Sensata MAGNUM ENERGY MM Series User manual

© 2016 Sensata Technologies i
Thank you from all of us at Sensata Technologies for purchasing this MM
Series inverter. The MM Series is a product under the Magnum Energy brand
from Sensata. We understand there are many purchasing options in the
marketplace, and are pleased that you have decided on a Magnum product.
This product was proudly assembled and tested in the United States.
We are committed to providing quality products and services. We hope your
experience with us is pleasant and professional.
Disclaimer of Liability
The use of this manual and the conditions or methods of installation, operation,
use, and maintenance of the MM inverter are beyond the control of Sensata
Technologies. Therefore, this company does not assume responsibility and
expressly disclaims liability for loss, damage, or expense whether direct,
indirect, consequential or incidental that may arise out of or be in any way
connected with such installation, operation, use, or maintenance.
Due to continuous improvements and product updates, the images shown in
this manual may not exactly match the unit purchased.
Restrictions on Use
The MM Series inverter may only be used in life support devices and systems
with the express written approval of Sensata Technologies. Failure of this
inverter can reasonably be expected to cause failure of that life support device
or system, or to affect the safety or effectiveness of that device or system.
If the MM Series inverter fails, it is reasonable to assume the health of the
user or other persons may be endangered.
Copyright Notice
Copyright 2016 by Sensata Technologies. All rights reserved. Permission to
copy, distribute, and/or modify this document is prohibited without written
permission from Sensata.
Document Information
Description – MM Series Owner’s Manual
Part Number and Revision – 64-0008 Rev C
Date Published – April 2016
This entire manual is available for download—with many of the diagrams
available in color—under the Library menu on our website.
Record the unit’s model and serial number in case you need to provide
this information in the future.
Model: Serial Number:
MM612 L1
MM1212/MM1212-G M1

© 2016 Sensata Technologies
ii
IMPORTANT PRODUCT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
This manual contains important safety instructions that must be followed
during the installation and operation of this product. Read all instructions
and safety information in this manual before installing or using this product.
• All electrical work must be performed in accordance with local, state,
and federal electrical codes.
• This product is designed for indoor/compartment installation. It must not
be exposed to rain, snow, moisture, or liquids of any type.
• Use insulated tools to reduce the chance of electrical shock or accidental
short circuits.
•Remove all jewelry such as rings, watches, bracelets, etc., when installing
or performing maintenance on the inverter.
• Always disconnect the batteries or energy source prior to installing or
performing maintenance on the inverter. Live power may be present at
more than one point since an inverter utilizes both batteries and AC.
Turning off the inverter may not reduce this risk. As long as AC power
is connected, it will pass through the inverter regardless of the ON/OFF
power switch setting.
•Always verify proper wiring prior to starting the inverter.
•Do not operate the inverter if it has been damaged.
• Do not dismantle the inverter; there are no user-serviceable parts
contained in this product. Attempting to service the unit yourself could
cause electrical shock. Internal capacitors remain charged after all power
is disconnected.
• No AC or DC disconnects are provided as an integral part of this inverter.
Both AC and DC disconnects must be provided as part of the system
installation.
•No overcurrent protection for the battery supply is provided as an integral
part of this inverter. Overcurrent protection of the battery cables must
be provided as part of the system installation.
• No overcurrent protection for the AC output wiring is provided as an
integral part of this inverter. Overcurrent protection of the AC output
wiring must be provided as part of the system installation.
Conventions Used in this Manual
Safety Symbols
To reduce the risk of electrical shock, fire, or other safety hazard, the following
safety symbols have been placed throughout this manual to indicate dangerous
and important safety instructions.
WARNING: This symbol indicates that failure to take a specified
action could result in physical harm to the user.
CAUTION: This symbol indicates that failure to take a specified
action could result in damage to the equipment.
Info: This symbol indicates information that emphasizes or
supplements important points of the main text.

© 2016 Sensata Technologies iii
IMPORTANT BATTERY SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
• Wear eye protection such as safety glasses when working with batteries.
• Remove all jewelry such as rings, watches, bracelets, etc., when installing
or performing maintenance on the inverter.
• Never work alone. Always have someone near you when working around
batteries.
•Use proper lifting techniques when working with batteries.
• Never use old or untested batteries. Check each battery’s label for age,
type, and date code to ensure all batteries are identical.
•Batteries are sensitive to changes in temperature. Always install batteries
in a stable environment.
• Install batteries in a well ventilated area. Batteries can produce explosive
gasses. For compartment or enclosure installations, always vent batteries
to the outside.
•Provide at least one inch of air space between batteries to provide
optimum cooling.
•Never smoke when in the vicinity of batteries.
• To prevent a spark at the battery and reduce the chance of explosion,
always connect the cables to the batteries first. Then connect the cables
to the inverter.
•Use insulated tools at all times.
• Always verify proper polarity and voltage before connecting the batteries
to the inverter.
•To reduce the chance of fire or explosion, do not short-circuit the batteries.
• In the event of accidental exposure to battery acid, wash thoroughly
with soap and water. In the event of exposure to the eyes, flood them
for at least 15 minutes with running water and seek immediate medical
attention.
•Recycle old batteries.
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS

