3. 2. Connecting the gas cylinder
3. 2. 1. When using Argon or Argon mixtures, you
will need to use the bull nose adaptor. If
you intend to use CO2 gas the regulator will
fit directly onto the cylinder. Fit the bull nose
adaptor to the cylinder with a spanner.
3. 2. 2. Fit the gas regulator on the bull nose
adaptor and connect it to the machine gas
hose (fig.2).
3. 2. 3. Set the regulator flow rate to 5-8 litres/min
depending on the material to be welded,
and whether there are draughts which are
strong enough to disturb the gas flow.
3. 3. Fitting a reel of wire - Ensure the welder
is unplugged from mains power.
( Refer to fig.4 )Your machine comes with a
mini spool of wire, but will accept up to 5kg spools without modification.
Firstly remove the nut, spring, metal washer and outer plastic retainer from
the threaded reel shaft.
3. 3. 1. Push the reel of wire over the threaded spindle and onto the flange of the
inner circular plastic retainer. Replace the nut, spring, metal washer and outer
plastic retainer. Tighten the nut whilst turning the reel until a slight braking
pressure is felt. Do not over tighten. Ensure the spool rotates clockwise, with
the wire drawing off the reel from the top as shown in fig 5.
3. 3. 2. Reduce the wire feed tension by turning the wire feed knob ( fig.6-A ) 2 or 3
turns anticlockwise. ( Do not unscrew the knob completely.) Pull the knob
towards you and allow it to disengage from the counter roller bracket and
hinge downwards to the position shown in fig.5. Push the counter roller
bracket upwards and away from the grooved drive roller as shown in fig.5.
3. 3. 3. Ensure that the correct size of drive roller is installed and that the roller is the
right way round to drive the the chosen wire. Refer to section 3.5.
3. 3. 4. Before releasing the wire from the reel ensure that the reel is not
freewheeling ( See section 3.3.1 ) As you release the wire keep a slight
tension on it to prevent coils coming off the reel. Straighten the first 50mm of
the wire and feed it into the flexible hose ( see fig.5A ), over the grooved
drive roller ( see fig.5B ), and into the torch liner collet ( see fig.5C ).
3. 3. 5. Now hinge the counter roller bracket back down onto the wire and secure it by
swinging the tension lever/knob up into the socket in the bracket. Turn the knob
clockwise by 2 or 3 turns to exert medium pressure. ( fig.6-A )
3. 3. 6. Before feeding the wire through to the torch remove the gas cup (fig 3.3.5.a) and
contact tip (b) from end of torch as follows:
a) Take torch in left hand with the torch tip facing to the right.
b) Grasp gas cup firmly in your right hand.
c) Turn gas cup clockwise only (c) and pull cup out to the right.
pWARNING! do not turn gas cup anti-clockwise, as this will damage internal spring.
d) Unscrew the copper contact tip (right hand thread) to remove.
3. 3. 7. Check welder is switched off 0, and that the earth clamp is away from the torch tip.
Connect the welder to the mains power supply and set the voltage switch to one.
3. 3. 8. Set the wire speed knob to position 5 or 6. Keeping the torch cable as straight as
possible and press the torch switch. The wire will feed through the torch.
3. 3. 9. When wire has fed through, switch welder off, unplug from mains.
a) Take torch in left hand and screw contact tip back into place. Cut the wire back to
within 3mm of the tip.
b) Grasp gas cup in right hand, push onto torch head and turn clockwise only.
pWARNING! do not turn gas cup anti-clockwise, as this will damage internal spring.
c) Cut wire so that it is just protruding the cup.
fig 1.
fig 2.
3. ASSEMBLY
To fit the mains power plug see safety instructions (Chapter 1).
SPECIFICATION.
This Manual contains instructions to assist you prepare your Mig Set for welding, together with information on maintenance, and trouble shooting. Read manual
carefully in order to get the best results from your machine. These instructions are not intended to show you how to be an expert welder. It is with continued
practice that you will achieve the desired results. Mig welding requires a steady hand, and time spent practising with scrap metal will be rewarded when you
progress to an actual workpiece.
The SUPERMIG150/5.V2 is a compact power source with integral wire feed which protects the wire from dust and dirt (especially in Body Shops). It is suitable for
welding with either CO2, Argon/CO2 mix or Argon gas. The unit has a forced air cooling system to slow transformer heating in order to increase the duty cycle and
a non live torch to prevent the risk of accidentally striking an arc. Your Mig is designed to operate with two diameters of welding wire, 0.6mm, & 0.8mm. (We
recommend that 0,8mm wire is used for welding stainless steel and aluminium).
