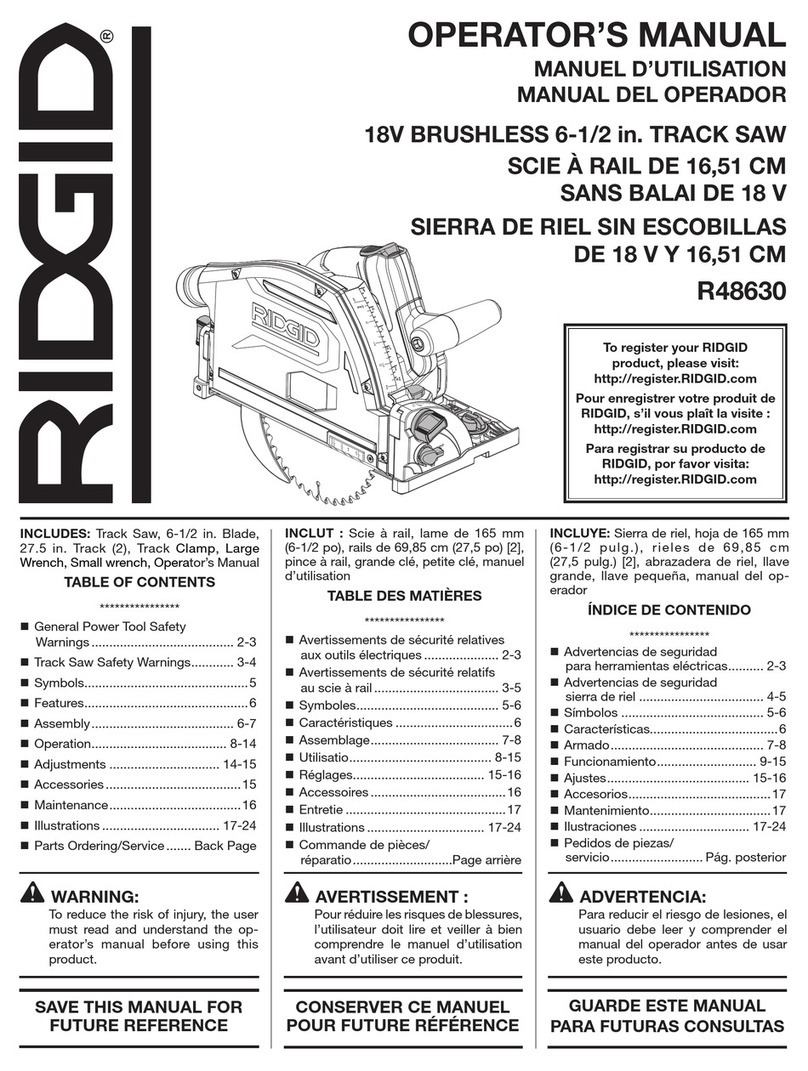
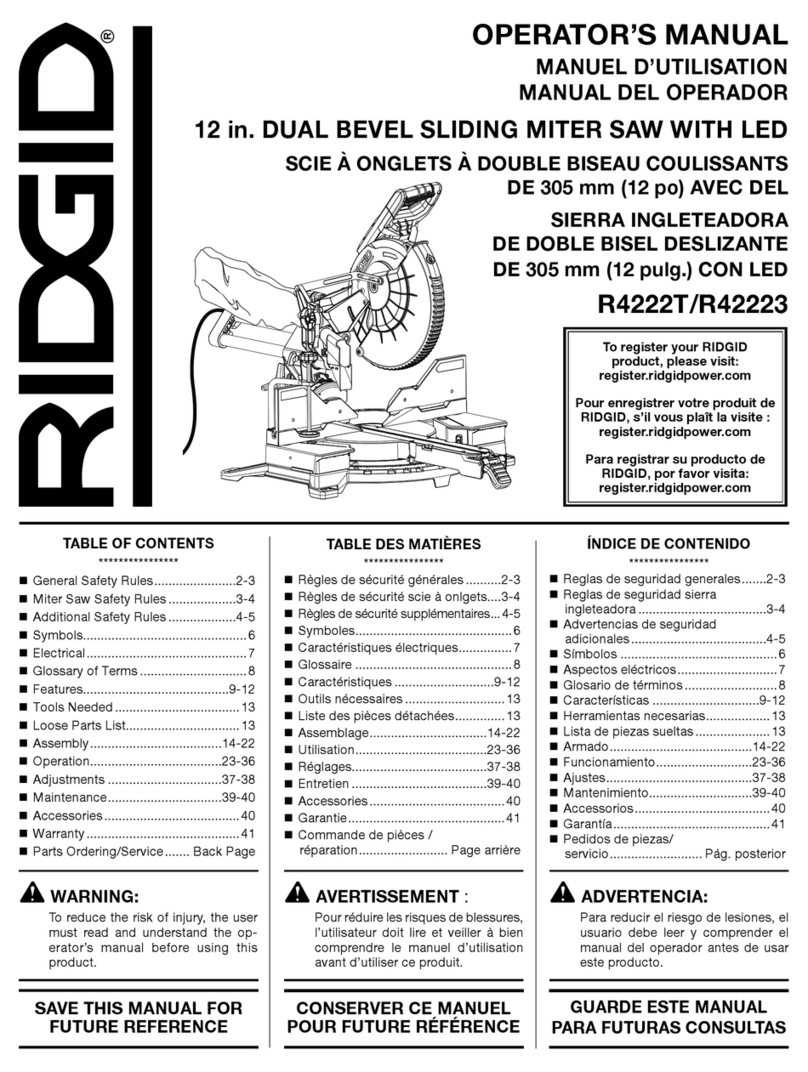
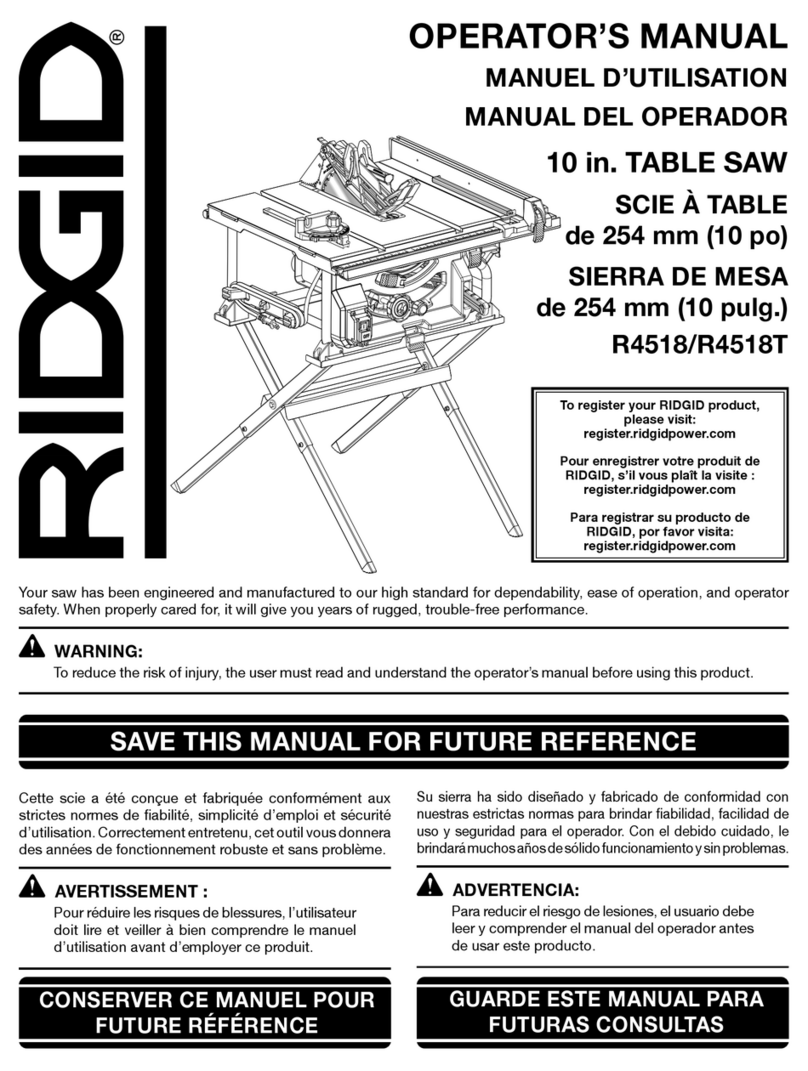
TABLE OF CONTENTS
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
SPECIFICATIONS
The RIDGID®#R4540 series 10 inch Portable Contractor Table
Saw is designed for portability and high quality performance. It
includes: basic machine, sturdy tubular steel stand, integral 2 1/2
inch dust chute, a fence system, T-slot miter gauge, 15-amp motor,
on/o switch, cast aluminum table, extension wing, see-through
blade guard with anti-kickback pawls, and 10 inch carbide blade.
