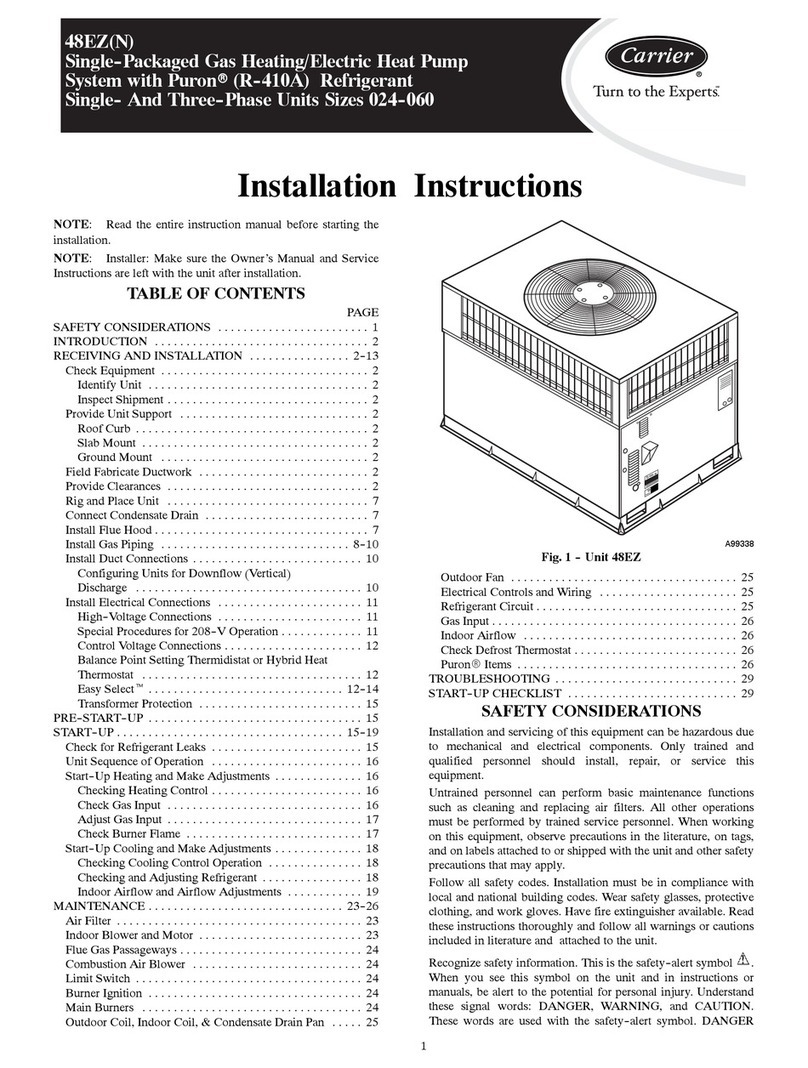
TM025 Rheem Heat Pump Service Instructions REV: B
Date of Issue: 02/08/07
This document is stored and maintained electronically by Service. All printed copies not bearing this statement in RED are deemed “uncontrolled”.
9
Compressor - An electro-mechanical device that adds heats to the refrigerant by
compressing it, known as “heat of compression” the resulting increase in refrigerant
temperature increases its pressure and causes the refrigerant to circulate through the
system.
Evaporator - A finned copper coil mounted on top of the water heater. The refrigerant
enters as a liquid, as it passes through the coil it absorbs heat from the surrounding
atmosphere and “boils off” (evaporates) to a gas.
Condenser - An insulated housing containing stainless steel chambers where heat
transfer occurs. The condenser (or heat exchanger) contains three chambers, one for
refrigerant, one for water and a third separating chamber containing air. The refrigerant
enters as a gas, as it passes through the condenser it transfers (“gives up”) the heat
absorbed via the evaporator to the water flowing through the condenser in a separate
chamber, during this process the refrigerant cools and changes state (condenses) back to
a liquid.
Receiver Filter Drier - This device, fitted between the condenser and thermal expansion
(TX) valve, receives and stores liquid refrigerant from the condenser for delivery to the
evaporator. The receiver also incorporates a filter and drier to trap impurities and remove
moisture from the sealed refrigeration system
Accumulator - This device, fitted in the suction line prior to the compressor, is designed to
accumulate and prevent liquid refrigerant from entering and damaging the compressor.
Any liquid refrigerant is evaporated or “boiled off” and converted to a vapour by the
accumulator.
Thermal Expansion (TX) Valve -A valve, installed between the condenser and
evaporator that controls (meters) the amount of refrigerant delivered to the evaporator.
The TX valve has an external temperature sensor fitted to the suction line and increases or
decreases the refrigerant flow to the evaporator depending on the detected suction line
temperature.
Thermal Cut Out (Overload) - A manual reset temperature sensitive device that
automatically cuts off the supply of electrical energy to the control board and/or boost
element.
Heating Unit (Element) - A tubular device containing an electric resistance element that
converts electrical energy to heat. Standard element ratings are 2.4 and 3.6kW.
Common Faults
When a complaint is lodged about the performance of a hot water system there are a
number of causes that should be checked and eliminated. In an attempt to pinpoint the
most likely cause it is important to discuss with the customer their reasons for the
complaint, the duration of the problem, any change in circumstances or usage and recent
weather conditions. This information in conjunction with the following listed common
complaints will assist you in locating the most likely cause. All procedures assume there is
water flowing through the water heater.
Discoloured water - This may be the result of discoloured water entering from the cold
water mains. Check if the cold water is also discoloured.
Excessive hot water usage - The complaints of insufficient hot water and no hot water
can on many occasions be attributed to hot water usage exceeding the capacity of the
water heater to provide hot water.