2
Table of Contents
Section Page
Table of Contents ..........................................................2
Safety Instructions For Table Saw .................................3
Safety Signal Words ...................................................3
Before Using The Saw ................................................3
When Installing Or Moving The Saw ........................... 3
Before Each Use .........................................................4
To Reduce the Risk of Injury From Jams, Slips Or
Thrown Pieces (Kickbacks Or Throwbacks) .............. 4
Plan Ahead To Protect Your Eyes, Hands,
Face and Ears ...........................................................5
Whenever Sawblade Is Spinning ................................5
Additional Safety Instructions For: Rip Type Cuts .......6
Additional Safety Instructions For: Crosscuts..............6
Glossary of Terms for Woodworking .............................7
Motor Specifications and Electrical Requirements ........8
Power Supply and Motor Specifications .....................8
General Electrical Connections ...................................8
110-120 Volt, 60 Hz. Tool Information ........................8
Wire Sizes ...................................................................9
Unpacking and Checking Contents .............................10
Unpacking .................................................................10
List of Loose Parts ....................................................10
Getting to Know Your Table Saw ................................11
Blade Guard Storage ................................................14
Wrench/Blade Storage ..............................................14
Rip Fence Storage ....................................................14
Miter Gauge Storage .................................................14
Alignment .....................................................................15
Tools Needed ............................................................15
Remove Foam Motor Support ...................................15
Checking Table Insert ...............................................15
Checking Heeling Adjustment or Parallelism of
Sawblade to Miter Gauge Groove ...........................16
Checking Blade Tilt, or Squareness of Blade
to Table ....................................................................17
To Check For Squareness, 90° Position ...................17
Adjusting Rip Fence Guide Bars ...............................19
Aligning Sliding Table Extension ...............................19
Rip Fence Alignment Adjustment ..............................20
Rip Fence Lock Lever Adjustment ............................20
Checking Sliding Table Extension ............................21
Installing Blade Guard ...............................................21
Aligning Blade Guard ................................................22
Removing and Installing Sawblade ...........................23
Miter Gauge Alignment .............................................24
Adjusting Bevel Lock .................................................25
Mounting Your Saw .....................................................25
Mounting Table Saw to Workbench or Legset ..........25
Section Page
Workbench Mounting Using Hardware ..................... 25
Table Saw Mounting Procedures .............................. 25
Mounting Your Saw ..................................................... 26
Mounting Table Saw to RIDGID Universal
Power Tool Legset #AC9910 .................................. 26
Workbench Mounting Using "C" Clamps .................. 26
Supporting Table Saw with Sawhorses .................... 26
Safety Instructions for Basic Saw Operations ............. 27
Before Each Use ....................................................... 27
To Reduce the Risk of Injury From Jams, Slips Or
Thrown Pieces (Kickbacks Or Throwbacks) ............ 27
Plan Ahead To Protect Your Eyes, Hands,
Face and Ears.......................................................... 28
Whenever Sawblade Is Spinning .............................. 28
Work Feed Devices ..................................................... 29
Push Stick ................................................................. 29
Push Block (For Use with Auxiliary Fence) ............... 29
Auxiliary Fence ......................................................... 30
Fence Facing ............................................................ 31
Basic Saw Operations ................................................. 32
Using the Miter Gauge .............................................. 32
Additional Safety Instructions for Crosscutting ......... 32
Crosscutting .............................................................. 32
Repetitive Crosscutting ............................................. 33
Miter Crosscutting ..................................................... 34
Bevel Crosscutting .................................................... 34
Compound Crosscutting ........................................... 34
Using the Rip Fence ................................................. 35
Additional Safety Instructions for Rip Cuts ............... 35
Ripping ...................................................................... 35
Bevel Ripping Narrow Work ...................................... 37
Using Featherboards for Thru Sawing ...................... 37
Using Featherboards for Non-Thru Sawing .............. 38
Resawing .................................................................. 38
Using Carbide Tipped Blades ................................... 39
Dadoing .................................................................... 39
Rabbeting ................................................................. 40
Ploughing and Molding ............................................. 40
Molding ..................................................................... 41
Maintaining Your Table Saw ....................................... 42
Maintenance ............................................................. 42
Replacing Carbon Brushes ....................................... 42
Lubrication ................................................................ 42
RIDGID Recommends the Following Accessories ...... 43
Troubleshooting ........................................................... 43
General ..................................................................... 43
Motor ......................................................................... 44
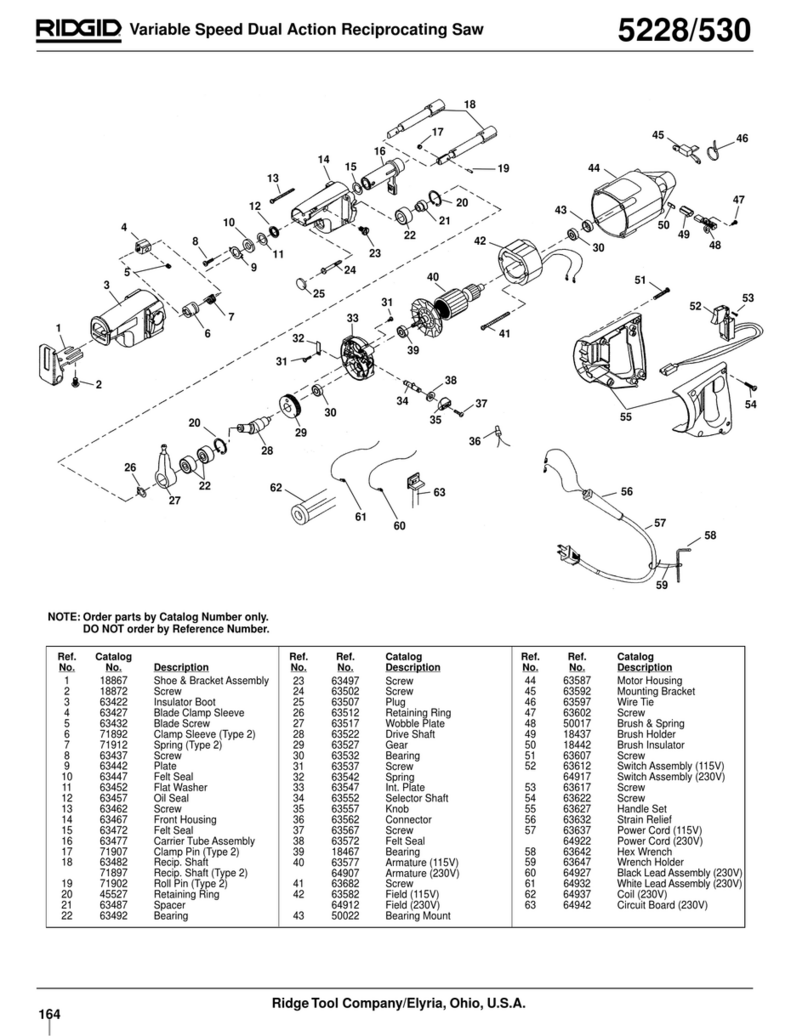
Repair Parts ................................................................ 45