Fiber Couplers Series 60FC-A19.5
Adjustment_60FC-A195 18.05.2021 © Schäfter+Kirchhoff GmbH
Schäfter+Kirchhof
f
GmbH
Kieler
Str
.
212
22525
Hamburg,
Germany
+49
40
85
39
9
7-0 [email protected] www.sukhamburg.com4
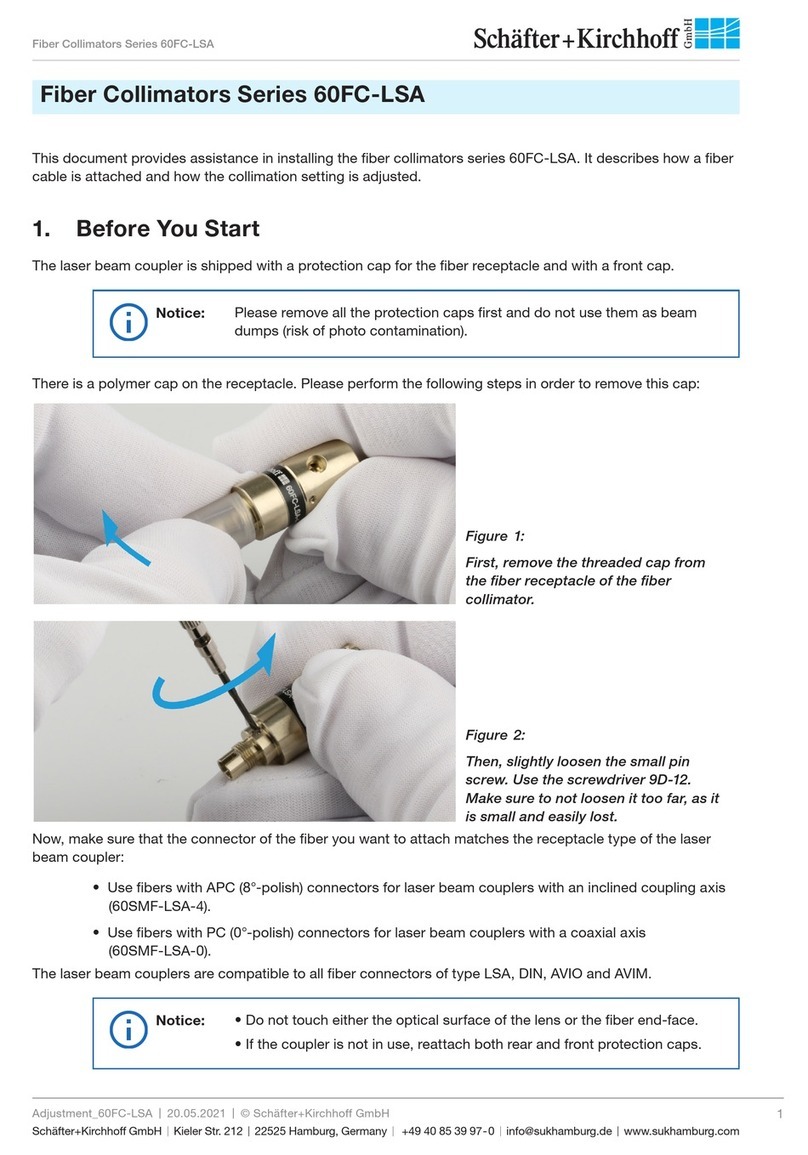
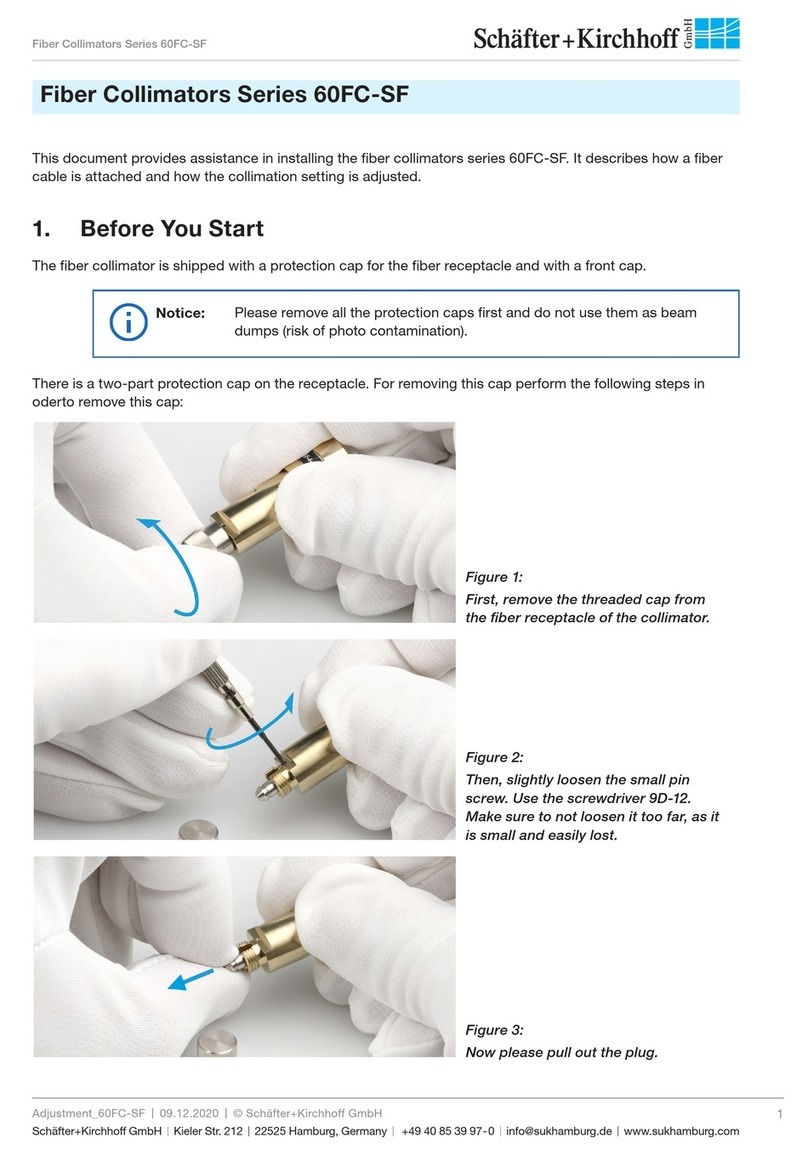
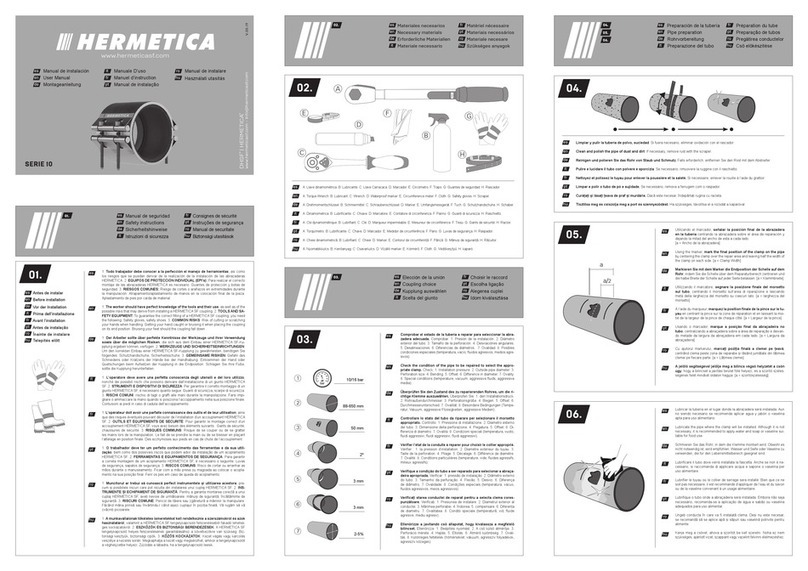
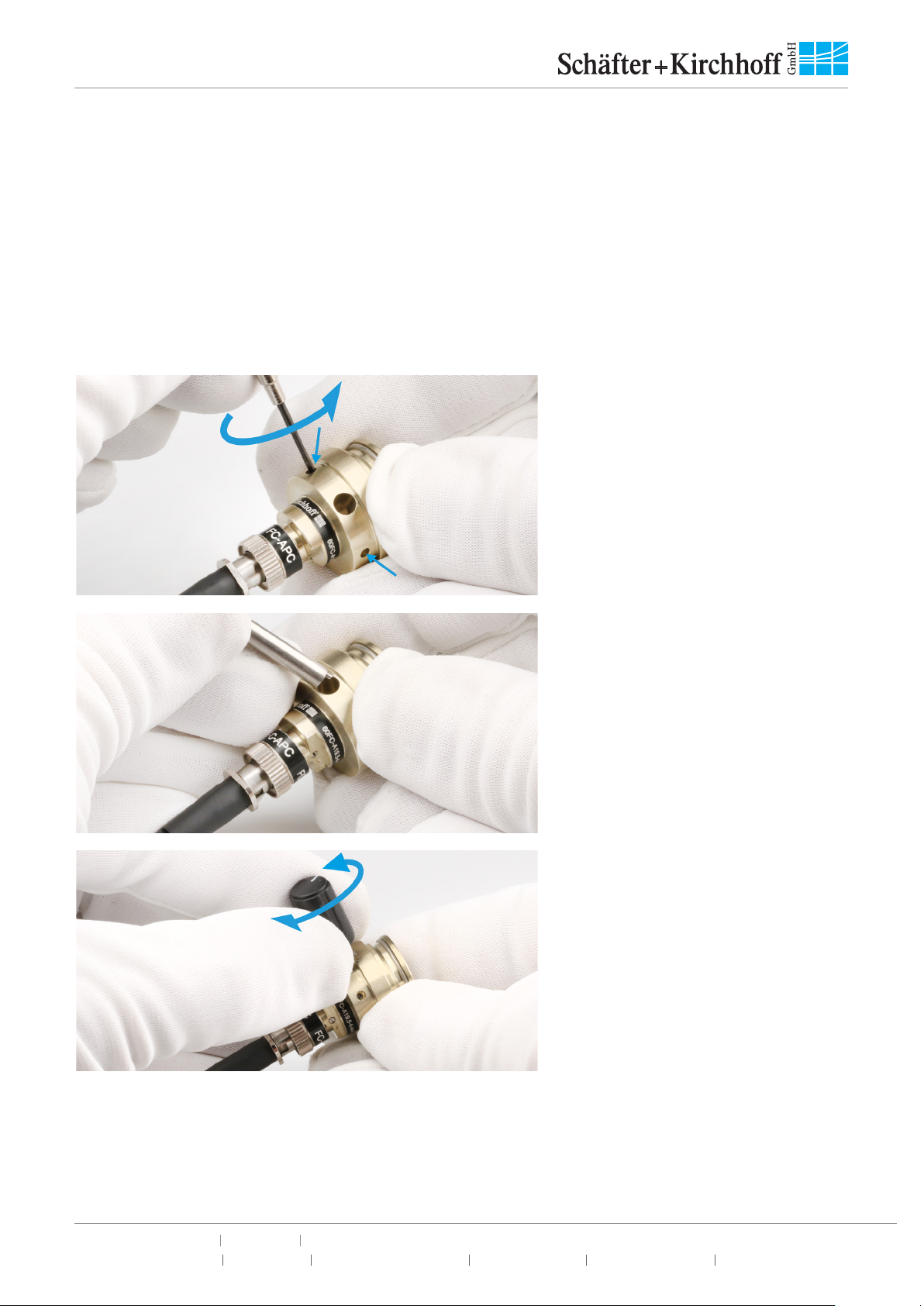
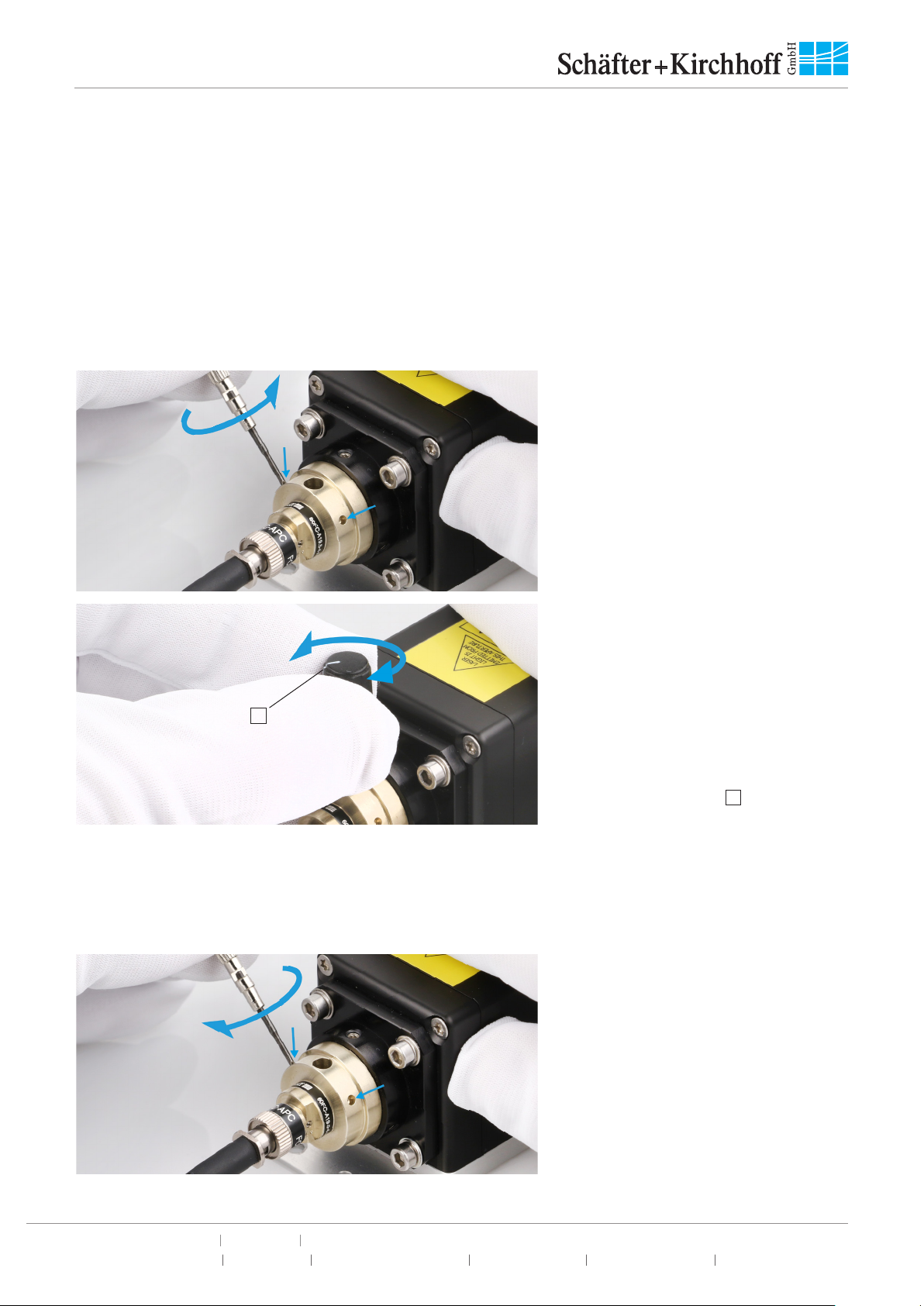
Figure 8:
Finally, gently tighten the fiber grub
screw to reduce the free play of the
ferrule in the receptacle.
