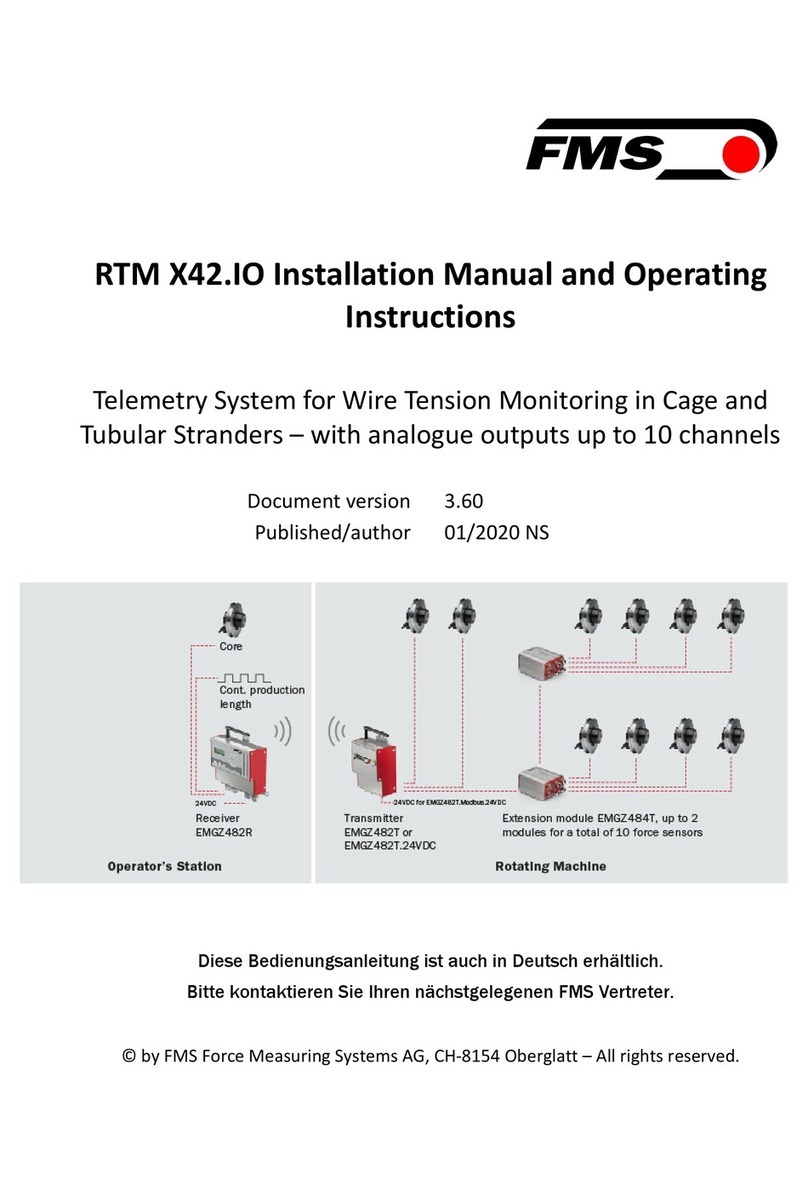
SEMIKRON SKiiP 3 User manual

Technical
Explanations
1 / 19
2017-08-30 –Rev02
© by SEMIKRON
This document is valid for the following part numbers:
- L5064101
- L5064102
- L5064103
with date code(JJWW) ≥1245.
Technical Explanation SKiiP®3 Parallel Board
Revision:
2
Issue Date:
30.08.17
Prepared by:
Schiller Anastasia
Approved by:
JL E-KAZ
SKiiP®3 Parallel Board
Please note:
Unless otherwise specified, all values in this technical explanation are typical values. Typical values are the average values
expected in large quantities and are provided for information purposes only. These values can and do vary in different applications.
All operating parameters should be validated by user’s technical experts for each application.
The document remains effective until replaced by subsequent revision of this document.