© 2016 Sensata Technologies
iv
Table of Contents
1.0 Introduction............................................................................. 1
1.1 MM Series Models.................................................................. 1
1.2 How an Inverter/Charger Works .............................................. 1
1.3 What Appliances run from a Modified Sine Inverter .................... 2
1.4 Appliances and Run Time ....................................................... 2
1.5 Standard Features and Benefits............................................... 2
1.6 Battery Temperature Sensor (MM1212 & MM1212-G) ................. 4
2.0 Installation .............................................................................. 5
2.1 Pre-Installation ..................................................................... 5
2.1.1 Unpacking and Inspection....................................................... 5
2.2 Locating and Mounting the Inverter ......................................... 5
2.3 Wiring Guidelines ................................................................ 10
2.4 DC Wiring .......................................................................... 10
2.4.1 DC Wire Sizing and Overcurrent Protection.............................. 10
2.4.2 DC Grounding ..................................................................... 12
2.4.3 DC Cable Connections .......................................................... 12
2.5 Battery Bank Wiring ............................................................ 13
2.5.1 Inverter to Battery Bank Wiring............................................. 14
2.6 AC Wiring (MM612 & MM1212 models)................................... 15
2.6.1 Neutral to Safety Ground Bonding.......................................... 15
2.6.2 AC Wiring Connections ......................................................... 15
2.6.3 AC Wire Size and Overcurrent Protection ................................ 16
2.6.4 AC Input Wiring .................................................................. 17
2.6.5 AC Output Wiring ................................................................ 17
2.6.6 Ground-Fault Circuit Interruption (GFCI) Breakers.................... 18
2.6.7 Inverter Warning Label......................................................... 18
2.7 Functional Test.................................................................... 19
3.0 Operation............................................................................... 20
3.1 Operating Modes ................................................................. 20
3.1.1 Invert Mode ........................................................................ 20
3.1.2 Standby Mode (MM1212/MM1212-G models)........................... 20
3.2 Battery Temperature Sensor Operation................................... 23
3.3 Protection Circuitry Operation ............................................... 23
3.4 Inverter Startup.................................................................. 25
3.5 Factory Default Settings....................................................... 26
4.0 Troubleshooting..................................................................... 27
5.0 Specifications......................................................................... 28
Appendix A – Remotes and Optional Equipment........................... 29
A-1 Remote Controls ................................................................. 29
A-2 Optional Equipment and Accessories ...................................... 29
Appendix B – Battery Information................................................ 30
B-1 Battery Bank Sizing ............................................................. 30
B-2 Battery Types ..................................................................... 30
B-3 Battery Configuration........................................................... 30

© 2016 Sensata Technologies v
List of Figures
Figure 1-1, MM Series Inverters........................................................... 1
Figure 1-2, Top Side Features.............................................................. 3
Figure 1-3, Front and Back Side Features.............................................. 4
Figure 1-4, Left Side Features ............................................................. 4
Figure 1-5, Battery Temperature Sensor ............................................... 4
Figure 2-1, Approved Mounting Orientations.......................................... 7
Figure 2-2, MM Series Inverter Dimensions ........................................... 7
Figure 2-3, Basic Installation Diagram (MM612/MM1212)........................ 8
Figure 2-4, Basic Installation Diagram (MM1212-G)................................ 9
Figure 2-5, DC Cable to Battery Terminals........................................... 12
Figure 2-6, DC Cable to Inverter’s DC Terminals .................................. 13
Figure 2-7, AC Wiring Connections (MM612/MM1212 only) .................... 17
Figure 2-8, Warning Label................................................................. 18
Figure 3-1, Automatic 4-Stage Charging Graph.................................... 21
Figure 3-2, BTS Temperature to Charge Voltage Change ....................... 23
Figure B-1, Series Battery Wiring....................................................... 30
Figure B-2, Parallel Battery Wiring ..................................................... 31
Figure B-3, Series-Parallel Battery Wiring............................................ 31
Figure C-1, Performing an Inverter Reset ............................................ 33
List of Tables
Table 1, Recommended DC Wire/Overcurrent Device ............................ 11
Table 2, Wire Color to AC Wire Connection .......................................... 15
Table 3, Minimum Wire Size to Circuit-breaker Size .............................. 16
Table 4, Inverter Battery Turn On/Off Levels........................................ 24
Table 5, Inverter Default Settings ...................................................... 26
Table 6, Troubleshooting Guide .......................................................... 27
Table 7, MM Series Specifications....................................................... 28
Table of Contents (Cont.)
Appendix C – Preventive Maintenance.......................................... 32
C-1 Recommended Inverter and Battery Care ............................... 32
C-2 RV/Marine Off-Season Storage.............................................. 32
C-3 Resetting the Inverter.......................................................... 32
C-3.1 Performing an Inverter Reset (i.e., soft reset).......................... 32
C-3.2 Performing a Power Reset (i.e., hard reset) ............................. 33
Appendix D – Warranty/Service Information ............................... 34
D-1 Warranty Information .......................................................... 34
D-2 How to Receive Repair Service .............................................. 35

