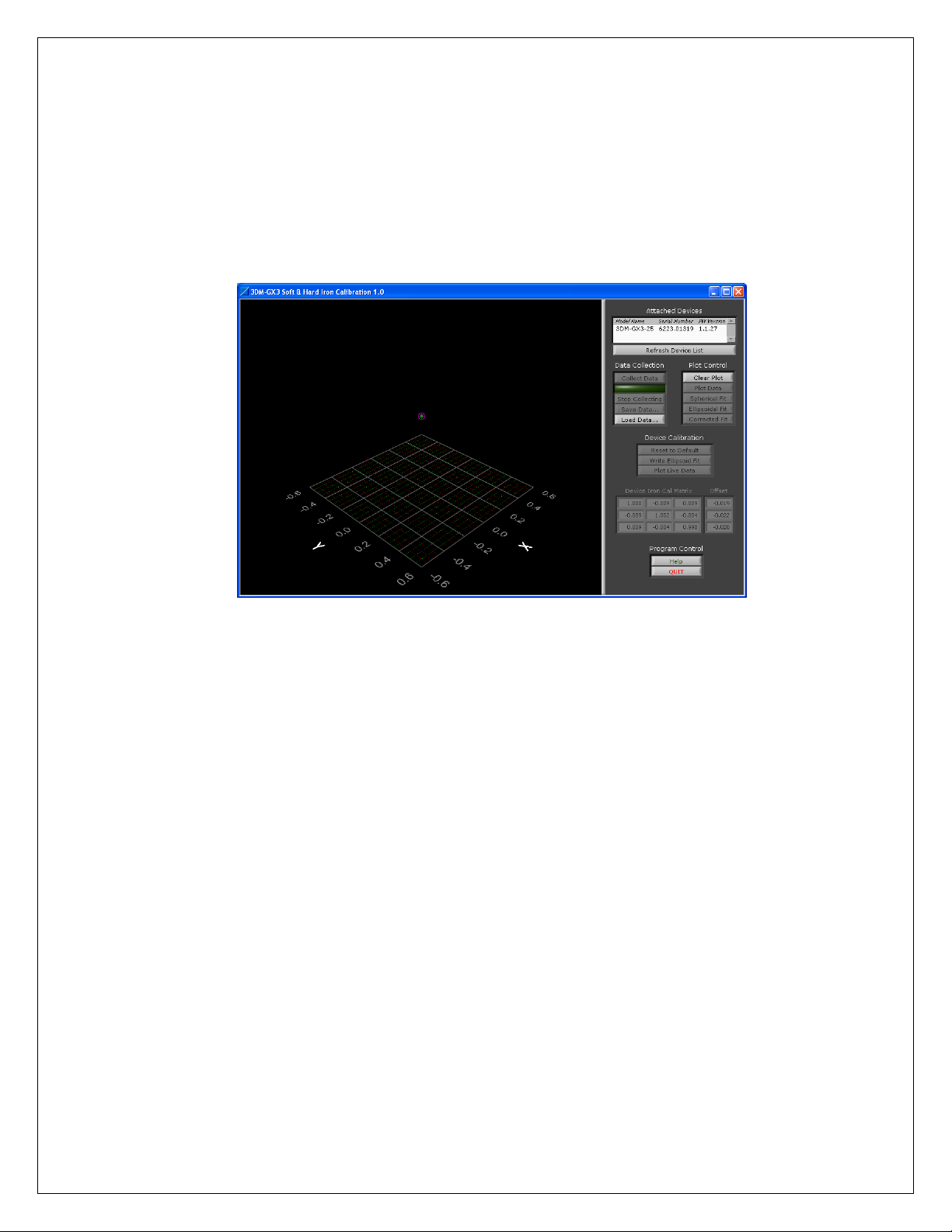
recommended. This can be accomplished using MicroStrain’s MIP Soft & Hard Iron
Calibration software.
Important
If you have a 3DM-GX3®-25 with a firmware version that is lower than 2.0.00, you need to use
the 3DM-GX3®Soft & Hard Iron Calibration. If you have version 2.0.00 or above, you may use
either 3DM-GX3®Soft & Hard Iron Calibration or the MIP Soft & Hard Iron Calibration
software.
Caution
Starting with 3DM-GX3®firmware version 1.1.27, the user has the option of turning off the
heading correction and/or the magnetometer. The default setting is to have both turned on.
Please make sure the magnetometer is turned ON before calibrating.
Instructions
Before starting, make sure you have installed the MIP Soft & Hard Iron Calibration software
from the installation CD or from the installer downloadable at www.microstrain.com.
1) Connect the 3DM-GX3®to your computer using either the RS-232 communication cable
and power supply or the USB communication cable. If you have not already done so,
follow the instructions in the 3DM-GX3®Quick Start Guide on the installation CD to
make sure the device is properly installed and communicating with your computer.