6
Programming
Communicating with IndustryPacks installed on the Flex/104A involves writing and
reading from four registers on the Flex/104A. The IP Access Register, Upper Address
Register, and Data Register are all used together to access registers on board the
IndustryPacks.
The first step in starting an access is to program the IP Access Register (formerly known
as the Address Register in the Flex/104). Programming this register determines which
IndustryPack slot is accessed, what space on the IndustryPack (I/O, Memory, ID, or
Interrupt space), and at what offset on the IP the access occurs.
Next, if a Memory space access is to be made, the Upper Address Register must be
programmed with the upper address bits of the IP bus. IF any other space on the IP is
accessed, this step can be skipped.
Finally, accessing the Data Register initiates the IP access. Reading the Data Register
causes a read of the IP at the space and offset that is programmed into the IP Access
Register. Similarly, a write to the Data Register writes the data in the Data Register into
the IP at the space and offset specified in the IP Access Register.
While the access is in process, the IP Wait bit in the Control and Status Register is
asserted high. Once the access is complete, the bit returns to zero. Before starting
another access, the programmer must check this bit and verify that it is zero. If the
IndustryPack fails to acknowledge the access within 64 µs, the Flex/104A terminates the
access and asserts the TM STAT bit in the Control and Status Register. To clear this bit,
the programmer must write a one to TM RST bit in the Control and Status Register.
The sections below explain each of these registers in more detail.
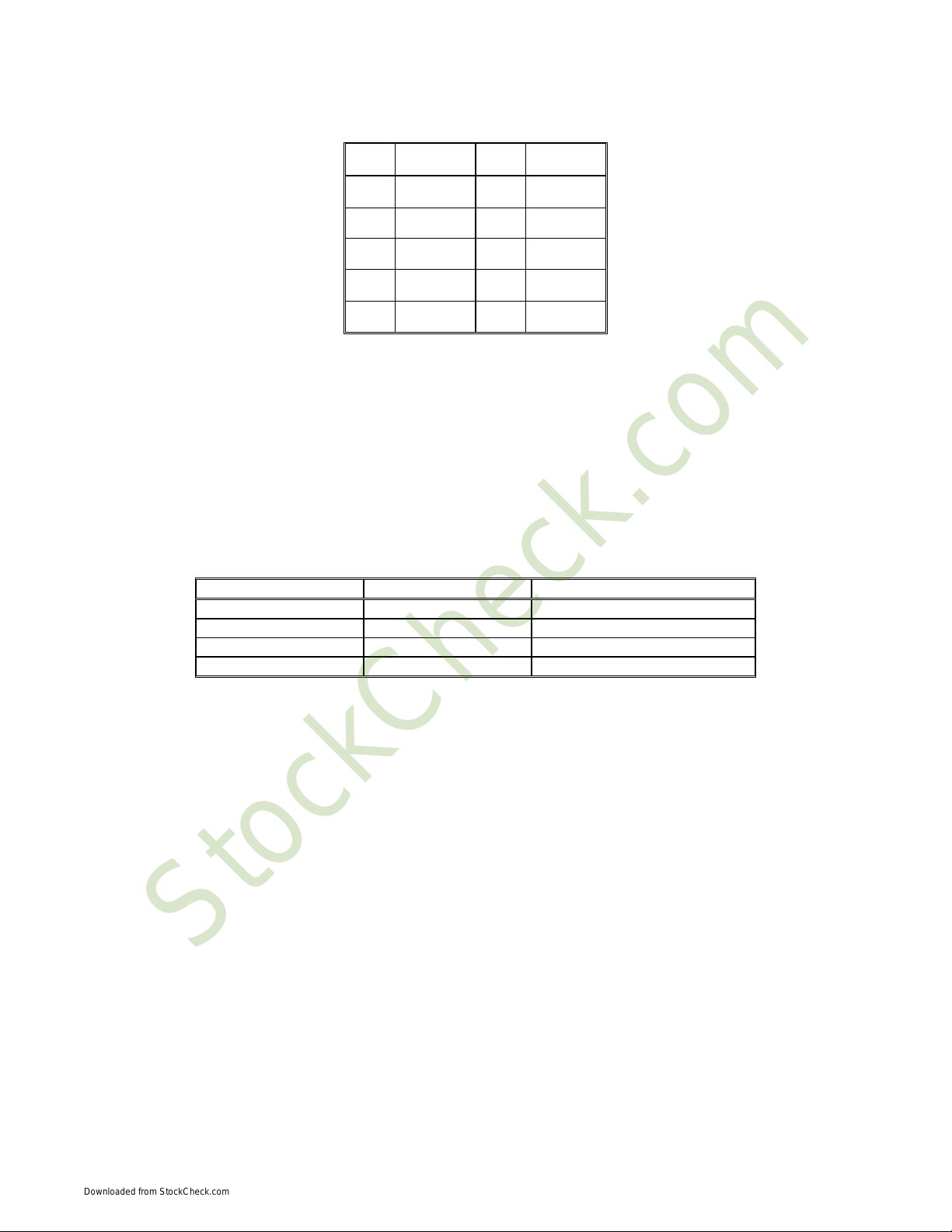
Register Map
The PC/104 programmer can access the IndustryPack modules on board the Flex/104A
using the set of registers listed below. These registers are located on the Flex/104A
card, not the IndustryPacks. Each register is at a unique offset address from the base
address. Base address for the Flex/104A is set using shunts E1 and E2. For more
information on the base address, refer to the Addressing section on page ?
Offset Register Name Read/Write
0x00 Data Register Read/Write
0x02 IP Access Register Write Only
0x04 Upper Address Register Write Only
0x06 Control and Status Read/Write
Figure 5 Register Map for the Flex/104A
Downloaded from StockCheck.com