Technical Explanation
SKiiP®3 Parallel Board
© by SEMIKRON
2017-08-30 –Rev02
2 / 20
Table of content:
1Related documents .........................................................................................................................................3
2Application and handling instructions..............................................................................................................4
3General description .........................................................................................................................................5
3.1 Overview...................................................................................................................................................5
4Block diagram..................................................................................................................................................6
5Dimensions......................................................................................................................................................7
6Pin Description ................................................................................................................................................9
6.1 Pin assignment of Controller Connector X1 .............................................................................................9
6.2 Pin assignment of SKiiP®3 Connectors (X3, X4, X5, X6).........................................................................9
7Auxiliary Power Supply..................................................................................................................................10
8Digital Input/Output Signals...........................................................................................................................10
8.1 TOP/BOT switching signals....................................................................................................................10
8.2 ERROR OUT Signal...............................................................................................................................11
8.3 Temperature ERROR OUT Signal .........................................................................................................11
9Analogue Output Signals...............................................................................................................................11
9.1 Measurement of output current ..............................................................................................................12
9.2 Measurement of SKiiP®3 temperature or DC-link voltage......................................................................13
10 Error indication with LED...............................................................................................................................14
11 Interlock time.................................................................................................................................................14
12 Shielding Concept .........................................................................................................................................15
13 Short pulse suppression and pulse extension...............................................................................................16
14 Paralleling of SKiiP systems..........................................................................................................................16
15 Mounting of SKiiP®3 F-Option.......................................................................................................................16
16 Logistics.........................................................................................................................................................17
17 Provisions and handling after use.................................................................................................................18

Technical Explanation
SKiiP®3 Parallel Board
© by SEMIKRON
2017-08-30 –Rev02
3 / 20
1 Related documents
Data sheet Parallel board SKiiP®3
Technical Explanation SKiiP®3 Rev.2
Data sheet SKiiP®3
Technical Explanation F-Option Board SKiiP®3
Data sheet F-Option Board SKiiP®3

Technical Explanation
SKiiP®3 Parallel Board
© by SEMIKRON
2017-08-30 –Rev02
4 / 20
2 Application and handling instructions
Please provide static discharge protection during handling. As long as the board is not completely
assembled, the input terminals have to be short-circuited. Persons working with devices have to wear a
grounded bracelet. Any synthetic floor coverings must not be statically chargeable. Even during
transportation the input terminals have to be short-circuited using, for example, conductive rubber.
Worktables have to be grounded.
The inputs of the board are sensitive to over-voltage. Voltages higher than VS+0,3V or below -0,3V
may destroy these inputs. Therefore, control signal over-voltages exceeding the above values have to
be avoided.

Technical Explanation
SKiiP®3 Parallel Board
© by SEMIKRON
2017-08-30 –Rev02
5 / 20
3 General description
3.1 Overview
SKiiP®3 subsystems are connected in parallel to achieve higher output current. The SKiiP®3 Parallel board is
designed for connecting up to four SKiiP®3 subsystems to one controller. The example of SKiiP®3 Parallel
board application is shown in the Figure 1. The switching signals from controller are routed to all paralleled
devices. Analogue signal measurements and error siganls from the paralleled devices are converted and
transferred to the controller.
Figure 1: An example of SKiiP®3 Parallel board application
For an EMI-safe transmission of the switching- and error-signals, there is the possibility to mount an optional
fiber-adapter F-Option board SKiiP®3 on top of the SKiiP®3 Parallel board. No mechanical housing is required
since the board is directly mounted on a metal frame inside the cabinet.
All different SKiiP®3 Parallel board product variants are based on one common board-layout but do have
different number of connected SKiiP®3 subsystems:
Type 1: Board setup for paralleling of two SKiiP®3 GB systems 1200V/1700V with and without F-Option
(using connector X3/X4 & vertical connector X1)
Type 2: Board setup for paralleling of three SKiiP®3 GB. systems 1200V/1700V with and without F-
Option (using connector X3/X4/X5 & vertical connector X1)
Type 3: Board setup for paralleling of four SKiiP®3 GB systems 1200V/1700V with and without F-
Option (using connector X3/X4/X5/X6 & vertical connector X1)
The pollution degree class 2 and IP00 shall be considered for the SKiiP®3 Parallel board.