MODEL IS EQUIPPED WITH:3Torch, 3Mini reel of 0.6mm wire, 3Argon/CO2 regulator, 3Bull nose adaptor 3Gas hose.
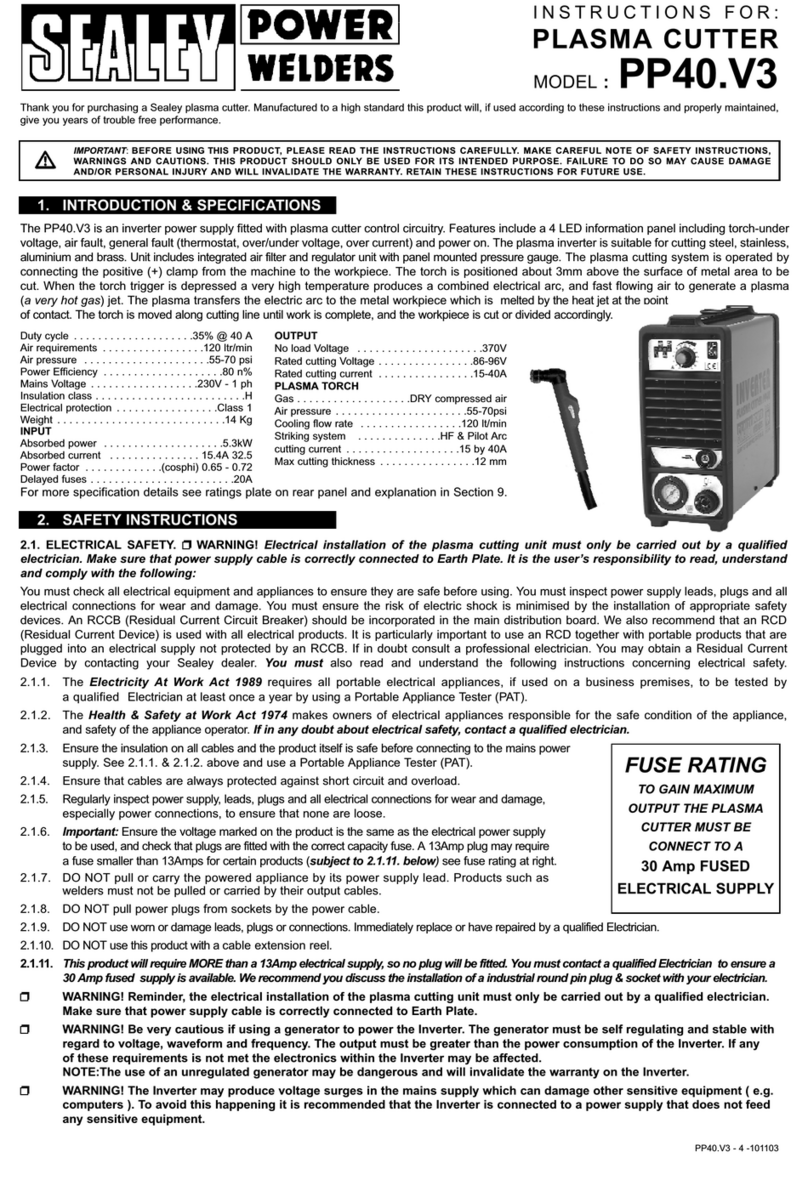
Welding Current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30-150 Amps
Duty Cycle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100% @ 30A
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80% @ 50A
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50% @ 70A
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10% @ 150A
2. INTRODUCTION & SPECIFICATION
Power efficiency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.3 Kva
Wire capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5kg
Power input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .230V - 1ph
Power efficiency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.3kVA
Weight . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26kg
fig 4
fig 3.
fig 5.
fig 6.
3. 1. Wheel Assembly
Fit the axle on to the bottom (rear) of the machine with the nuts,
bolts and washers provided. Push the wheels on to the axle and
hold them in place by pushing the wheel retainers supplied onto
the ends of the axles.( See fig.1) Fit front stay by screwing it into
the centrally placed threaded insert on the underside of the
chassis close to the front face of the unit.
SUPERMIG150/5.V2 - (1) - 241002