S3C6410-TFAAndroid development started
S3C6410-TFAsoftware and S3C6410-TFA is fully compatible, so the path is set, the default configuration file,
have followed the S3C6410-TFA of manuals, based on the actual situation may be slightly different, if in
doubt, please contact us: Info@Esys.ir
Before, for the Android system, we mainly used to solve the Android file system UBIFS fast programming,
and provides a running Android through SD card method, and their steps are very simple to use.
After a period of exploration and learning, we have mastered the basic knowledge of Android application
development system, now provides the latest Android system, already contains a number of commonly
used functions, such as the most popular 3G wireless Internet access, Bluetooth, SD WiFi, excellent
automatically mount disk identification, graphical interface cable card settings and so on.Especially the 3G
dial-up, it can automatically recognize the USB card dialer, and supports WCDMA, CDMA2000, TD-SCDMA
and other formats on the card.
Now, you can use the Android 2.3 it!
This manual will focus on Introduction to Android development or basic knowledge, such as the Bootloader
compiled production, kernel compilation production, production, and so the firmware.
Android BootLoader used with traditional Linux system kernel and the difference is not great, compilation
methods and procedures basically no difference, but slightly different configuration file.Android's main
secret is that it's part of the file system, we are referring to the Android system will be it, so in this section
referred to the Android system is actually used by the Android system the target file system.
To this section, we recommend that you first understand and master the "Linux Developer's Guide" to
create a development environment chapters.
In addition, "Android Application Development Guide" has been released, mainly on how to build an
Android application development environment and how to use S3C6410-TFAand S3C6410-TFAfor USB
debugging, the documentation is located under the CD-ROM A "development documentation and tutorials \
02 Android Programming Developer's Guide "directory.
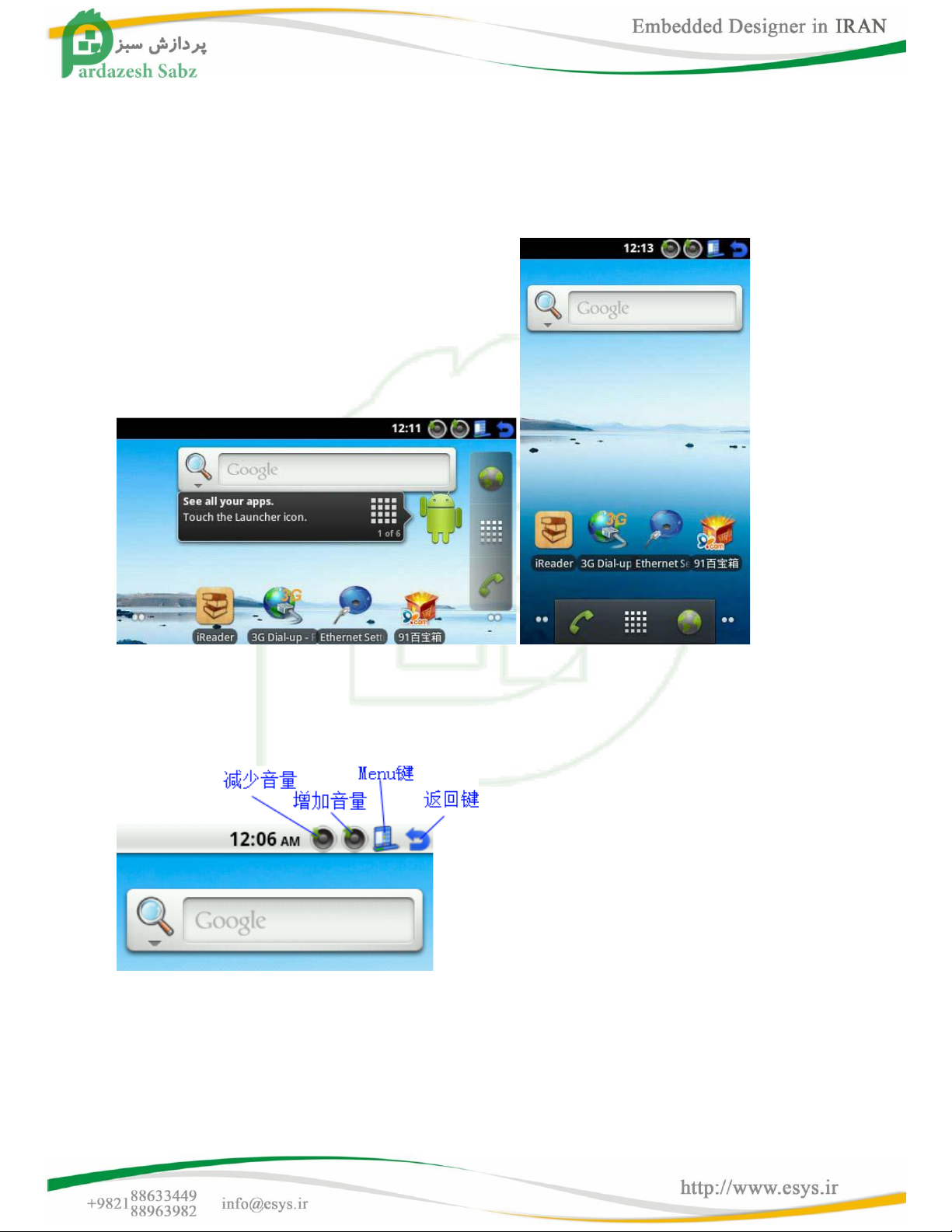
1 installation and use Android
Description: Memory capacity of 128M with the development board, running directly through the SD card
ext3 format Android may sometimes not run smoothly; use 256M memory capacity of the development
board is no problem, we recommend to the Nand Flash to Android programming in operation.
1.1 Install Android installation methods, see "Brush Guide" on the key layout