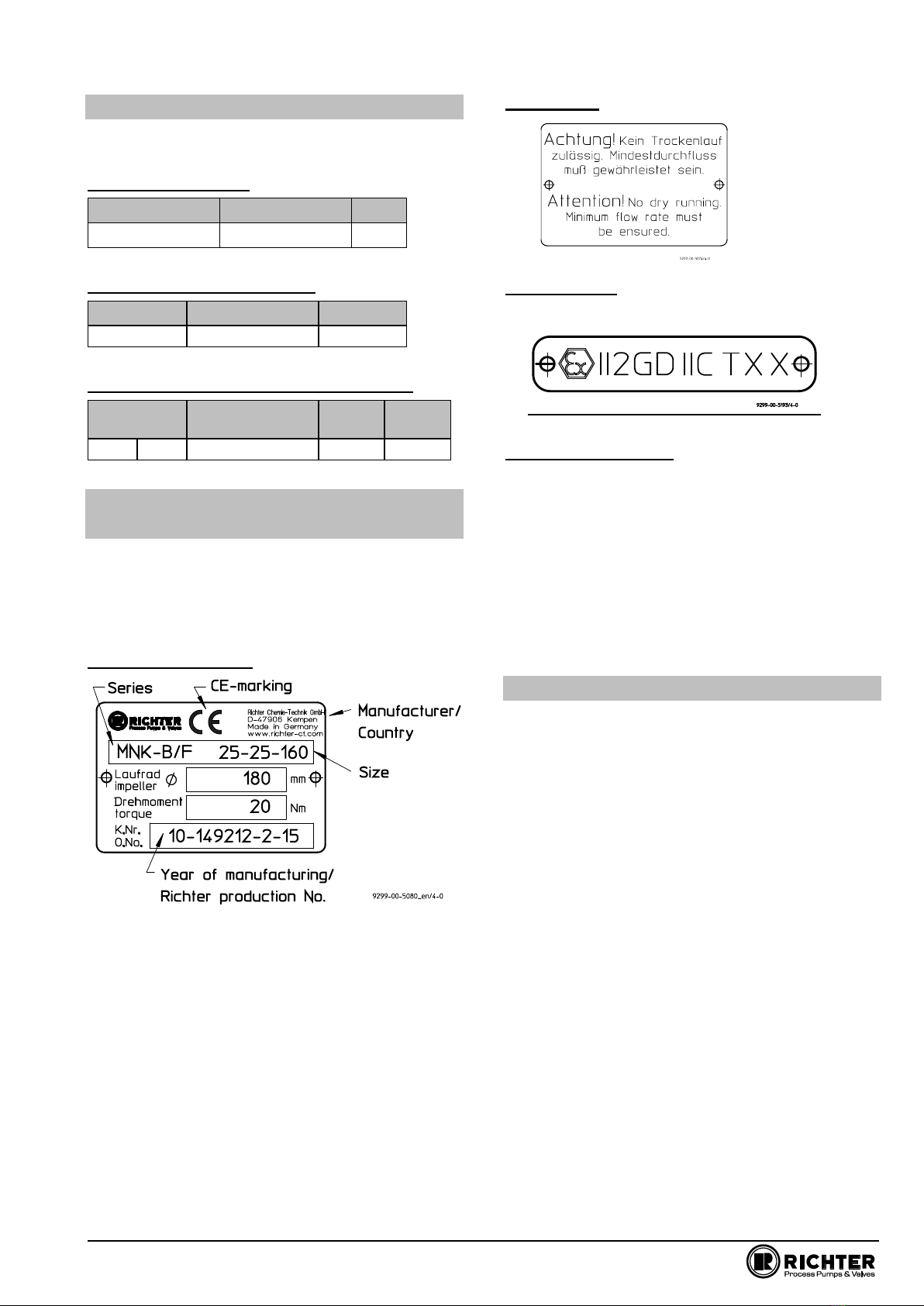
Series MNK-B, size 25-25-100 Page 5
9230-056-en Revision 14
TM 9542 Edition 06/2016
2 Notes on safety
This operating manual contains fundamental
information which is to be observed during installation,
operation and maintenance.
It must be read before installation and
commissioning!
This operating manual must always be available at the
place of use of the machine/plant.
In addition to the general notes on safety under the
main heading “Safety”, special notes on safety are
included at other points and must be observed.
Installation, operation and maintenance are to be
performed by qualified staff.
The area of responsibility, authority and supervision of
the staff must be exactly regulated by the customer.
If the staff does not have the necessary expertise,
they are to be trained and instructed.
If necessary, this can be provided by the
manufacturer/supplier on behalf of the machine
operator.
General hazard symbol! People may be put
at risk.
Safety symbol! The pump and its function
may be put at risk if this safety symbol is not
observed.
EU marking! Explosion-protected equipment
must be identified for work in potentially
explosive areas.
Warning of a magnetic field!
Warning of electric power!
This warning sign must be used if people
with a pacemaker are at risk, e.g. from a
strong magnetic field.
It is imperative to observe signs attached directly to
the pump / unit, e.g.:
Direction of rotation arrow
Warning against dry-running
and they are to be kept legible.
Non-observance of the notes on safety may result
in the loss of any and all claims for damages.
Non-observance may involve the following hazards :
Failure of important functions of the machine/plant.
Failure of electronic equipment and measuring
instruments due to magnetic fields.
Risk to people and their personal property from
magnetic fields.
Risk to people from electric, mechanical and
chemical effects.
Risks to the environment through leaks of
hazardous substances.
If the unit is used in potentially explosive
areas, special attention is to be paid to the
sections identified with “Ex” in this
operating manual.
2.1 Intended use
Richter pumps of the series MNK-B are plastic-lined
magnetic drive centrifugal pumps for the leak-free
conveyance of aggressive, toxic, pure and
inflammable liquids.
The pump is equipped with a permanent magnetic
synchronous drive.
For vertical installation of the pumps, please consult
the manufacturer.
The observance of the specified physical
limits is important for perfect functioning and
safe operation, especially with regard to
explosion protection to prevent potential sources of
ignition (see Section 2.6):
It must be ensured that the pump is always filled
with liquid during operation.
For safe pump operation, we recommend a flow
rate which lies between 0.3 and 1.1 Qopt. The
maximum operating temperature must never be
exceeded. See Section 2.6.7. In case of doubt,
you must consult the manufacturer.
The manufacturer must be consulted in the event
of entrainment of gas >2% as well as solids in
order to avoid a lack of lubrication and dry-running.
The plant NPSH value (NPSHA) should be 0.5 m
higher than the NPSH value of the pump
(NPSHR). See also Section 5.4.1.
Inadmissible modes of operation, even for a
short period, may result in serious damage to
the unit.
In connection with explosion protection, potential
sources of ignition (overheating, electrostatic and
induced charges, mechanical and electric sparks) may
result from these inadmissible modes of operation;
their occurrence can only be prevented by adhering to
the intended use.
Furthermore, reference is made in this connection to
the Directive 95/C332/06 (ATEX 118a) which contains
the minimum regulations for improving the
occupational health and safety of the workers who
may be at risk from an explosive atmosphere.
This unit must not be operated above the
values specified in the data sheet as regards
the fluid to be conveyed, flow rate, speed,
density, delivery head and operating temperature as
well as the motor rating.
The instructions contained in the operating
manual or contract documentation must be
observed; if necessary consult the manufacturer.