Technical Explanation
SKiiP®3 Parallel Board
© by SEMIKRON
2017-08-30 –Rev02
6 / 20
4 Block diagram
Figure 2: Block diagram of main functions of SKiiP®3 Parallel board
The main functions of the SKiiP®3 Parallel board are shown in the Figure 2. They are:
24V routing from supply connector X2 to all four SKiiP®3 DIN41651-connectors X3/X4/X5/X6
Generation of +15V for F-Option-Board. It will be supplied by the controller connector X1 (+15V)
Monitoring the +15V; -15V; in case of failure the ERROR signal will be activated.
Providing the maximum temperature value or maximum DC-link voltage of all connected SKiiP®3
subsystems (Analogue Out, Pin 12 / connector X1)
Providing the sum of currents of all connected SKiiP®3 subsystems (Analogue Out, Pin 14 / connector
X1)
Routing the TOP/BOT switching signals from the controller (Digital IO, Pin 4 and Pin 2 / connector X1)
to all four SKiiP®3 connectors X3/X4/X5/X6 (incl. Short-Pulse-Suppression, TOP/BOT-Interlock and
min. Pulse-Time)
Linking the error and temperature error signals from the connected SKiiP®3 subsystems to the
corresponding error signal (Digital IO, Pin 3 and Pin 5 / connector X1)
Providing grounding option via metal screws or over the supply connector X2 for the shield of all four
SKiiP®3 connectors X3/X4/X5/X6.

Technical Explanation
SKiiP®3 Parallel Board
© by SEMIKRON
2017-08-30 –Rev02
7 / 20
5 Dimensions
The mechanical dimensions for SKiiP®3 Parallel board without F-Option are shown in the Figure 3 and Figure
4. The optional connector X7 is schown on the both drawings.
Figure 3: Mechanical dimensions of SKiiP®3 Parallel board without F-Option (Top view)
Figure 4: Mechanical dimensions of SKiiP®3 Parallel board without F-Option (side view)
180
73
93
160
10
10
X6 X5
X4X3
X1
X2
X7
Diameter of all holes is 4.3 mm
2
3
1
optional
SKiiP3 Parallelboard
Dimension
Rev01
17.07.12 KornAn
29.5
29.5
29.5
29.5
29.5
27,3
SKiiP3 Parallelboard Height
Rev01
17.07.12
KornAn

Technical Explanation
SKiiP®3 Parallel Board
© by SEMIKRON
2017-08-30 –Rev02
8 / 20
The mechanical dimensions for SKiiP®3 Parallel board with F-Option (shown in the Figure 5) are the same as
without F-Option with exeption of height, which is given in the Figure 6. The optional connector X7 is schown on
the both drawings.
Figure 5: Mechanical dimensions for SKiiP®3 Parallel board with F-Option (Top view)
Figure 6: Mechanical dimensions for SKiiP®3 Parallel board with F-Option (Side view)
X3 X4
X6 X5
X1
X7
X2
2
3
1
F-Option
(optionally)
optional
L50312xx
Distance bolt min. 20mm
SKiiP3 Parallelboard
With F-Option
Rev01
17.07.12 KornAn
Please note: Diameter of all holes is 4.3 mm. The length of cable connection between SKiiP®3 Parallel
board and SKiiP®3 subsystems should not exceed 2m. Shielded cables should be used.

Technical Explanation
SKiiP®3 Parallel Board
© by SEMIKRON
2017-08-30 –Rev02
9 / 20
6 Pin Description
6.1 Pin assignment of Controller Connector X1
The Parallel board is equipped with a 14-pin DIN connector. Please refer to the Technical Explanation SKiiP®3
Rev.2 for more detailed information.
Figure 7: PCB Connector for the controller
Table 1: Controller connector X1 pin assignment
Pin
Signal name
Function
Specification
1
Shield
Shielding
For shielded cable
2
BOT IN
PWM signal input for low side IGBTs
Input
+15V/0V-Logic
10kΩimpedance
3
ERROR OUT
Common error status signal output
Open collector output
LOW = no error
Max. 30V/15mA
4
TOP IN
PWM signal input for high side IGBTs
Input
+15V/0V-Logic
10kΩimpedance
5
Temp. ERROR
OUT
Common over-temperature error signal
output
Open collector output
LOW = no error
Max. 30V/15mA
6
N. C.
Not used
7
N. C.
Not used
8
+15V
Supply voltage output for optional level
shifter or F-Option
+15V ±4%
Max. output current: 100mA
9
10
GND
Power supply ground
11
12
TEMP_ANA
Temperature measurement analogue
signal output (maximum SKiiP
temperature)
Output voltage range:
0…+10V
Max. output current: 5mA
13
GND_ANA
Ground for analogue signals
14
I_ANA
Current measurement analogue signal
output (sum of AC-currents)
Output voltage range:
-10V…+10V
Max. output current: 5mA
6.2 Pin assignment of SKiiP®3 Connectors (X3, X4, X5, X6).
Please refer to the Technical Explanation SKiiP®3 Rev.2 for pin assignment of the connectors X3, X4, X5, X6.