The free play in between the connector ferrule and receptacle is only a few microns, but necessary for
inserting the ferrule without force.
The tightened grub screw and the right-hand orientation rule for the connector, ensure a high reproducibility
in mode field position and angle, which is especially important for attaching and reattaching polarization-
maintaining fibers reproducibly.
3. Adjusting the Focus Setting
Focus adjustment (adjustment of the coupling lens in z-direction) is a demanding task and should be
performed preferably using a collimating telescope.
The fiber coupler is shipped pre-adjusted for the labeled wavelength and,
often, it is not necessary for the customer to readjust the coupling lens
position. This is why you can skip this step in most cases.
Notice:
To check the collimation setting of the fiber coupler, couple a radiation source of appropriate wavelength into
the fiber connected to the fiber coupler.
Refer to the laser instruction manual for all instructions regarding laser
safety!
• Do not stare directly into the laser beam (which can cause permanent
damage to the eyes).
• Do not stare at the reflected beam from reflective objects.
• Do not point the laser beam to other individuals.
Depending on the fiber type used with the fiber coupler there are two options:
• If you use the fiber coupler with a multi-mode fiber, use the factory setting. In case of
in-coupling high power levels into a multi-mode fiber, a fine-adjustment of a fiber coupler already
installed is described in Chapter 7.
• If you use the fiber coupler with a single-mode or polarization-maintaining fiber, you can use the
following procedure:
Direct the beam to a target about half a Rayleigh length zRaway:
zRπ∙∅2
beam
=
2 λ∙8