© 2016 Sensata Technologies
1
Introduction
1.0 Introduction
Congratulations on your purchase of an MM Series inverter from Sensata
Technologies. This product is designed to be powerful, yet simple to use, and
engineered to provide you with years of trouble-free use.
Please read this chapter to familiarize yourself with the features and benefits
of your particular MM Series model.
Figure 1-1, MM Series Inverters
1.1 MM Series Models
MM612 – a 600-watt inverter with 7-amp AC transfer relay. The AC input and
output are provided with pigtail wires to allow hardwiring to an AC distribution
panel. Features neutral-to-ground switching for mobile applications.
MM1212 – a 1200-watt inverter/charger with 12-amp AC transfer relay and
70-amp, 4-stage PFC charger. The AC input and output are provided with pigtail
wires to allow hardwiring to a main AC distribution panel and an inverter sub-
panel. Features neutral-to-ground switching for mobile applications. Includes
a 15’ battery temperature sensor.
MM1212-G – a 1200-watt inverter/charger with 12-amp AC transfer relay
and 70-amp, 4-stage PFC charger. AC input is provided by a standard 3 ft.
plug-in power cord, and the AC output is provided by a standard GFCI two-
plug outlet. Features neutral-to-ground switching for mobile applications.
Includes a 15’ battery temperature sensor.
1.2 How an Inverter/Charger Works
An inverter takes direct current (DC) from your batteries and turns it into
alternating current (AC), like you use at home. With MM Series models that
have the battery charger feature, it also takes alternating current (when
connected to a generator or to shorepower) and transforms it into direct
current to recharge your batteries.
There are three modes of operation associated with this inverter:
Inverter Mode: DC from the batteries is transformed into AC for powering
your boat or RV accessories.
Standby Mode (MM1212/MM1212-G models): The unit operates as a battery
charger to convert incoming AC power into DC power to recharge the batteries
while continuing to pass the incoming AC power directly to the inverter’s
output—to power any AC loads.
MM612/MM1212 MM1212-G

© 2016 Sensata Technologies 2
1.3 What Appliances run from a Modified Sine Inverter
Today’s inverters come in two basic output waveforms: modified sine (which
is actually a modified square wave) and pure sine wave. Modified sine wave
inverters approximate a pure sine waveform.
The output of a modified sine wave inverter will run most electronic and
household items—including but not limited to TV, VCR, satellite dish receiver,
computers, and printers. Some devices such as rechargeable power supplies
for phones, drills, and other like devices may not run or be damaged by
modified sine wave inverters.
1.4 Appliances and Run Time
The MM Series inverter can power a wide range of household appliances
including small motors, clocks, and other electrical devices. As with any
appliance using batteries for power, there is a certain length of time that it
can run—this is called “run time”. Actual run time depends on several variables
including the size and the type of appliance, the type of batteries installed in
your application, as well as the battery’s capacity and age. Other factors such
as the battery’s state of charge and temperature can also affect the length
of time your appliances can run.
Depending on your inverter capacity, larger electrical appliances such as coffee
pots and hair dryers can be used for short durations. However, loads that are
used for longer periods such as stoves or water heaters can quickly drain your
batteries and are not recommended for inverter applications. All electrical
appliances are rated by the amount of power they consume. The rating is
printed on the product’s nameplate label, usually located on its chassis near
the AC power cord. Even though it is difficult to calculate exactly how long
an inverter will run a particular appliance, the best advice is trial and error.
Your MM Series inverter has a built-in safeguard that automatically protects
your batteries from being over-discharged.
1.5 Standard Features and Benefits
The MM Series inverter converts 12 volts direct current (VDC) power from
your battery to 120 volts alternating current (VAC) power. On models with the
multi-stage battery charger feature, the incoming AC power is optimized using
Power Factor Correction (PFC) technology to keep the inverter’s battery bank
fully charged. This inverter’s die-cast aluminum baseplate ensures maximum
durability and a cooler, more efficient operation. The inverter is equipped with
the following features:
•600 or 1200 watts continuous (depending on model) at 25°C (77°F)
•Numerous protection features to ensure safe operation
• AC transfer switch circuitry; allowing incoming AC power to continue to
pass through to power loads even if the inverter is off
• Dead battery charging (MM1212 & MM1212-G models) for batteries that
are extremely low
•Automatic 4-stage battery charger with power factor correction and
temperature compensation—for optimum battery charging (models with
battery charger and using the Battery Temperature Sensor)
• True RMS output voltage regulation to ensure the inverter will deliver
the correct amount of power—within the DC input voltage range and the
continuous output power level
• Quick connection accessory and remote ports—easily accepts several
optional remote controls and the Battery Temperature Sensor
Introduction