Technical Explanation
SKiiP®3 Parallel Board
© by SEMIKRON
2017-08-30 –Rev02
10 / 20
7 Auxiliary Power Supply
Connector X2 is used to supply the parallel board and the connected SKiiP subsystems.
Table 2 shows the 24V Power supply connector pin assignment.
Pin
Signal name
Function
Specification
1
Shield
Shielding
For shielded cable
2
GND
Ground
3
+24V
Supply voltage input for Parallel
board and SKiiP®3 “A” to “D”
See Table 3
Table 3 shows the required features of an appropriate power supply for a SKiiP®3 system.
Table 3: Requirements of the auxiliary power supply
Power supply
Supply voltage should be +24V (+/- 20%)
Maximum rise time of 24V
50ms
Rated current
1,5 times of the maximum driver input current
Minimum peak current of auxiliary supply
2 times of the maximum driver input current
(At least 8A for 4 connected SKiiP®3 subsystems)
For further information please refer to the Technical Explanation SKiiP®3, Rev.2.
8 Digital Input/Output Signals
8.1 TOP/BOT switching signals
The main purpose of SKiiP®3 Parallel board is the routing of the TOP/BOT switching signals from controller
connector X1 to all four SKiiP®3 connectors X3/X4/X5/X6. The routing includes the following tasks:
- Logic Level detection of TOP/BOT signals;
- Short pulse suppression and extension of TOP/BOT signals (See Chapter 13);
- Generation of Interlock time for all connected SKiiP®3 (See Chapter 11 for detailed information and
corresponding data sheet for tTD time value).
The characteristics of switching signal can be found in the Table 4.
Table 4: Digital signal characteristic TOP/BOT input
Signal name
TOP In
BOT In
input threshold voltage (High)
12,3V
input threshold voltage (Low)
4,6V
Table 2: 24V Power supply connector pin assignment
Please note: Use for 24V power supply wire size of 2.5 mm2to withstand max. nominal current of 8A.
The minimal possible supply voltage on SKiiP®3 Parallel board is therefore 19,2 V, which should be
measured at SKiiP®3 Parallel board input, not at controller output (voltage drop on connection cable).
Please note: Power supply cable should be twisted or screened to enhance the EMC robustness.

Technical Explanation
SKiiP®3 Parallel Board
© by SEMIKRON
2017-08-30 –Rev02
11 / 20
8.2 ERROR OUT Signal
The SKiiP®3 Parallel board combines all ERROR signals of the SKiiP®3 subsystems as well as the internal
±15V-Observer failure signal, to one unidirectional ERROR OUT signal and routes it to the customer’s
controller. This output is short-circuit proof.
The ERROR signal is active when one of the connected SKiiP systems is in ERROR mode or when the parallel
board is in error mode.
The characteristics of switching signal can be found in the Table 5.
Table 5: Digital signal characteristic ERROR and HALT input
Signal name
ERROR OUT
Description
SKiiP®3: Open collector output without internal pull
up resistor. No capacitor to GND
8.3 Temperature ERROR OUT Signal
The SKiiP®3 Parallel board combines all Temperature ERROR signals of the SKiiP®3 to one unidirectional
Temperature ERROR OUT signal and routes it to the customer’s controller. This output is short-circuit proof.
Temperature ERROR is active, when one of the connected SKiiP subsystems is in Temperature ERROR
mode.
9 Analogue Output Signals
On the user controller board a differential amplifier should be used which is connected to the analogue output
and the corresponding ground signals (TEMP_ANA, I_ANA, GND_ANA). This ensures accurate measurement
of the analogue signals because there is no voltage drop on the analogue ground wires due to the high input
impedance of the differential amplifier. Please refer to the Technical Explanation SKiiP®3, Rev.2 for further
information and for recommended electrical circuit.
The analogue signal ground line is not used for supply currents when a differential amplifier is used on the
controller side.

