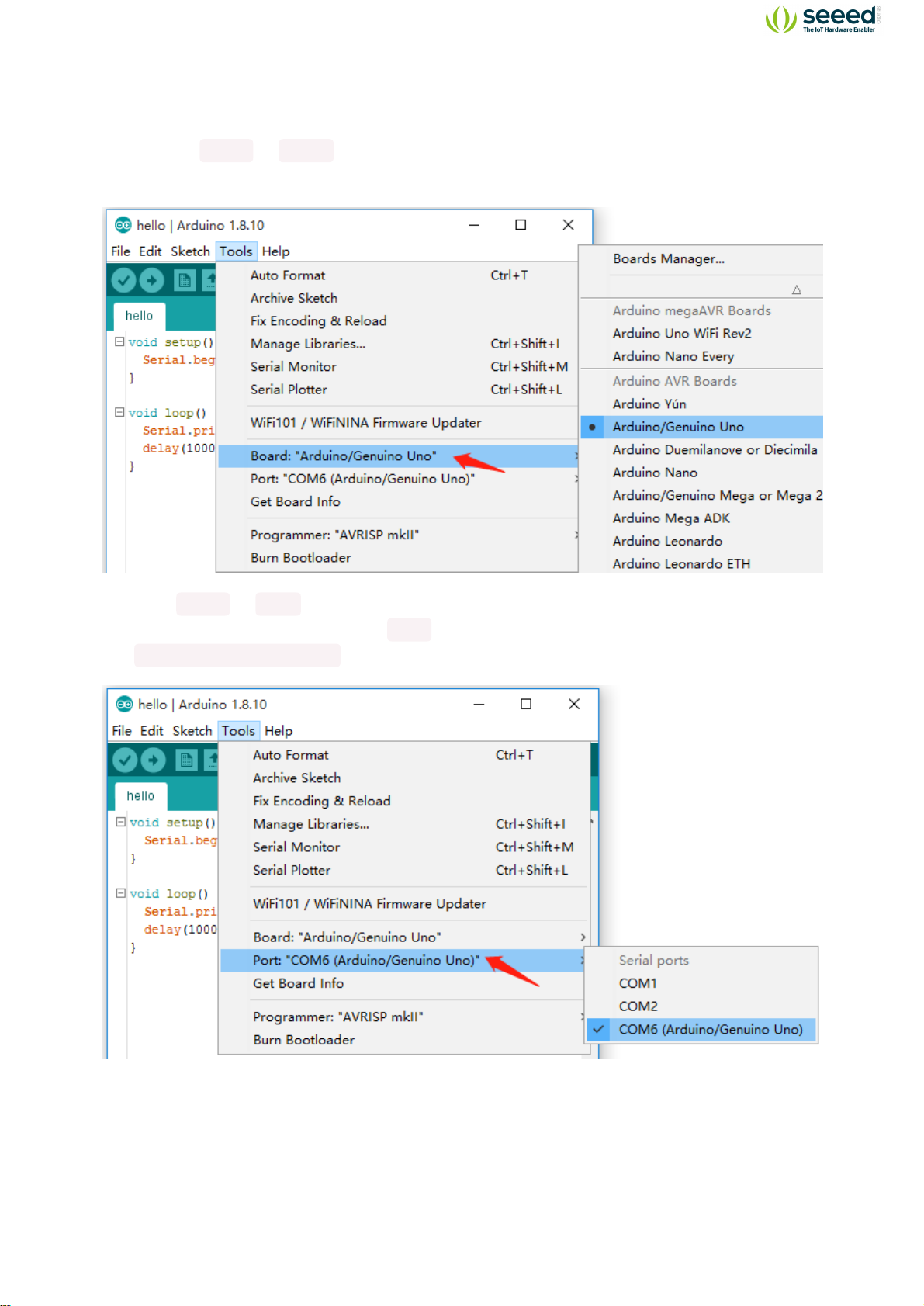
Grove Beginner Kit for Arduino is one of the best Arduino Beginner Kit for beginners. It includes
one Arduino compatible Board and 10 additional Arduino sensors and all in one-piece of PCB
design. All the modules have been connected to the Seeeduino through the PCB stamp
holes so no Grove cables are needed to connect. Of course, you can also take the modules
out and use Grove cables to connect the modules. You can build any Arduino project you like
with this Grove Beginner Kit For Arduino.