© 2016 Sensata Technologies
3
6
7b
12
3
4
5
8
7a
= MM1212-G only
Figure 1-2, Top Side Features
Introduction
1. Inverter Status Indicator – this green light emitting diode (LED)
illuminates to provide information on the inverter’s operation.
2. Power
ON/OFF Switch –momentary pushbutton switch that turns the
inverter on or off.
3. Negative DC Terminal (black) – the inverter’s connection to the
negative terminal on the 12 VDC battery bank.
4. Positive DC Terminal (red) – the inverter’s connection to the positive
terminal on the 12 VDC battery bank.
5. Output Circuit Breaker (AC Out) –this circuit breaker provides another
layer of overload protection. This is not a branch circuit-rated breaker
.
Separate AC output breakers are required on the output.
6. Input Circuit Breaker (AC In) – this circuit breaker protects the unit’s
internal wiring and pass-thru relay.
7. a) AC Wiring Compartment – provides access for all AC input and output
hardwiring connections on the inverter (MM612 & MM1212 models only).
b) GFCI Outlet – a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) outlet with
test and reset capability (MM1212-G model only).
8. Mounting Flanges (x4) – used to secure the inverter to a shelf/wall.
9. Warning and Information Label –provides pertinent information for
safely using the inverter.
10. REMOTE Port Connection –a RJ11 connector that allows an optional
remote control to be connected.
11. ACCESSORY Port Connection – a RJ11 connector (only available for
models with the battery charger) to allow the Battery Temperature Sensor
(BTS) or various MM accessories (e.g., MM-DCLD) to be connected. The
BTS provides information that enables the multi-stage PFC battery charger
to “fine tune” the battery charge voltages.
12. Intake
Vent –ventilation openings to pull in air to help keep the inverter
cool for peak performance.
13. Exhaust
Vent –ventilation openings that allow heated air to be removed
by the internal cooling fan.
14. Model/Serial Number Label –includes model/serial number and
provides specifications and information on the inverter and charger. See
the Specifications on page 28 for more information.

© 2016 Sensata Technologies 4
Introduction
Figure 1-3, Front and Back Side Features
Front Side 9
10
11
12
16
17
15
= Power cord with
MM1212-G only
15. AC Output Connection – AC knockout (output) for hardwiring (MM612
& MM1212 models only). Note: MM1212-G models include an attached
3 ft. standard plug-in power cord.
16. AC Input Connection – AC knockout (input) for hardwiring (MM612
& MM1212 models only). Note: MM1212-G models have a GFCI outlet.
17. DC Ground Terminal – this connection is used to tie the exposed chassis
of the inverter to the DC grounding system. This terminal accepts CU/AL
conductors from #14 AWG to #6 AWG (2.1 mm2to 13.3 mm2).
Figure 1-4, Left Side Features
Back Side
13
14
1.6 Battery Temperature Sensor (MM1212 & MM1212-G)
A plug-in external Battery Temperature Sensor (BTS) is provided for units with
the battery charger feature. When installed, the BTS automatically adjusts
the battery charger’s BULK, ABSORB, and FLOAT voltage set-points based on
temperature for better charging performance and longer battery life. If the
temperature sensor is NOT installed and the batteries are subjected to large
temperature changes, battery life may be shortened.
Figure 1-5, Battery Temperature Sensor
FRONT VIEW
SIDE VIEW
~1"
(2.6 cm)
~½”
(~1.3 cm)
0.375" diameter
(~1 cm)
Cable
~¾”
(~2 cm)
~2"
(5.1 cm)

© 2016 Sensata Technologies
5
Installation
2.0 Installation
2.1 Pre-Installation
Before installing the inverter, read the entire Installation section. The more
thorough you plan in the beginning, the better your inverter needs will be met.
WARNING: Installations should be performed by qualified
personnel, such as a licensed or certified electrician. It is the
installer’s responsibility to determine which safety codes apply and
to ensure that all applicable installation requirements are followed.
Applicable installation codes vary depending on the specific location
and application of the installation.
Info: Review the “Important Product Safety Information” on page
ii and the “Important Battery Safety Instructions” on page iii before
any installation.
The basic system diagrams shown in Figures 2-3 & 2-4 should be reviewed
to assist you in planning and designing your installations.
2.1.1 Unpacking and Inspection
Carefully remove the MM Series unit from its shipping container and inspect
all contents. Verify the following items are included:
•MM Series inverter
•Red and black DC terminal covers
•AC access cover with two screws
•Two 1/2” hex-head Flange nuts (installed on the DC terminals)
•Battery Temperature Sensor (MM1212 & MM1212-G models only)
•MM Series Owner’s Manual
If items appear to be missing or damaged, contact your authorized
Magnum Energy dealer or Sensata Technologies.
If at all possible, keep your shipping box. It will help protect your inverter
from damage if it ever needs to be returned for service.
Save your proof-of-purchase as a record of your ownership; it will also be
needed if the unit should require in-warranty service.
Record the unit’s model and serial number in the front of this manual in case
you need to provide this information in the future.
2.2 Locating and Mounting the Inverter
WARNINGS:
•Do not mount the inverter near any flammable or combustible
fluid or components.
•Provide adequate clearance/ventilation to the inverter.
•Mount only on a “non-combustible” surface.
• Maximum ambient temperature around the inverter must not
exceed 77°F (25°C) to meet power specifications.
The inverter should only be installed in a location that meets the following
requirements:
Clean and Dry – The inverter should not be installed in an area that allows
dust, fumes, insects, or rodents to enter or block the inverter’s ventilation
openings. This area also must be free from any risk of condensation, water, or
any other liquid that can enter or fall on the inverter. The inverter uses stainless

