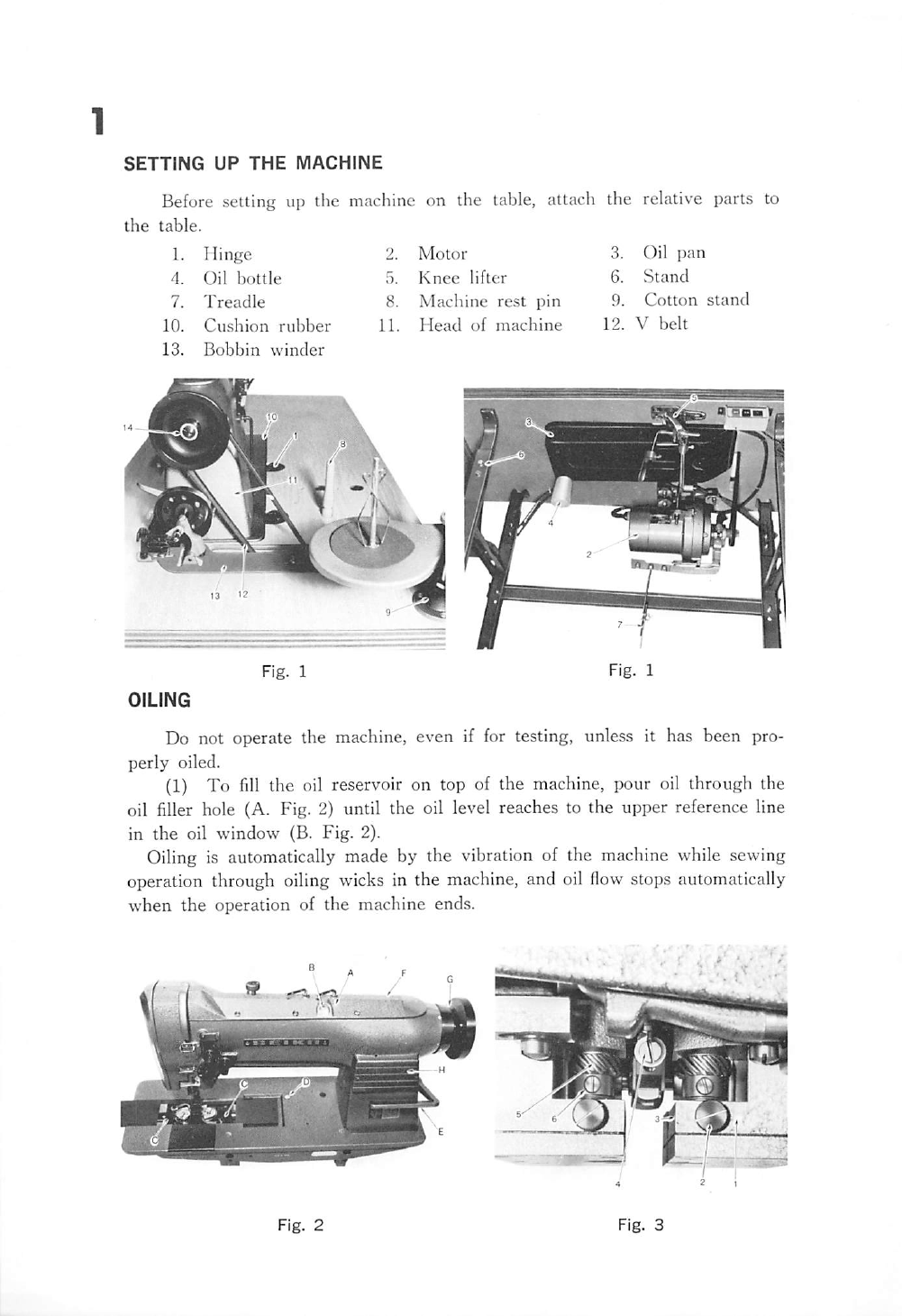
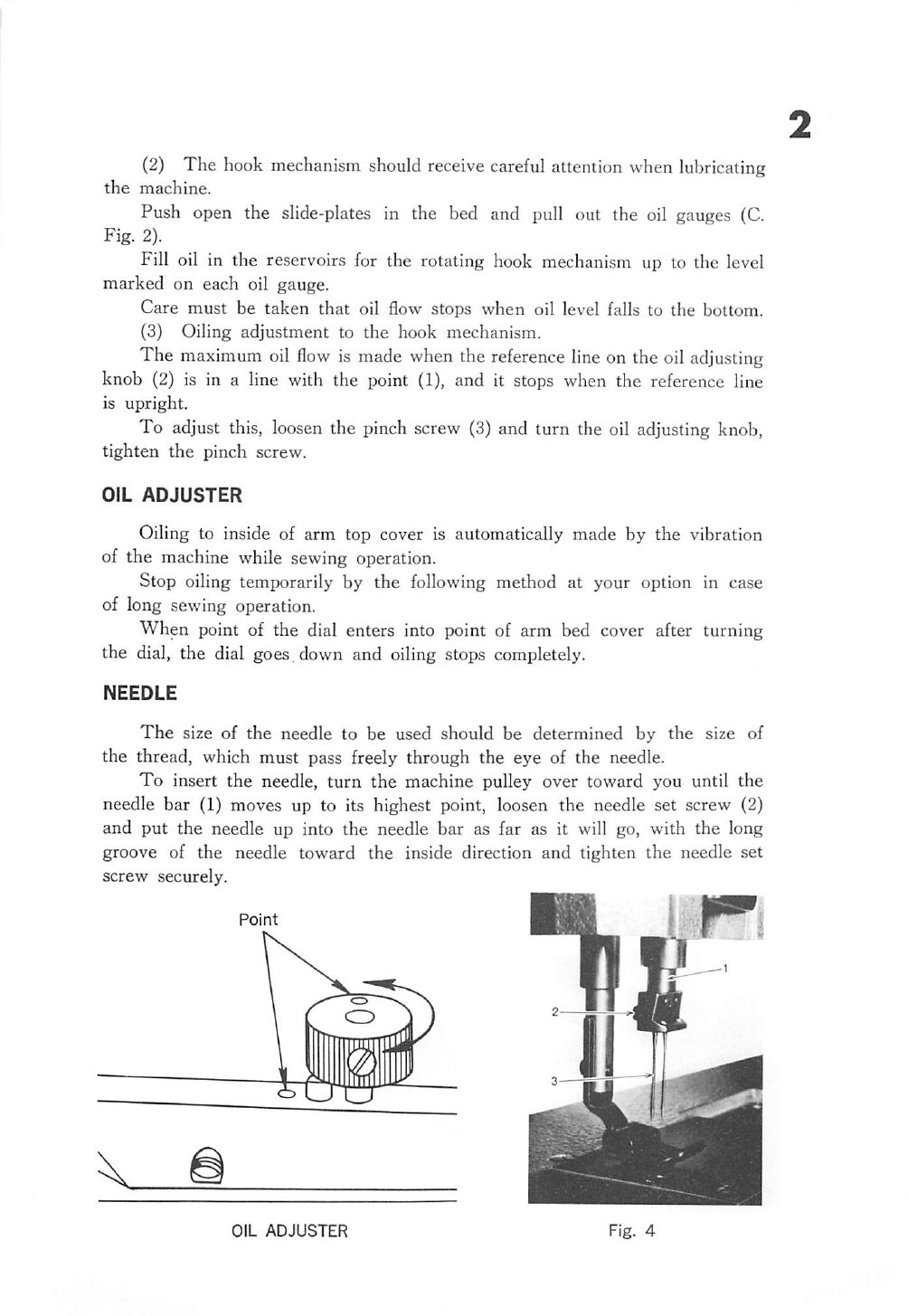
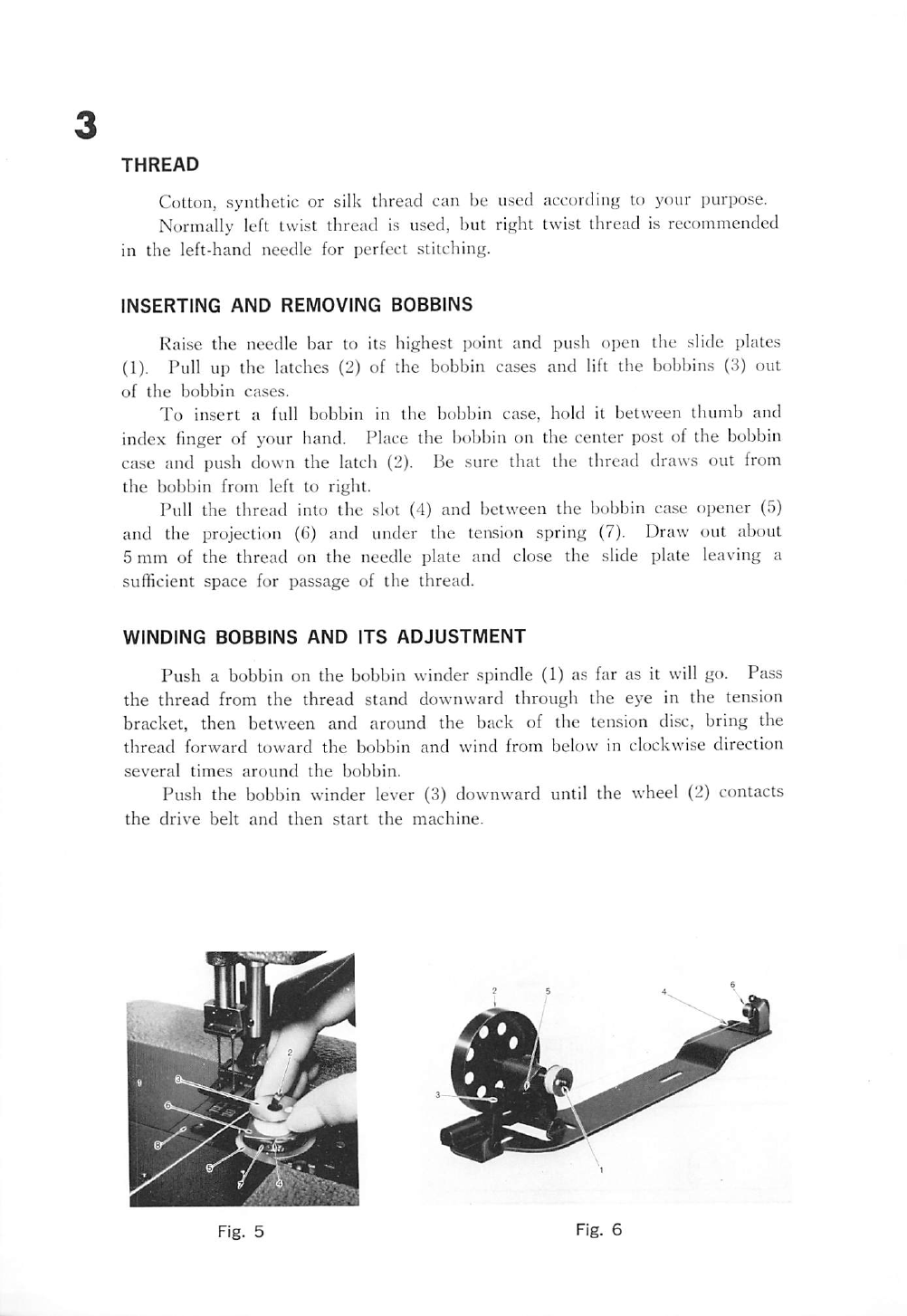
After
the
bobbin
is filled
with
thread,
release
will
cause
wheel
to
disengage
from the belt and winding will stop. Cut the thread and remove the bobbin
from
the
spindle.
Adjustment screw (5) can be turned in or out to increase or decrease the
amount
of
thread
wound
on
the
bobbin.
When fine thread is wound on bobbins, use light tension, it is regulated
by turning the knurled nut (6) on the tension bracket at the rear of the
bobbin
winder.
Bobbin can be wound while the machine is sewing.
If the thread does not wind evenly on the bobbin, loosen the screw (4)
in the tension bracket and move the bracket to right or left as may be
required, then tighten the screw.
THREADING
THE
MACHINE
Raise the needle bar to its highest point.
From the thread stand, lead the thread to the thread guide
(1),
(A) on
top of the
machine,
down
to the upper
guide
hole
of the thread
guide
(2),
(B)
from right to left. Pass the thread in weaving
fashion
through the other
two holes in (2), (B) and from right to left over and between the tension
discs (3), (C). Now pull the thread downward from right to left beneath
and around thread controller (4), (D), continue to pull the thread upward
through the fork in the thread controller and against the pressure of the
check spring (5), (E) and through the thread guide (6), (F) pull the thread
upward through the eye in the take-up lever (7), (G) down through the
thread guide (6), (F) again and then through the thread guide (8), (H) and
(9), (I) down through the hole (10), (J) in the needle holder and from inside
to outside through the eye (11), (K) of the needle.
?
28
ltj
Fig.
7
From the library of: Superior Sewing Machine & Supply LLC