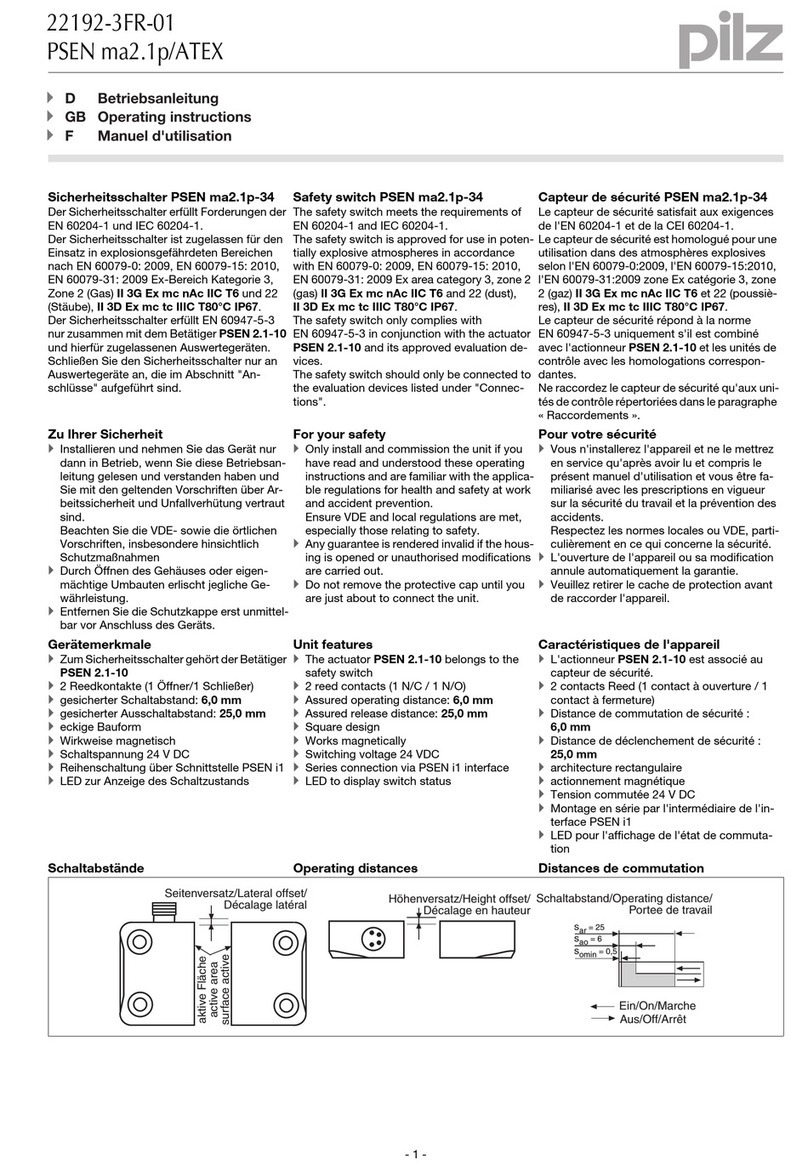
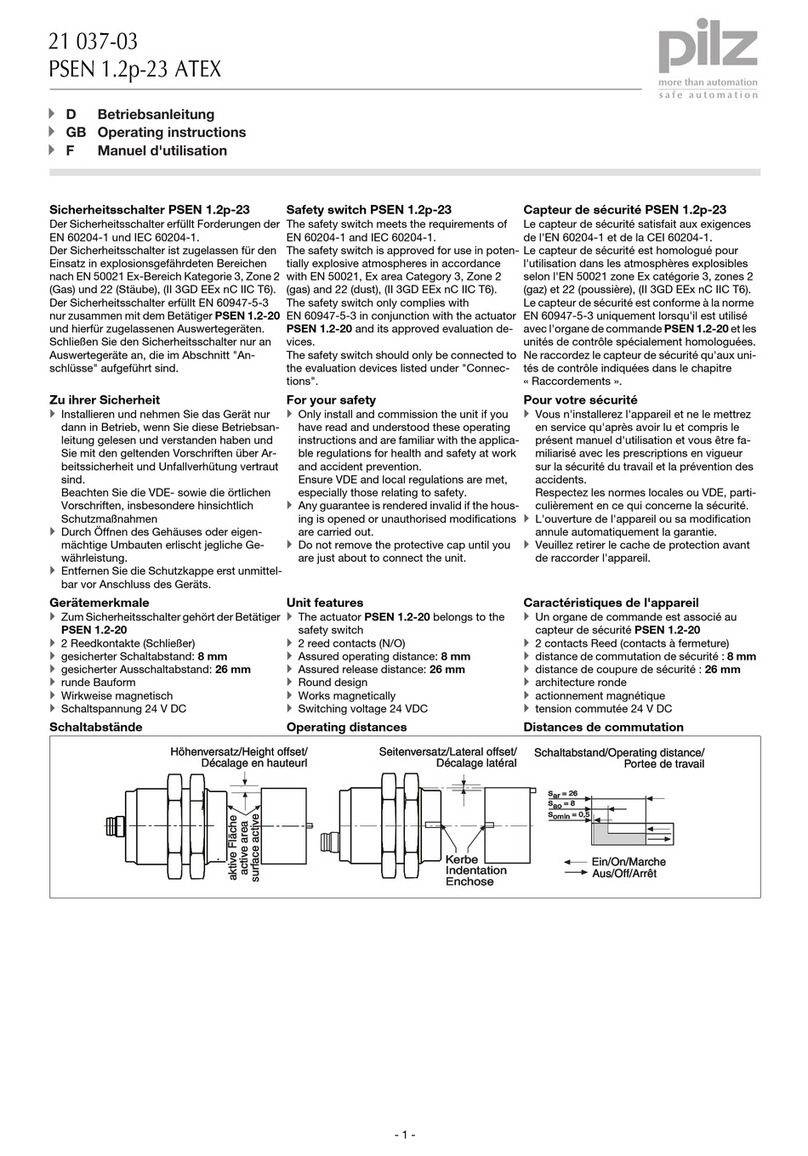
PSSnet SHL
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix Wankel Str. 2, 73760 Ostfildern, Deutschland 5
Relevant for North America: For use in Class 2 circuits.
The device may only be connected to a supply voltage of class 2 that
fulfills the requirements of the National Electrical Code, Table 11(b). If
the voltage is being supplied redundantly (two different voltage sourc-
es), the combined supply voltages must fulfill the requirements of the
National Electrical Code, Table 11(b).
Relevant for North America: For use in Class 2 circuits.
Only use copper wire/conductors of class 1, 75 °C.
Relevant for North America
for devices certified for hazardous locations:
Power, input and output (I/O) wiring must be in accordance with
Class I, Division 2 wiring methods [Article 501-4(b) of the National
Electrical Code, NFPA 70] and in accordance with the authority having
jurisdiction.
For devices installed in explosive gas atmospheres according to
ATEX RL 94/9 EG (only for devices labelled accordingly):
Relevant for Europe (ATEX RL 94/9 EG): II 3G Ex nA II T3 ... T4
- refer to the device label.
Must be mounted in a suitable certified IP 54 housing –
tested to 4 J impact due to low risk of mechanical danger.
For ambient temperatures below -10 °C and above +60 °C use wiring
suitable for both the minimum and maximum temperatures.
Connectors may be connected exclusively in dead-voltage state.
DIP switches may be switched exclusively in dead-voltage state.
The device does not contain any service components. Internal fuses
are only triggered if there is a fault in the device. If the device is not
functioning correctly, or if it is damaged, switch off the voltage supply
and return the device to the plant for inspection.
Only switch on the supply voltage to the device if
- the housing is closed,
- the terminal blocks are wired up correctly and
- the terminal blocks are connected.
Supply voltage for PoE power supply units (optional)
Connect the protective conductor with the ground screw before you
set up the other connections. When removing the connections, you re-
move the protective conductor last.
Make sure that the cross-section of the protective conductor cable is
the same size as or bigger than the cross-section of the voltage supply
cables.
Only use connection cables that are permitted for the specified tem-
perature range.