Doides have a important orientation, marked with a black stripe. This stripe is white on the PCB.
Place the four diodes in D1, D , D3 and D4.
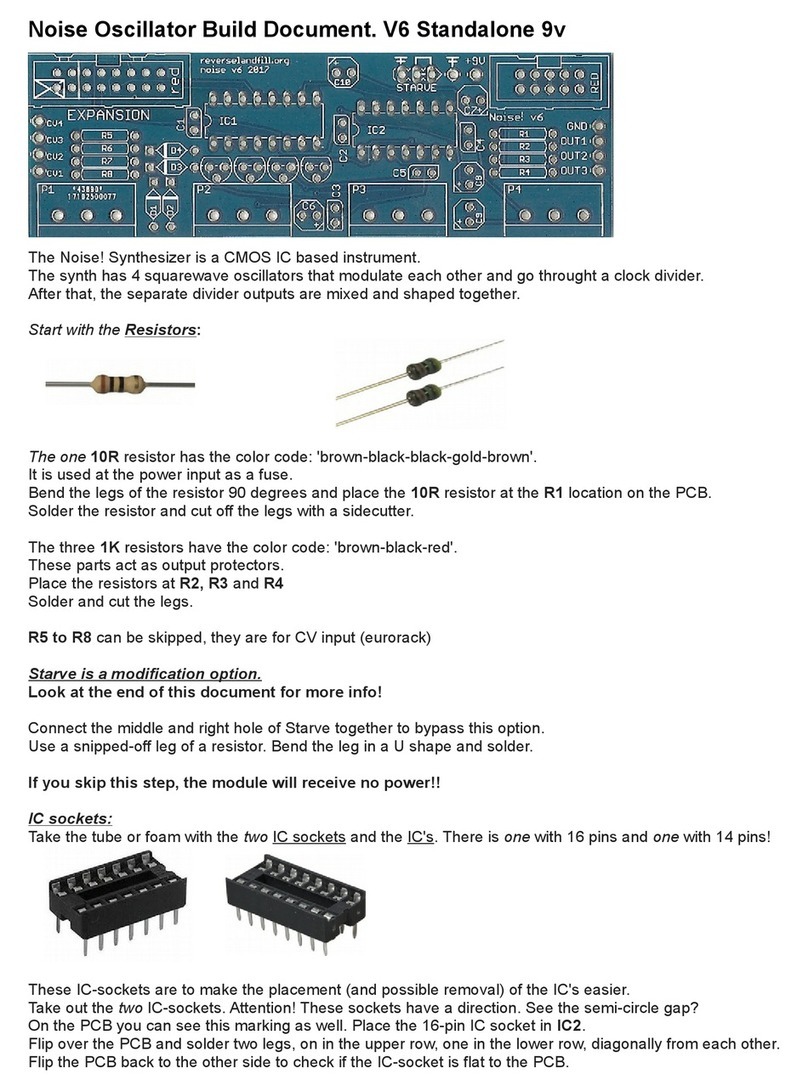
IC sockets
Take the tube or foam with the three IC sockets and the IC's. There is one with 16 pins and two with 14 pins!
These IC-sockets are to make the placement (and possible removal) of the IC's easier.
Take out the two IC-sockets. Attention! These sockets have a direction. See the half moon-shaped ap?
On the PCB you can see this markin as well. Place the 16-pin IC socket in IC .
Flip over the PCB and solder two le s, on in the upper row, one in the lower row, dia onally from each other.
Flip the PCB back to the other side to check if the IC-socket is flat to the PCB.
If not, push the socket to the PCB and reheat the two solderd le s. It should click to the PCB.
Place the 14 pin IC sockets in IC1 and IC3 and use the same method as before to solder it in.
Solder all remainin le s.
Capacitors!
There are a lot of capacitors in the kit.
They determine the frequency ran e of the oscillators, stabilise the power and outputs.
We start with the four small li ht yellow capacitors.
C1, C , C5 en C6 are 100nF (.1K63)
C3 = 680pF (you can also use a 100pF)
C4 = 220nF / 100nF (.22J63)
Now for the bi er capacitors:
These parts have a polarity. The lon le is the PLUS, The short le is MINUS.
There is also a MINUS symbol printed on the side.
The value of these components is printed on the side as well.
Start with the one 47uF.
(take care to et the ri ht one, there are also four 4.7uF capacitors!)
Place the one 47uF capacitors in C11. Lon le oes into the PLUS!!
Now we do the three 4.7uF. These o in C7, C8, C9 and C10.
Transistoren
Place the four transistors in Q1, Q , Q3 and Q4.
These parts are heat sensitive, so make sure that you don't overheat them.