Technical Explanation
SKiiP®3 Parallel Board
© by SEMIKRON
2017-08-30 –Rev02
12 / 20
9.1 Measurement of output current
The SKiiP®3 Parallel board sums all the output current values from the connected SKiiP®3 subsystems. The
value of sum current must be divided by the number of connected SKiiP®3 subsystems to get the current value
per SKiiP®3 (See Figure 8). Please see the data sheet SKiiP®3, page 2 for the ITRIPSC value for corresponding
SKiiP®3 subsystem.
Figure 8: Measurement of AC-output current by SKiiP®3 Parallel board
I ana out
[V] 10V
-10V
2*ITRIPSC
Controller
SKiiP®3
‚A‘
SKiiP®3
‚C‘
Iout
Iout
[A]
I ana
out [V]
I ana out
[V]
2 SKiiP®3 Sum Current
3 SKiiP®3 Sum Current
4SKiiP®3 Sum Current
± ΔIout SKiiP®3
Parallel board 4-
fold as example
3*ITRIPSC 4*ITRIPSC
- 2*ITRIPSC
- 3*ITRIPSC
- 4*ITRIPSC
SKiiP®3
‚B‘
SKiiP®3
‚D‘
The measured current is normalized to a corresponding voltage at the DIN41651 connector of the parallel
board. (See Table 6). The values given in the Table 6 are related only to the SKiiP®3 Parallel board. For
SKiiP®3 current measurement parameters please refer to the SKiiP®3 Technical Explanation Rev.2 Chapter
“AC-Current sensor”.
Table 6: Signal characteristics of current measurement
Signal Charakteristics
Value
Output signal
I_ANA / GND_ANA at connector X1
Max. output current II-out
5mA
Output voltage range VI-Out
-10V to +10V (normalized, independent from number of
SKiiP3 subsystems)
Amplification ratio
Type 1: 0,5 signal ratio connected SKiiP®3 (A/V) * 2
Type 2: 0,33 signal ratio connected SKiiP®3 (A/V) * 3
Type 3: 0,25 signal ratio connected SKiiP®3 (A/V) * 4
Accuracy of analogue signal
±1%1)
Small signal bandwidth
50kHz
1) Considering the aging drift of precision input resistors the accuracy can maximal increase to ± 1.8% for “Sum
of current” over full temperature range.

Technical Explanation
SKiiP®3 Parallel Board
© by SEMIKRON
2017-08-30 –Rev02
13 / 20
9.2 Measurement of SKiiP®3 temperature or DC-link voltage
SKiiP®3 is either configurated for DC-link voltage measurement (U-option) or for temperature measurement.
The corresponding analogue signal from connected SKiiP®3 subsystem is handled to the SKiiP®3 Parallel
board. The parallel board compares the values measured by each SKiiP®3 subsystem and provides the
maximal value to the controller. The analogue signal is available on the DIN connector Pin 12 with the
characteristic given in the Table 7. For futher information please refer to the Technical explanation SKiiP®3.
Table 7: Signal characteristics of current measurement
Parameters UTEMP
Specification @ -40°C <= Ta<= 85°C
Output signal
TEMP_ANA / GND_ANA or UDC_ANA / GND_ANA
Max. output current IT-out
5mA
Output voltage range VT-Out
0V to 10V
Analogue temperature signal TEMP_ANA @
115°C (typ)
Alternatively analogue DC-link volatge signal.
Specification see SKiiP®3 data
sheet/TESKiiP®3.
10V
Analogue temperature signal TEMP_ANA @
30°C
Alternatively analogue DC-link volatge signal.
@ VDC=0V.
1V
0V
Amplification ratio
1 (signal ratio identical to the connected SKiiP®3)
Signal bandwidth (-3dB)
(Input to Output)
Max. 50 Hz
Signal accuracy (Input to Output; over full temp.
range)
± 1%2)
2) Considering the aging drift of precision input resistors the accuracy can maximal increase to ± 1.6% for
temperature signal over full temperature range.

