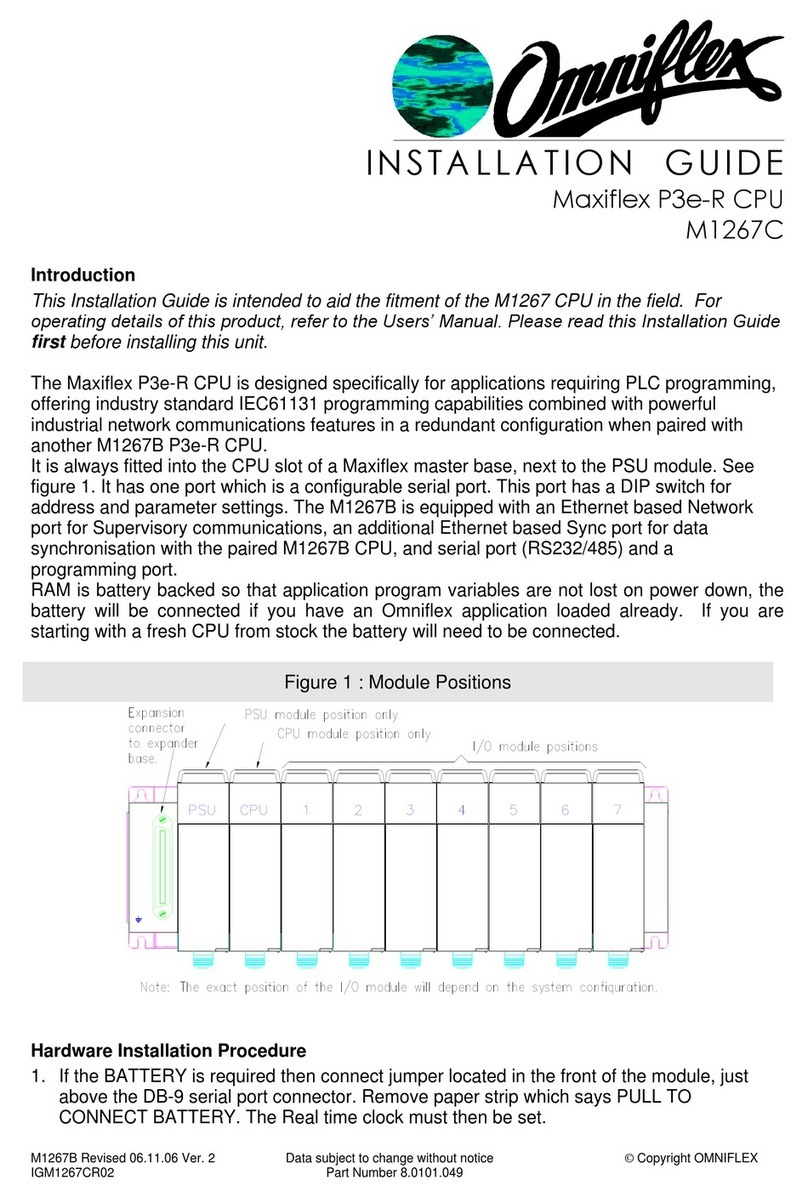
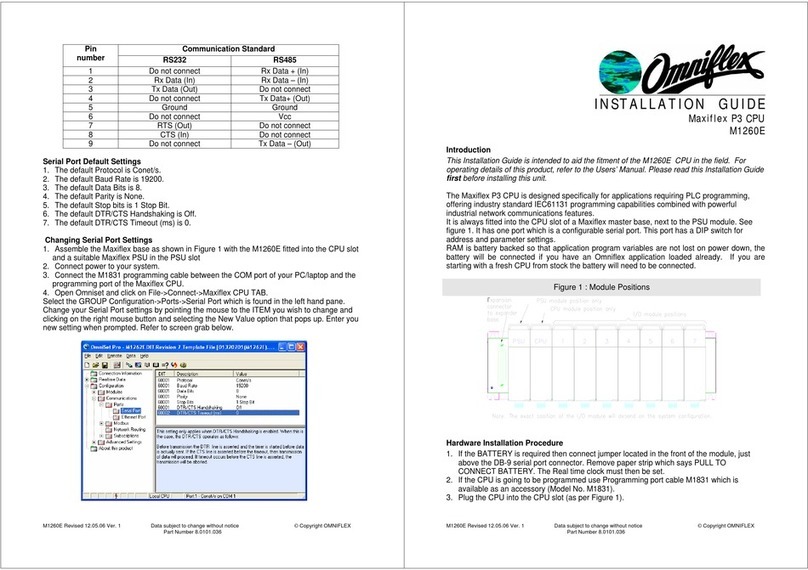
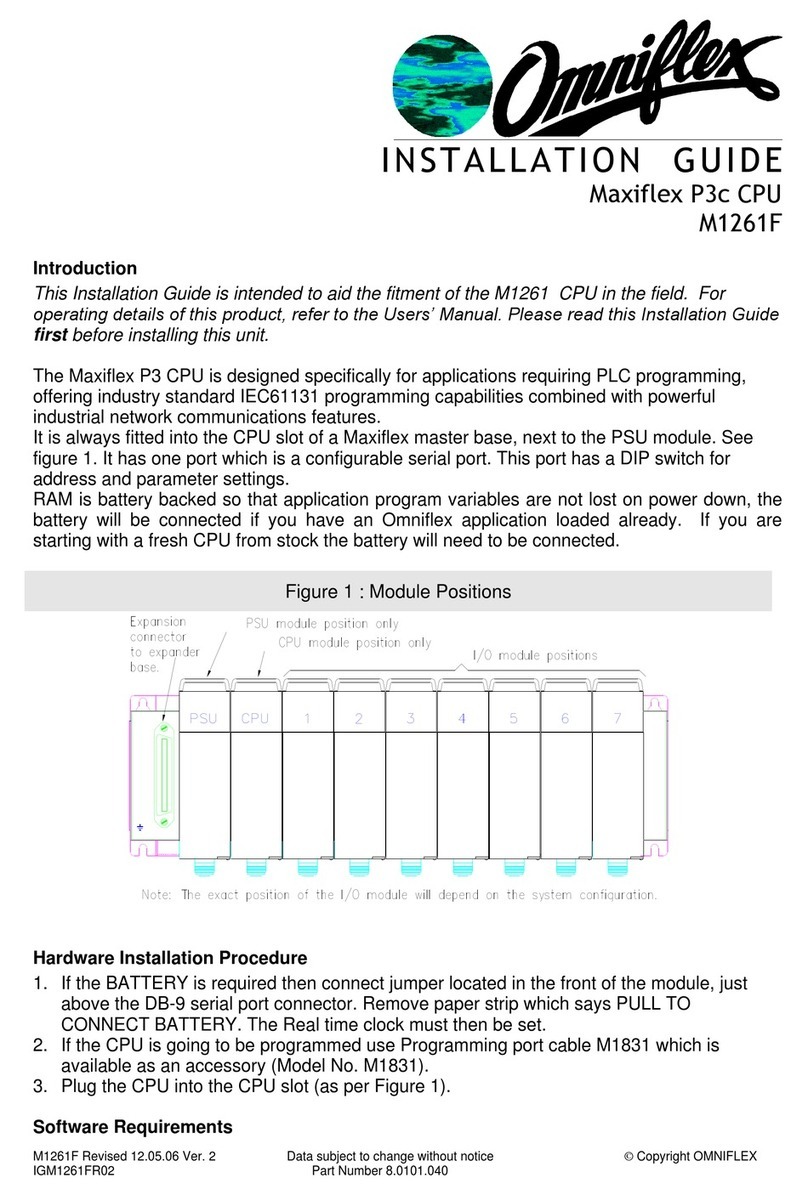
7.6 M1321A –8DI-C - 8 way Individually Isolated Contact Input Module...........................39
7.7 M1322A - 16DI - 16 way Digital Input Module (9-30Vdc) M1323A - 16DI - 16 way Digital
Input Module (18-60Vdc) ...........................................................................................................40
7.8 M1326A –32DI –32 way Digital Input Module............................................................40
7.9 M1330A –8DI8RO 8way Digital Input /8 way Relay Output Module............................41
7.10 M1341B –16DO –16way Digital Output Module.........................................................41
7.11 M1342A –32DO –32way Digital Output Module.........................................................42
7.12 M1372A –8RO –8way Relay Output Module .............................................................42
7.13 M1403A –16AI –16way Analogue Input Module........................................................43
7.14 M1412A –8AO –8 way Analogue Output Module.......................................................43
7.15 M1431B –8VC ISO –8 way Isolated Voltage/Current Input Module...........................44
7.16 M1432C –8TC ISO –8 way Isolated Thermocouple/milliVolt Input Module................47
7.17 M1433B –6RTD ISO –6 way Isolated Resistance Bulb Input Module........................50
7.18 M1760A –32SOE –32 way Sequence of Events Input Module - 24V Input M1761A –
32SOE –32 way Sequence of Events Input Module - 48V Input ...............................................52
8. The Subscription Service Explained .................................................................................55
8.1 Introduction to Subscriptions........................................................................................55
8.2 Setting up subscriptions...............................................................................................55
8.3 Number of subscriptions allowed.................................................................................57
8.4 Subscription Application Example................................................................................57
9. Queue Service Explained ...................................................................................................59
9.1 Introduction to the Queue Service ...............................................................................59
10. Modbus Master Operation Explained ................................................................................ 60
10.1 Introduction to Modbus Master Driver..........................................................................60
10.2 Modbus Master Parameters ........................................................................................60
10.3 Query Configuration.....................................................................................................62
10.4 Query Triggers.............................................................................................................63
10.5 Status DIT Registers....................................................................................................64
11. Configuring the P3 CPU...................................................................................................... 65
11.1 Overview......................................................................................................................65
11.2 Setting the Serial Port Address Switch ........................................................................65
11.3 Setting the Conet/c Network Port Address Switch.......................................................67
11.4 Preparing the Omniset configuration software to configure the P3 CPU......................68
11.5 Synchronise Omniset and the P3 CPU........................................................................70
11.6 Configuring the Programming Port ..............................................................................71
11.7 Configuring the I/O Module List using Omniset............................................................71
11.8 Configuring the Real-time Clock..................................................................................73
11.9 Configuring the Serial Port from Omniset ....................................................................74
11.10 Configuring the Ethernet Network Port ........................................................................76
12. Programming the P3 CPU................................................................................................... 78
12.1 Introduction to IEC61131-3 Programming....................................................................78
12.2 Programming the Maxiflex P3 CPU.............................................................................79