© 2016 Sensata Technologies 6
Installation
steel fasteners, plated copper busbars, and a powder-coated aluminum base.
Also, the internal circuit boards are conformal coated. The above measures
are undertaken to help fight the harmful effects of corrosive environments.
However, the life of the inverter is uncertain if used in any of these types
of environments, and inverter failure under these conditions is not covered
under warranty.
Cool – The inverter should be protected from direct exposure to the sun or any
equipment that produces extreme heat. The ambient air temperature should
be between 32°F (0°C) and 104°F (40°C)—the inverter’s output specifications
are rated at 77°F (25°C), so the cooler the better within this range.
Ventilated – In order for the inverter to provide full output power and avoid
over-temperature fault conditions, do not cover/block the inverter’s ventilation
openings or install this inverter in an area with limited airflow. Allow as much
clearance around the inverter’s intake and exhaust ventilation openings as
possible (Figure 1-3, Items 12 & 13). At the minimum, allow an airspace
clearance of 3” (7.5 cm) on all sides to provide adequate ventilation.
If installed in an enclosure, a fresh air intake opening must be provided
directly to the front side (intake vent) and an exhaust opening on the back
side (exhaust vent) of the inverter. This will allow cool air from the outside
to flow into the inverter, and heated air to exit away from the inverter and
the enclosure. When mounted in an enclosed compartment, airflow must
be at least 59 cfm in order to maintain no more than a 68°F (20°C) rise in
compartment temperature. Minimum clearances can be reduced if airflow is
increased, but in no case should clearance around the inverter be less than
2” (5 cm) on all sides.
Safe – Keep any flammable/combustible material (e.g., paper, cloth, plastic,
etc.) that may be ignited by heat, sparks, or flames at a minimum distance
of 2 feet (60 cm) away from the inverter. Do not install this inverter in any
area that contains extremely flammable liquids like gasoline or propane, or
in locations that require ignition-protected devices.
Close to the battery bank – As with any inverter, it should be located as
close to the batteries as possible. Long DC wires tend to lose efficiency and
reduce the overall performance of an inverter. However, the unit should not
be installed in the same compartment as the batteries or mounted where it
will be exposed to gases produced by the batteries. These gases are corrosive
and will damage the inverter; also, if these gases are not ventilated and if
allowed to collect, they could ignite and cause an explosion.
Accessible – Do not block access to the inverter’s remote control and
accessory ports. Also allow enough room to access the AC and DC wiring
connections, as they will need to be checked and tightened periodically.
Mounting Orientation – To meet regulatory requirements, the MM Series
inverter can only be mounted on a horizontal surface (shelf or table) or a
vertical surface (wall or bulkhead) either right-side up or up-side down, as
shown in Figure 2-1. The inverter must be mounted on a “non-combustible”
surface, and this surface and the mounting hardware must be capable of
supporting at least twice the weight of the inverter. After determining your
mounting position, use the base of the inverter’s chassis as a template to
mark your mounting screw locations. Remove the inverter, and then drill pilot
holes into the mounting surface.

© 2016 Sensata Technologies
7
Installation
If this unit is used in a mobile application, you may want to place flexible
washers or bushings between the mounting surface and the inverter’s
mounting flanges to reduce vibration.
Refer to Figure 2-2 for unit dimensions. After the inverter has been properly
mounted, proceed to the DC Wiring section.
Wall Mounted (right-side up)
Shelf Mounted
(right-side up)
Shelf Mounted
(up-side down)
Wall Mounted (up-side down)
Figure 2-1, Approved Mounting Orientations
Figure 2-2, MM Series Inverter Dimensions
~6¾” (17.1 cm)
~16⅝” (42.2 cm)
10” (25.4 cm)
~4¾”
(12.1 cm)
~8½” (21.6 cm)
~7½” (19.1 cm)

© 2016 Sensata Technologies 8
Installation
Figure 2-3, Basic Installation Diagram (MM612/MM1212)
AC
Main Panel
Overcurrent
Device
Battery
Bank
AC IN
AC
Loads
DVD
TV Tools
AC
Sub-Panel
AC
Outlet
AC
OUT
DC
Ground
DC
Disconnect

© 2016 Sensata Technologies
9
Installation
Figure 2-4, Basic Installation Diagram (MM1212-G)
Overcurrent
Device
Battery
Bank
AC IN
AC Loads
AC
OUT
DC
Ground
DC
Disconnect
DVD
Tools
TV

