5.CIRCUIT
DESCRIPTIONS
FUNCTION
S|{IICH
7=l20(a
C
=100pF
PHONO
2
PHONO
'I
CARTRIDGE
LOAD
+
siA-s|5clcltr
OUT
Fig.
1. Schematic
diagram
for
equalizer
amplifier
5.1 EOUALIZER
AMPLIFIER
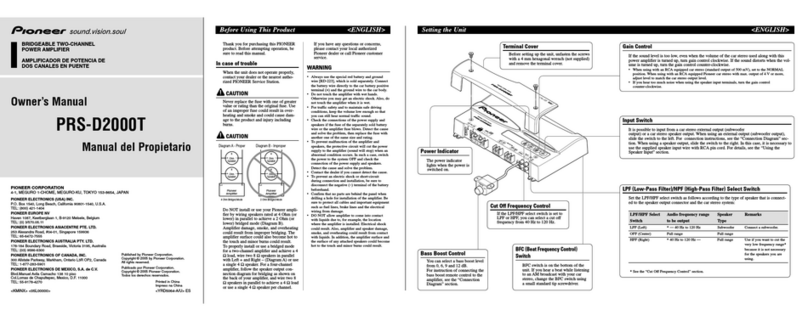
The circuit diagram for the equalizer amplifier is
shown
in Fig. 1. The two separate
phono inputs are
selected
by the FUNCTION selectoron the front
panel.The input resistanceand input capacitance
canboth beadjustedto 4 different levels
(R=l0kCl,
25kO,50kA and100kO, C=1-00pF,200pF, 300pF
and400pF) by meansof the CARTRIDGE LOAD
control knobs(R and C) which switchesin and out,
additional resistors and capacitors in parallel with
the input terminal. Hence, optimum load condi-
tions for different phono carbridges can be ad-
justed, as well as modifying the cartridge's fre-
quency response in the high frequency range and
thus producing variations in its characteristics.
Thefirst stage
of the equalizeramplifier (Q, & Qr)
isadifferential amplifier using PNPtransistors. The
next stage
(Q.) isa bootstrap circuit employing C1,
R1 to provide high voltage gain. The output stage
(Q+& Qr) is a complementary-symmetrical SEPP
circuit, whose high voltage utility factor results in
a high output voltage. This gives the equalizer
amplifier a very wide dynamic range, and a con-
siderable
overload input level of 300mV (RMS at
lkHz) with no more than 0.05V"distortion.
The equalizerelements(Cr, Cr, Rz and R3)consist
of polypropylene film capacitors (tolerance !2Vo)
and metal film resistors (tolerance xIVo). Phono
equalizer
RIAA deviation has been reduced to less
thant0.2dB (20H2 - 2OkHz\.
5.2 TONE
CONTROLS
The SA-9500 II featurestwo sets
of tone controls
(Tkin Tone Controls) with different turnover fre-
quencies for bass and treble. And each of these
controls may beusedindependently.
Incoming signalsare amplified to the required level
by the 2 stageamplifier which usesa differential
amplifier at first stage. T\vo tone control circuits
(C-B feedback NFB type) are connected together
in series. The second stage is the normal tone
control (MAIN), while the other is a seeondary
tone control at a different turnover frequency
(SUB). On the TREBLE side,this (SUB) tumover
frequency is higher than the MAIN, while on the
BASS side,it is lower.
The basicprinciples of the NFB type tone control
circuit areoutlined in Fig. 2.
R" YR" R,
TREBLE
Fig.2. Basic
circuitry of NFB type tone control circuit