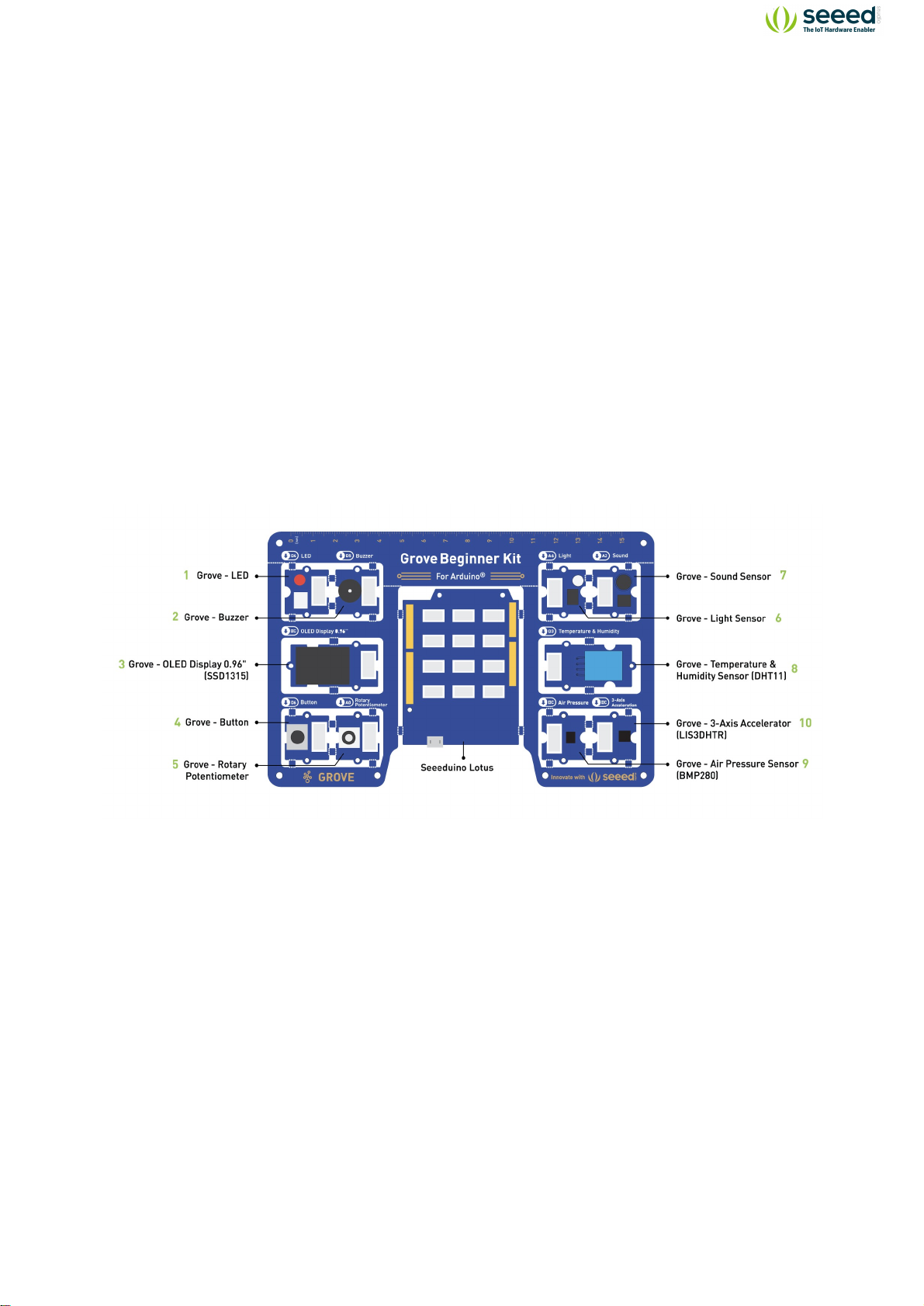
Hardware Overview
Note: Dimensions - 17.69 * 11.64 * 1.88cm
1. Grove - LED: Simple LED module
2. Grove - Buzzer: Piezo Buzzer
3. Grove - OLED Display 0.96”: 128×64 dot resolution High brightness,self-emission and high
contrast ratio Big screen on a compact design Low power consumption.
4. Grove - Button: Push button for human input interfaces
5. Grove - Rotary Potentiometer: Rotary knob for human input interfaces
6. Grove - Light: Detects surrounding light intensity
7. Grove - Sound: Detects surrounding sound intensity
8. Grove - Temperature & Humidity Sensor: Detects surrounding temperature and humidity
values
9. Grove - Air Pressure Sensor: Detects surrounding atmospheric pressure
10. Grove - 3-Axis Accelerator: Detects object acceleration
11. Seeeduino Lotus: Arduino Compatible Board with Grove Ports