Technical Explanation
SKiiP®3 Parallel Board
© by SEMIKRON
2017-08-30 –Rev02
14 / 20
10 Error indication with LED
Two LED are placed on the Parallel board for error indication. The location of the LEDs is shown in the Figure 9
Figure 9: LED position on the SKiiP3 Parallel board
The description of the error indication is done in the Table 8.
Table 8: LED states and meanings
Operating mode
LED lights
V901
V902
IDLE (no clocking, no error)
grün
grün
By clocking and no error
grün
orange
By clocking and Error
rot
orange
No clocking and Error
rot
grün
11 Interlock time
Generation of dominant Interlock time for all connected SKiiP®3 (See data sheet Parallel board SKiiP®3). Thus
the internal Interlock time (tTD=3 µs) of SKiiP®3 subsystems is not valid anymore. The SKiiP®3 Parallel Board
sets the dominant interlock time tTD=4µs for all SKiiP®3 subsystems.
Please note: Only above listed states are possible in regular operation mode. If some other state is
present, there is no supply voltage for the board or the LED/LEDs are out of functioning.

Technical Explanation
SKiiP®3 Parallel Board
© by SEMIKRON
2017-08-30 –Rev02
15 / 20
12 Shielding Concept
Figure 10: Shielding concept of the SKiiP®3 Parallel board
X3 X4
X6 X5
X1
Controller
X7
Optional
analog signals
& shield
Power
Supply 24V
X2
2
3
1
SKiiP®3 ‚A‘
SKiiP®3 ‚D‘
SKiiP®3 ‚B‘
SKiiP®3 ‚C‘
Option 2:
Direct Chassis
Connection with
Screws (4x)
Option 1:
Chassis Connection
through Cable
Shield Plane
(Bottom
Layer)
Power-GND Plane
(2nd Layer)
The shield from all DIN41651 connectors (X1/X3/X4/X5/X6/X7) and the power connector (X2) is centrally
merged with the shield plane within the board.
The shield plane is directly connected with the power ground plane by vias. These vias are placed alongside
each egde of the PCB.
It is recommended for good EMC robustness to connect the shield plane respectively the Power-GND to
chasses. That can be done on the parallel board or on controller. If grounding is done on both sides controller
and on parallel board then the impedance between the both grounding points has to be low to prevent
interferences.
Grounding should be done with a HF-compliant connection. There are two ways to connect the shield layer to
the Chassis/PE:
Chassis-shield connection Option 1: Attaching a cable or earth strap to the rear panel metal frame and
connecting it at the other end to pin 1 of connector X2. This option
should be considered if the board is not attached to the rear panel
metal frame with screws.
Chassis-shield connection Option 2: Connecting the SKiiP®3 parallel board to the rear panel metal frame
with 4 metal screws. Electrical connection is done through metal
screws. This is the prefered option for good ground connection.
Please note: The shield connection should be performed with metal screws with head diameter less
than 8 mm.

Technical Explanation
SKiiP®3 Parallel Board
© by SEMIKRON
2017-08-30 –Rev02
16 / 20
13 Short pulse suppression and pulse extension
The short pulse suppression time is defined as tSIS in the SKiiP®3 Parallel board data sheet. The function
suppresses short turn-on and off-pulses at the pins TOP IN and BOT IN of the DIN connector of connected
SKiiP®3 subsystems. Thus it adds to every commutation ~ 625ns delay time.
In this way the IGBTs are protected against spurious noise which can occur due to bursts on the signal lines.
Pulses shorter than tSIS are suppressed. If the pulse is longer than tsis=625ns but shorter than 1µs, it will be
automatically extended to 1µsby the Parallel board. Otherwise it is possible, that the rest of pulse after short
pulse suppression of Parallel board will be faulty determined by the SKiiP®3 as spurious noise and will be
suppressed. The short pulse suppression and extension are shown in the Figure 11.
Figure 11: Short pulse suppression and extension
14 Paralleling of SKiiP systems
Please refer to SKiiP®3 Technical Explanation Rev.2 Chapter “Paralleling of SKiiP”for further information.
15 Mounting of SKiiP®3 F-Option
For mounting of SKiiP®3 F-Option the following components could be used:
Plastic standoff adapters: round, length 20 mm, screw thread M4, material Polyamid 6,6, diamether 8 mm
(for example: 05.44.320)
Plastic round head screw: M 4 x 8, DIN 85/ISO 1580, PA 6.6, trench (for example: 01.45.436)
Plastic screw nut: M4 metric (Example: 02.05.049)
As long as a SKiiP®3 F-Option is mounted on a SKiiP®3 Parallel board, it will be supplied by the internal 15V
supply voltage from the connector X1.
Table 9: Digital signal characteristic of +15V separate supply
Parameters +15V Separate Supply
Specification @ -40°C <= Ta<= 85°C
Ouput signal
+15VDC OUT at connector X1
Circuit supply voltage
VS(+15V ±4% / max. 50mA)