© 2016 Sensata Technologies 10
Installation
2.3 Wiring Guidelines
• Before connecting any wires, determine all wire routes to and from the
inverter throughout the RV or vehicle/boat.
•Conductors passing through walls, bulkheads, or other structural members
must be protected to minimize insulation damage such as chafing, which
can be caused by vibration or constant rubbing.
• Always check for existing electrical, plumbing, or other areas of potential
damage prior to making cuts in structural surfaces, bulkheads, or walls.
•Make sure all wires have a smooth bend radius and do not become kinked.
•AC & DC overcurrent protection must be provided as part of installation.
• Do not attempt to use a vehicle metal frame in place of the DC negative
connection or DC ground. The inverter requires a reliable negative and
ground return path directly to the battery.
• DC wires and cables should be tied together with wire ties or electrical
tape approximately every 6 inches (40.1 cm). This helps improve the
surge capability and reduces the effects of inductance, which improves the
inverter waveform and reduces the wear of the inverter’s filter capacitors.
•Use only copper wires with a minimum temp rating of 75°C (167°F).
• To ensure the maximum performance from the inverter, all connections
from the battery bank to the inverter should be minimized; the exceptions
are the DC overcurrent disconnect in the positive line and a shunt in the
negative line. Any other additional connection will contribute to additional
voltage drops, and these extra connections points may loosen during use.
• All wiring to the battery terminals should be checked periodically (once a
month) for proper tightness. The torque requirement for the DC terminals
is between 10 to 12 foot-pounds (13.6 to 16.3 N-m). If you don’t have
a torque wrench, ensure all DC terminals are tight and cannot move.
CAUTION: Be aware that overtightening and misthreading the
nuts on the DC terminals can cause the bolts to strip and snap/
break off.
2.4 DC Wiring
This section describes the inverter’s required DC wire sizes and the
recommended disconnect/overcurrent protection, and how to make the DC
connections to the inverter and the battery bank.
2.4.1 DC Wire Sizing and Overcurrent Protection
It is important to use the correct DC wire to achieve maximum efficiency from
the system and reduce fire hazards associated with overheating. See Table
1 to select the minimum DC wire size needed based on your inverter model.
If the distance from the inverter to the battery bank is greater than 3 feet
(91.4 cm), use the bottom part of Table 1 to help determine the minimum
recommended cable sizes for longer distances. Always keep your wire runs
as short as practical to prevent low voltage shutdowns, and to keep the DC
breaker from nuisance tripping (or open fuses) because of increased current
draw. Undersized cables can also lower the inverter’s peak output voltage as
well as reduce its ability to surge heavy loads.
Info: The DC wires must be color coded with colored tape or heat
shrink tubing; RED for positive (+), BLACK for negative (–), and
GREEN for DC ground.

© 2016 Sensata Technologies
11
Installation
Table 1, Recommended DC Wire/Overcurrent Device
If the inverter is expected to operate at a distance greater than three feet
from the battery bank, the DC wire will need to be increased to overcome the
increase in resistance—which affects the performance of the inverter. Continue
to use the overcurrent device and DC ground wire previously determined from
Table 1 and then, refer to the bottom part of Table 1 to determine the minimum
DC wire size you need for various distances based on your inverter model.
2.4.2 DC Overcurrent Protection
For safety and to comply with electrical code regulations, you must install a
DC overcurrent protection device in the positive DC cable line to protect your
DC cables. This DC overcurrent device must be DC rated and can be a fuse or
circuit breaker. It must be correctly sized according to the size of DC cables
being used, which means it is required to open before the cable reaches its
maximum current carrying capability, thereby preventing a fire. See Table 1
to select the DC overcurrent device needed based on the minimum wire size
according to your inverter model.
Electrical systems in mobile installations typically do not require using a DC
disconnect, although an overcurrent protection device is still required. Because
the DC disconnect is not required, a fuse is usually used as the overcurrent
device in these installations. These installations also do not normally use
The DC wires must have soldered and crimped lugs, crimped copper
compression lugs, or aluminum mechanical lugs. Soldered connections alone
are not acceptable for this application.
Inverter Model
MM612 MM1212/MM1212-G
Maximum Continuous
Current180 amps 160 amps
DC Grounding Electrode
Wire Size2#6 AWG
(13.3 mm2)
#8 AWG
(8.36 mm2)
Minimum DC Wire Size3
[75°C rating in free air]
#6 AWG
(13.3 mm2)
[95 amps]
#1 AWG
(42.4 mm2)
[195 amps]
Maximum DC Fuse Size490 amps with time
delay
175 amps with time
delay
Increased
size for
longer
distance
5 to 10
feet =
#6 AWG
(13.3 mm2)
#1 AWG
(42.4 mm2)
10 to 15
feet =
#4 AWG
(21.1 mm2)
#1/0 AWG
(53.3 mm2)
Note1– Maximum Continuous Current is based on the inverter’s continuous power rating
at the lowest input voltage with an inefficiency factor.
Note2– Per the NEC, the DC grounding electrode conductor can be a #6 AWG conductor
if that is the only connection to the grounding electrode and that grounding electrode
is a pipe, rod, or plate electrode.
Note3– Wire size is based on the requirements needed to increase efficiency and reduce
stress to the inverter.
Note4– The next larger standard size overcurrent device may be used if the derated
cable ampacity falls between the standard overcurrent devices found in the NEC.

