Régulateur électronique réf. 10727
A savoir:
Le régulateur électronique réf. 10727 a été mis sur point surtout en vue d’une utilisation de concert avec
les transformateurs réf. 10718 et 10725 ainsi que le transformateur avec fiche intégrée réf. 8010727100.
Il est également possible d’alimenter le régulateur électronique réf. 10727 par les transformateurs réf.
10718 ou 10725 (voir Fig.1-3). Mais attention : Vu le fait que la tension de sortie de ces transformateurs
est légèrement plus élevée que celle du transformateur avec fiche intégrée, votre matériel moteur roulera
un peu plus vite qu’avec ce dernier et dépassera ainsi éventuellement la vitesse maxi du prototype.
Mise en service :
Le régulateur est à utiliser de préférence avec les transformateurs réf. 10728 et 10725 ainsi que le trans-
formateur avec prise intégrée réf. 8010727100 qui l’alimentent en 15 V c.a. ou c.c.; à la sortie «traction»
le régulateur débite une tension constante de 18 V (tension maximale par im-pulsion) linéairement régla-
ble par variation de la largeur des impulsions (voir Fig. 4)
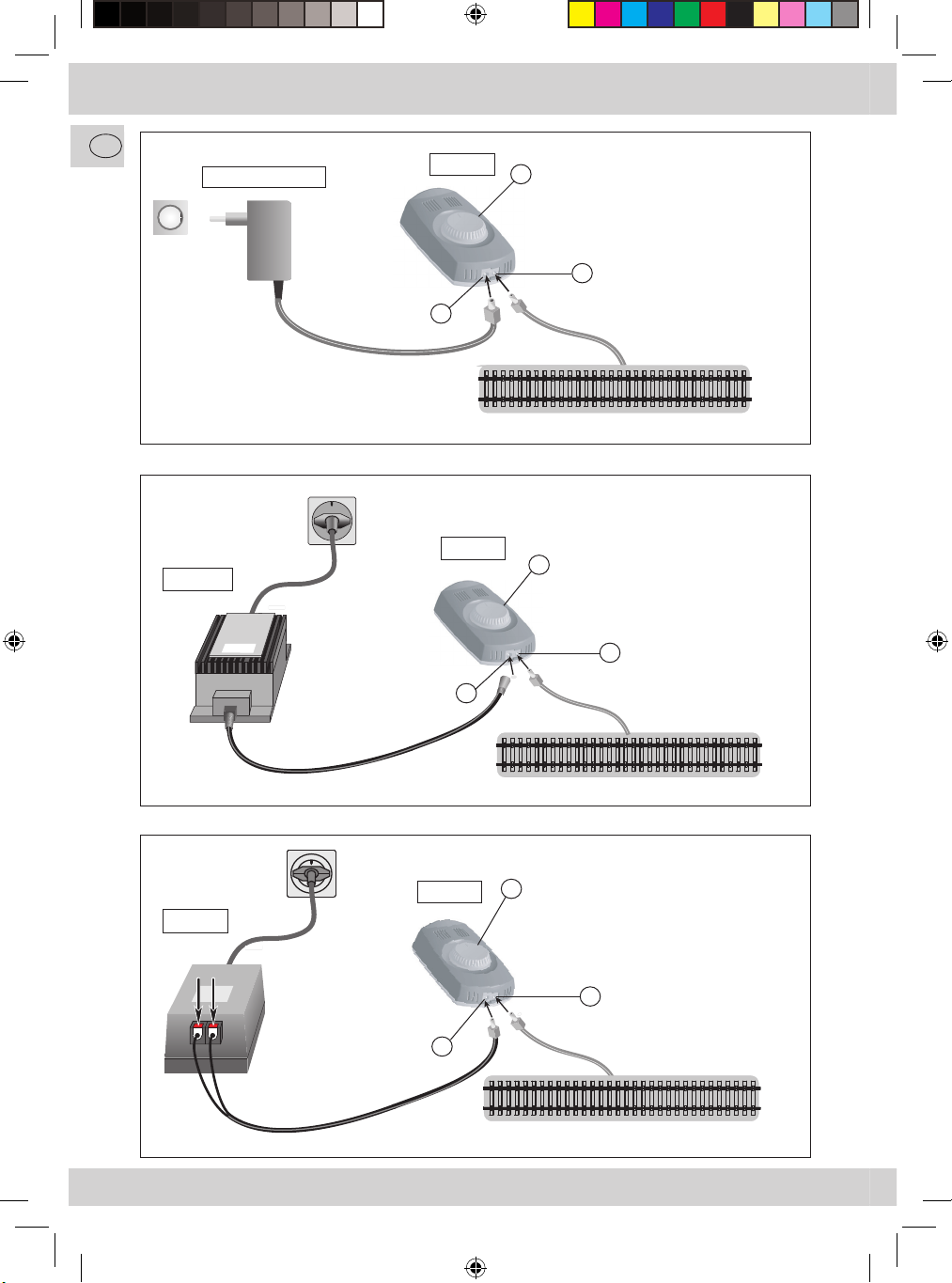
1. Prise «alimentation du régulateur»
Votre transformateur est à raccorder à cette prise (voir Fig.1-3).
2. Prise «sortie voie»
Cette prise est à relier avec la voie de votre réseau (voir Fig. 1-3).
3. Bouton régulateur
Par ce bouton vous allez déterminer la direction de marche et la vitesse de votre machine: De plus
que
vous vous éloignez de la position centrale, de plus la vitesse de la machine augmente. Le bouton
remis à la position centrale (position «0») le courant de traction est coupé et le régulateur est
électriquement déconnecté de votre réseau, sans que vous avez besoin de retirer la fiche de la prise
«sortie voie». Cette position sert également pour rear-mer le régulateur en cas que sa protection
électronique anti-court-circuit a déclenchée.
Application :
Alimentation du matériel moteur en courant continu «traction» régulé par variation de la lar-geur des
impulsions. Attention: Cette technique n’est pas appliquable à des modèles munis de moteurs à rotor
sans fer (Faulhaber, Escap, Canon et autres). Une utilisation de ce régulateur pour alimenter ces moteurs
peut causer une destruction de ces derniers.
Comme le régulateur ne dispose pas d’une séparation galvanique entre son «entrée ali-mentation» et
sa sortie «courant continu traction», il ne faut utiliser un seul et même transformateur pour plusieurs
régulateurs sauf si tous les engins moteurs de votre ré-seau sont alimentés exclusivement ou par la
voie ou par la caténaire! Une exploitation mixte (certaines machines alimentées par les rails, d’autres
par la caténaire) n’est pos-sible qu’en cas que chaque régulateur dispose de son transformateur indi-
viduel et ex-clusif. Une alimentation groupée (veut dire: alimentation de tous les régulateurs «voie»
par un transformateur et tous les régulateurs «caténaire» par un autre) risque de causer des influences
réciproques des deux groupes et donc des réactions imprévisibles des vé-hicules moteurs. Si votre
réseau est uniquement exploité par prise de courant par les rails ou par prise de courant par la caté-
naire, un transformateur peut alimenter sans problèmes plusieurs régulateurs à la fois, sous condition
que les différents cantons sont séparés l’un de l’autre par une isolation bipolaire (si votre réseau est
exploité unique-ment par prise de courant par la voie il faut deux éclisses, une au rail gauche et une
au rail droite de la voie, par sectionnement; s’il s’agit d’un réseau exploité uniquement par caténaire,
ensuite il faut une isolation supplémentaire dans la caténaire exactement au même endroit où se
trouvent les éclises isolantes dans les rails!).