Technical Explanation
SKiiP®3 Parallel Board
© by SEMIKRON
2017-08-30 –Rev02
17 / 20
16 Logistics
Figure 12: Part Marking Information

Technical Explanation
SKiiP®3 Parallel Board
© by SEMIKRON
2017-08-30 –Rev02
18 / 20
17 Provisions and handling after use
Components which are obsolete or defective must be disposed according to local regulations

Technical Explanation
SKiiP®3 Parallel Board
© by SEMIKRON
2017-08-30 –Rev02
19 / 20
List of figures:
Figure 1: An example of SKiiP®3 Parallel board application ..................................................................................5
Figure 2: Block diagram of main functions of SKiiP®3 Parallel board ....................................................................6
Figure 3: Mechanical dimensions of SKiiP®3 Parallel board without F-Option (Top view)....................................7
Figure 4: Mechanical dimensions of SKiiP®3 Parallel board without F-Option (side view) ....................................7
Figure 5: Mechanical dimensions for SKiiP®3 Parallel board with F-Option (Top view) ........................................8
Figure 6: Mechanical dimensions for SKiiP®3 Parallel board with F-Option (Side view) .......................................8
Figure 7: PCB Connector for the controller ............................................................................................................9
Figure 8: Measurement of AC-output current by SKiiP®3 Parallel board............................................................ 12
Figure 9: LED position on the SKiiP3 Parallel board........................................................................................... 14
Figure 10: Shielding concept of the SKiiP®3 Parallel board................................................................................ 15
Figure 11: Short pulse suppression and extension ............................................................................................. 16
Figure 12: Part Marking Information.................................................................................................................... 17
List of tables:
Table 1: Controller connector X1 pin assignment ..................................................................................................9
Table 2: 24V Power supply connector pin assignment ....................................................................................... 10
Table 3: Requirements of the auxiliary power supply.......................................................................................... 10
Table 4: Digital signal characteristic TOP/BOT input .......................................................................................... 10
Table 5: Digital signal characteristic ERROR and HALT input........................................................................... 11
Table 6: Signal characteristics of current measurement..................................................................................... 12
Table 7: Signal characteristics of current measurement..................................................................................... 13
Table 8: LED states and meanings ..................................................................................................................... 14
Table 9: Digital signal characteristic of +15V separate supply............................................................................ 16
Symbols and Terms
A detailled explanation of the terms and symbols can be found in the "Application Manual Power
Semiconductors" [2]
References
[1] www.SEMIKRON.com
[2] A. Wintrich, U. Nicolai, W. Tursky, T. Reimann, “Application Manual Power Semiconductors”,
ISLE Verlag 2011, ISBN 978-3-938843-666
HISTORY
SEMIKRON reserves the right to make changes without further notice herein

Technical Explanation
SKiiP®3 Parallel Board
© by SEMIKRON
2017-08-30 –Rev02
20 / 20
DISCLAIMER
SEMIKRON reserves the right to make changes without further notice herein to improve reliability, function or
design. Information furnished in this document is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
representation or warranty is given and no liability is assumed with respect to the accuracy or use of such
information, including without limitation, warranties of non-infringement of intellectual property rights of any third
party. SEMIKRON does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit
described herein. Furthermore, this technical information may not be considered as an assurance of
component characteristics. No warranty or guarantee expressed or implied is made regarding delivery,
performance or suitability. This document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied and may
be superseded by updates without further notice.
SEMIKRON products are not authorized for use in life support appliances and systems without the express
written approval by SEMIKRON.
SEMIKRON INTERNATIONAL GmbH
P.O. Box 820251 • 90253 Nuremberg • Germany
Tel: +49 911-65 59-234 • Fax: +49 911-65 59-262
sales.skd@semikron.com • www.semikron.com
This manual suits for next models
3
Table of contents
Popular Control System manuals by other brands
Aqua Control
Aqua Control SL3 Deluxe Wi-Fi manual

sky vision
sky vision Linx 300 Preinstallation manual

Contro l4
Contro l4 Rroom-based control system user guide

Firestone
Firestone 2554 installation instructions

Gema
Gema OptiFlex A1 Operating instructions and spare parts list

Crestron Electronics
Crestron Electronics 4 Series product manual