NOTICE: The manual cover illustrates the current production model. All other illustrations contained in the manual are representative
only and may not be exact depictions of the actual labeling or accessories included. They are intended for illustrative purposes only.
Max depth of cut at 90 degrees: 3 1/2 inch
Max depth of cut at 45 degrees: 2 1/2 inch
Max rip to right of blade: 25 inch
Max rip to left of blade: 12 inch
MOTOR SPECIFICATIONS:
Amps 15
Voltage 120
No Load RPM 5,000
Blade Diameter 10 inch
This tool can only be used with woodworking saw blades.
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION .............................................2
FEATURES..........................................................................3
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS ...............................4
SAFETY-SYMBOLS-DEFINITIONS......................................4
GENERAL POWER TOOL SAFETY WARNINGS....................5
TABLE SAW SAFETY RULES ...............................................6
TERMINOLOGY..................................................................6
TABLE SAW SPECIFIC SAFETY RULES.................................. 6
SAW BLADE GUARD, ANTI-KICKBACK PAWLS AND RIVING
KNIFE ASSEMBLY............................................................... 8
KICKBACKS.......................................................................8
AVOID KICKBACK ..............................................................8
PROPOSITION 65 WARNING ............................................8
POWER CONNECTIONS .....................................................9
POWER SOURCE................................................................ 9
EXTENSION CORDS...........................................................9
UNPACKING.......................................................................9
PACKAGE CONTENTS....................................................... 10
HARDWARE BAG CONTENTS ............................................ 11
ASSEMBLY .......................................................................13
ASSEMBLING THE STAND................................................. 13
ATTACHING STAND TO SAW............................................. 14
HEIGHT ADJUSTMENT KNOB INSTALLATION..................... 15
BLADE AND GUARDS ....................................................... 15
ATTACH THE BLADE......................................................... 15
THROAT PLATE................................................................ 16
ANTI-KICKBACKS PAWLS AND BLADE GUARD.................... 17
BLADE GUARD................................................................. 17
INSTALLING FENCE ......................................................... 18
REMOVING FENCE........................................................... 18
ON-BOARD STORAGE....................................................... 19
MAKING ADJUSTMENTS..................................................20
LEVELING THE THROAT PLATE......................................... 20
ADJUSTING BLADE PARALLEL TO
MITER GAUGE GROOVE (HEEL)........................................ 20
SQUARING THE BLADE VERTICALLY ................................. 22
ADJUSTING THE BEVEL STOPS......................................... 22
ADJUSTING THE BLADE HEIGHT....................................... 23
CHANGING THE BEVEL .................................................... 23
USING THE MITER GAUGE ............................................... 23
OPERATION AND ADJUSTMENT OF RIP FENCE.................. 23
USING COLOR-CODED SCALES......................................... 24
RIVING KNIFE POSITION AND ALIGNMENT...................25
RIVING KNIFE HEIGHT SETTING ...................................... 25
RIVING KNIFE ALIGNMENT .............................................. 26
HORIZONTAL ALIGNMENT................................................ 26
VERTICAL ALIGNMENT..................................................... 26
MOVING THE SAW........................................................... 27
OPERATION.....................................................................27
DUST COLLECTOR........................................................... 28
TURNING THE SAW ON/OFF............................................. 28
MAKING CUTS .................................................................29
RIP CUTS........................................................................ 30
BEVEL RIPPING............................................................... 30
CROSSCUTTING............................................................... 31
BEVEL CROSSCUTTING .................................................... 31
MITER CUTS ................................................................... 31
COMPOUND MITER CUTS................................................. 32
LARGE PANEL CUTS......................................................... 32
NON-THROUGH CUTS...................................................... 32
MAKING A NON-THROUGH CUT........................................ 32
CUTTING AIDS AND ACCESSORIES.................................33
PUSH STICK.................................................................... 33
AUXILIARY MITER GAUGE FACING.................................... 34
AUXILIARY FENCE (FLIP DOWN)....................................... 34
PUSH BLOCK .................................................................. 34
GROOVING AND RABBETING ........................................... 34
FEATHERBOARD ............................................................. 35
CUT OFF GAUGE.............................................................. 35
JIGS................................................................................ 35
MAINTENANCE ................................................................36
TROUBLESHOOTING........................................................37
ACCESSORIES..................................................................37
PARTS, SERVICE OR WARRANTY ASSISTANCE...............38
2 3