© 2016 Sensata Technologies 12
Installation
conduit, so the fuse must be installed in the ungrounded conductor (usually
the positive DC cable line) within 18 inches (45.7 cm) of the battery—to
protect the DC wiring system.
If using a fuse, we recommend using a class-T type or equivalent. This fuse
type is rated for DC operation, can handle the high short-circuit currents,
and allows for momentary current surges from the inverter without opening.
2.4.2 DC Grounding
The inverter should always be connected to a permanent, grounded wiring
system. The idea is to connect the metallic chassis of the various enclosures
together to have them at the same voltage potential, which reduces the
possibility for electric shock. For the majority of installations, the inverter
chassis and the negative battery conductor are connected to the system’s
ground bond via a safety-grounding conductor (bare wire or green insulated
wire) at only one point in the system. Per the NEC, the size for the grounding
conductor is usually based on the size of the overcurrent device used in the
DC system. Refer to Table 1 to select the appropriate DC ground wire based
on the overcurrent device used for your inverter model.
If using this inverter in a vehicle, DO NOT connect the battery negative (–)
cable to the vehicle’s safety ground. Connect it only to the inverter’s negative
battery terminal. If there are any non-factory installed DC appliances on board
the vehicle, DO NOT ground them at the safety ground. Ground them only at
the negative bus of the DC load center (as applicable).
2.4.3 DC Cable Connections
When connecting the DC cable to the battery or to the inverter’s DC terminals,
the hardware should be installed in the correct order to prevent high resistance
connections which will heat up and could cause the connections to melt. Use
Figures 2-5 and 2-6 as a guide to stack the hardware correctly. Tighten the
terminal connections from 10 to 12 foot-pounds (13.6 to 16.3 N-m).
CAUTION: Do not put anything between the DC cable ring lug and
the battery terminal post or the inverter’s DC terminal. If antioxidant
grease or spray is used, apply it once all the connections have been
made and are properly tightened.
CAUTION: Overtightening or misthreading nuts on the DC terminals
will cause the bolts to strip and snap/break-off.
BATTERY
DC cable
with ring lug
bolt
flat washer
nut
lock washer
battery
post
battery terminal
Battery Temperature Sensor
(charger models)
Verify the DC cable lugs are
flush with battery terminals.
Torque the battery terminals
from 10 to 12 ft-lbs.
Figure 2-5, DC Cable to Battery Terminals

© 2016 Sensata Technologies
13
Installation
CAUTION: The inverter is NOT reverse polarity protected (negative
and positive connected backwards). Verify the correct voltage
polarity BEFORE connecting the DC wires, or damage may occur.
Crimped and sealed copper ring terminal lugs with a 5/16” hole should be
used to connect the DC wires to the inverter’s DC terminals.
Figure 2-6, DC Cable to Inverter’s DC Terminals
DC cable
with ring lug
DC
terminal cover
(snaps on)
Inverter’s
DC
terminal
½” Flange nut
(nut with star-washer)
2.5 Battery Bank Wiring
WARNING: Lethal currents will be present if the positive and
negative cables attached to the battery bank touch each other.
During the installation and wiring process, ensure the cable ends
are insulated or covered to prevent touching/shorting the cables.
Info: DO NOT connect the DC wires from the battery bank to the
inverter until: 1) all DC/AC wiring is complete, 2) the correct DC and
AC overcurrent protection have been installed, and 3) the correct
DC voltage and polarity have been verified.
Info: For optimum performance, a minimum battery bank of 200
AHr is recommended.
Depending upon the type of batteries you use in the installation (6 or 12 VDC),
the batteries must be wired in series, parallel, or series-parallel to provide 12
VDC (see Appendix B – Battery Information, for guidance on wiring batteries
together). The interconnecting DC wires must be sized and rated exactly
the same as those that are used between the battery bank and the inverter.
Place the batteries as close as practical to the inverter, preferably in an
insulated and ventilated enclosure. Allow adequate space above the batteries
to access the terminals and vent caps (as applicable). Also, allow at least 1”
(2.5 cm) of space between the batteries to provide good air flow. DO NOT
mount the batteries directly under the inverter.
Info: To ensure the best performance from your inverter system do
not use old or untested batteries. Batteries should be of the same
size, type, rating, and age.
CAUTION: Install batteries in a well ventilated area. Batteries
can produce explosive gasses. For compartment or enclosure
installations, always vent batteries to the outside.

