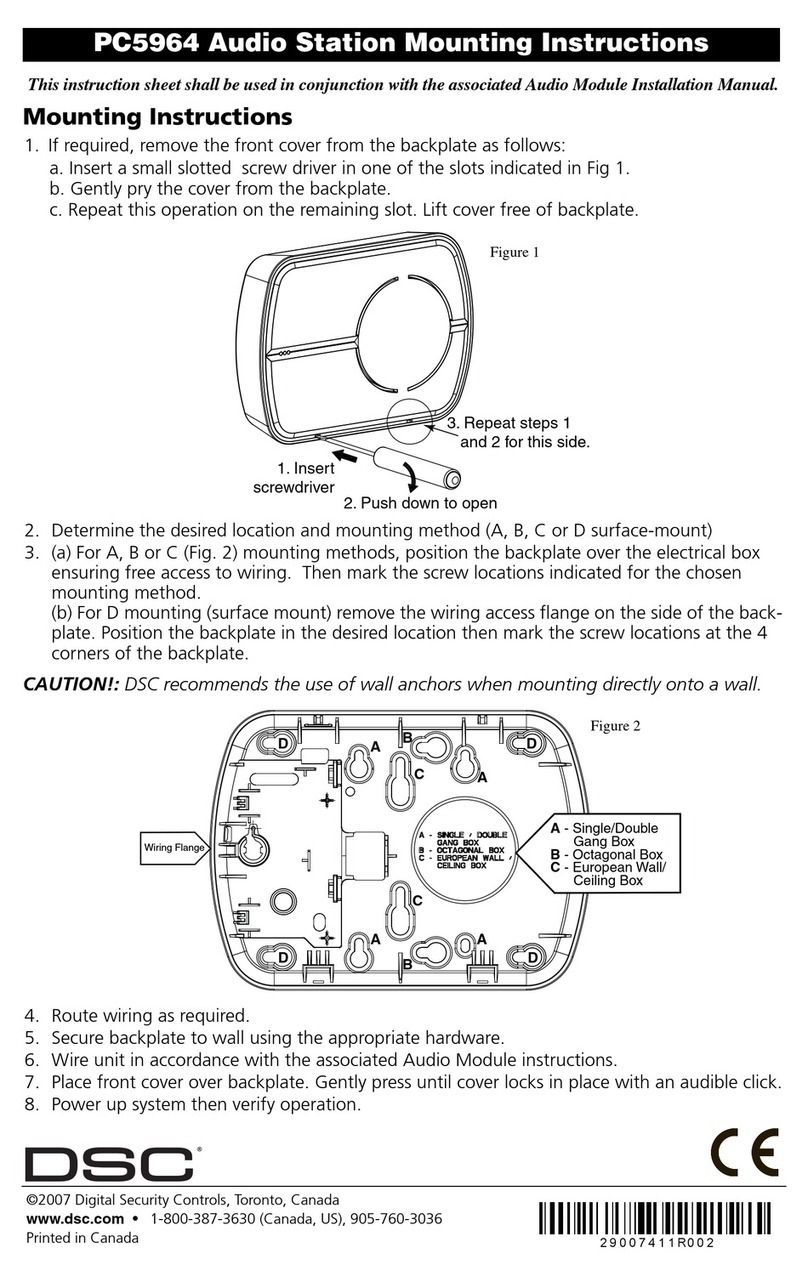
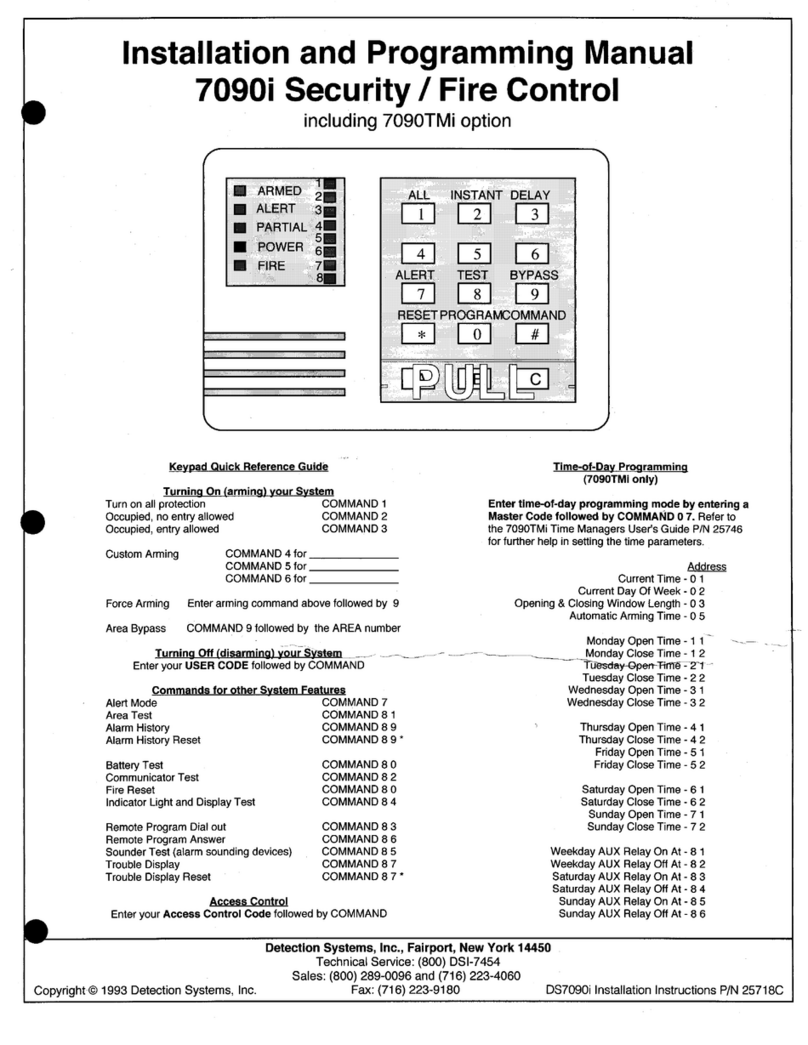
PL-298 MFA-4p Page 3
Table of Contents
Table of ContentsTable of Contents
Table of Contents
Specifications
SpecificationsSpecifications
Specifications................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
..................................
....
.. 5
55
5
Installation
InstallationInstallation
Installation ................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
.......................................
..............
....... 7
77
7
Dimensions......................................................................................................................................................8
NEMA 4 Enclosure – Main Amplifier..................................................................................................8
MFA-4p Open Style.......................................................................................................................................9
Main circuit board....................................................................................................................................9
Layout
LayoutLayout
Layout
Main Amplifier........................................................................................................................................ 10
Interconnection
InterconnectionInterconnection
Interconnection................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
.............................................................
..........................................................
............................. 11
1111
11
MSP-1, 3, or 9 Probe........................................................................................................................ 11
MSP-12 Probe with IMA ................................................................................................................ 11
MSP-12C ............................................................................................................................................. 11
XPP-5 ................................................................................................................................................... 12
Table: Cable length from RMA or IMA to Main Amp ........................................................ 12
Wiring
WiringWiring
Wiring ................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
.............................................
..........................
............. 13
1313
13
MFA-4P Main Amp Wiring for Automatic Start Delay................................................................ 13
Schematic Diagram - Remote Mounted / Pre-amplifier............................................................. 14
Schematic Diagram MFA-4 Main Amplifier................................................................................... 15
Operating Principles
Operating PrinciplesOperating Principles
Operating Principles................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
.....................................................
..........................................
..................... 17
1717
17
MFA-4p.......................................................................................................................................................... 17
Probe.............................................................................................................................................................. 17
Pre-Amplifier (IMA and RMA) ................................................................................................................ 18
Main Amplifier............................................................................................................................................. 18
Calibration .................................................................................................................................................... 19
Pre-amble ................................................................................................................................................ 19
Main Amplifier ....................................................................................................................................... 19
Underspeed............................................................................................................................................. 19
Overspeed ............................................................................................................................................... 20
Signal Generator Interface...................................................................................................................... 21
Probes
ProbesProbes
Probes................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
.............................................
..........................
............. 23
2323
23
Mini Sensing Probe MSP-1 ..................................................................................................................... 23
High Temperatures MSP-3...................................................................................................................... 23
Stainless Steel Probe MSP-9.................................................................................................................. 24
Mounting Details .............................................................................................................................. 24
Standard MSP-12....................................................................................................................................... 25
MSP-12C ....................................................................................................................................................... 25
Hazardous Locations XPP-5.................................................................................................................... 26