© 2016 Sensata Technologies 14
Installation
2.5.1 Inverter to Battery Bank Wiring
WARNING: Ensure all sources of DC power (i.e., batteries, solar,
wind, or hydro) and AC power (utility, shorepower or AC generator)
are de-energized (i.e., breakers opened, fuses removed) before
proceeding.
CAUTION: The inverter is NOT reverse polarity protected. If this
happens, the inverter will be damaged and will not be covered
under warranty. Before connecting the DC wires from the batteries
to the inverter, verify the correct battery voltage and polarity using
a voltmeter. If the positive terminal of the battery is connected to
the negative terminal of the inverter and vice versa, severe damage
will result. If necessary, color code the cables with colored tape or
heat shrink tubing; RED for positive (+), and BLACK for negative
(–) to avoid polarity confusion.
Info: The DC overcurrent device (i.e., fuse or circuit breaker) must
be placed in the positive (RED) DC cable line between the inverter’s
positive DC terminal and the battery’s positive terminal (RED); as
close to the battery as possible.
DC Ground Wire
Route an appropriately sized DC grounding wire (GREEN or bare wire) from
the inverter’s DC Ground Terminal (Figure 1-4, Item 17) to a dedicated system
ground. Recommended tightening torque is 45 in-lbs (5.1 N-m).
DC Negative Wire
Route an appropriately sized DC negative wire (BLACK) from the negative
terminal of the first battery string to the inverter’s negative terminal (see
Figure B-3 for reference).
Battery Temperature Sensor (MM1212/MM1212-G models only)
Connect the RJ11 connector end of the BTS to the ACCESSORY Port (Figure
1-3, Item 11) on the inverter. Connect the other end of the BTS to the negative
terminal of the fi
rst battery string (in same place as the negative DC wire
above)—refer to Figure 2-5 for the correct hardware placement.
DC Positive Wire
Mount the DC fuse block and disconnect (or circuit breaker) as near as practical
to the batteries, and then remove the fuse (or open the circuit breaker).
WARNING: DO NOT close the DC fuse/DC disconnect (or close DC
circuit breaker) to enable battery power to the inverter at this time.
This occurs in the Functional Test after the installation is complete.
Route and connect an appropriately sized DC positive wire (RED) from the DC
fuse block (or circuit breaker assembly) to the inverter’s positive DC terminal.
Connect a short wire (same rating as the DC wires) to one end of the fuse
block and the other end of the short wire to the positive terminal of the last
battery string (see Figure B-3). This is essential to ensure even charging and
discharging across the entire battery bank.
Ensure the DC wire connections (on the batteries, inverter, and fuse lugs/DC
circuit breaker) are flush on the surface of the DC terminals and the hardware
(lock washer and nut) used to hold these connections are stacked correctly
(see Figures 2-5 & 2-6).
Verify all DC connections are torqued from 10 to 12 ft-lbs (13.6 to 16.3 N-m).
Table of contents
Other Sensata Inverter manuals

Sensata
Sensata Magnum Energy MS Series User manual

Sensata
Sensata Magnum Energy CSW3012-X User manual

Sensata
Sensata Magnum-Dimensions MagnaSine MS-G Series User manual

Sensata
Sensata Dimensions 12LP15 User manual

Sensata
Sensata 24TX60 User manual

Sensata
Sensata ADI-300/3000D User manual

Sensata
Sensata 12/800N User manual

Sensata
Sensata MIL-24XM15N User manual

Sensata
Sensata Dimensions 12LPC15 User manual
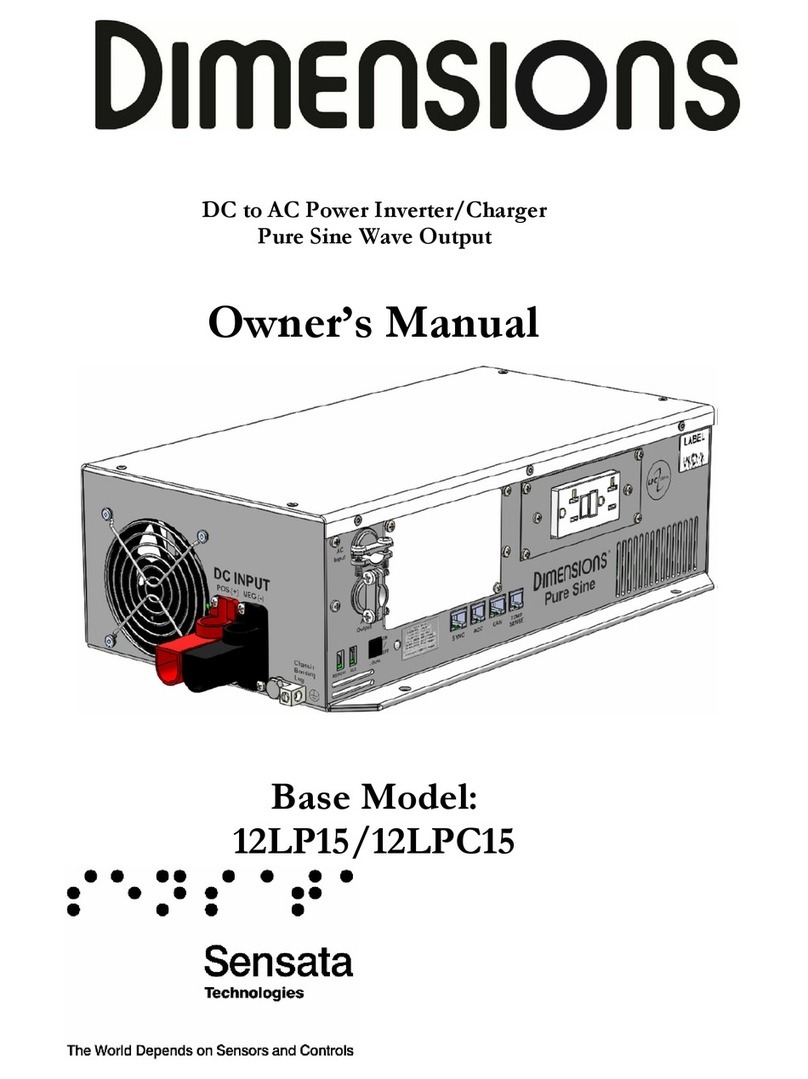
Sensata
Sensata Dimensions 12LP15 User manual