SEPTENTRIO mosaic Series User manual

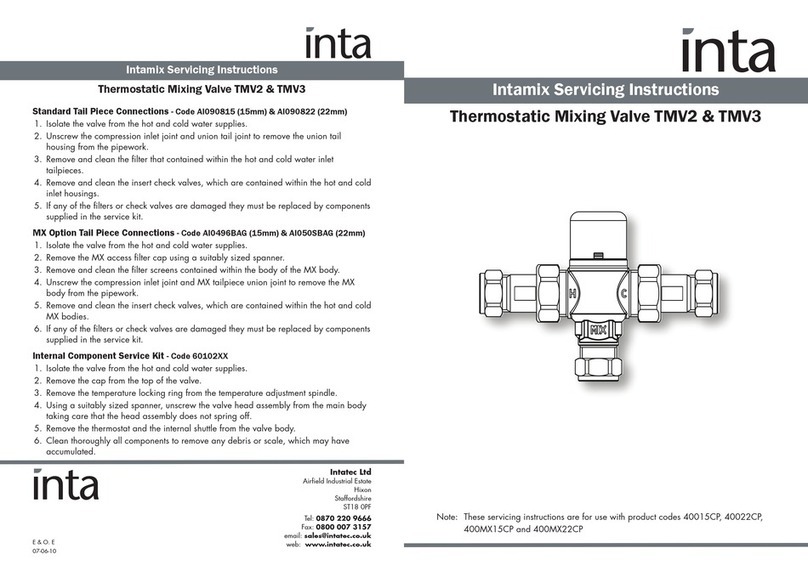
Mosaic Hardware Manual
Version 1.7.0

2
2
2
mosaic Hardware Manual
Version 1.7.0
September 7, 2022
© Copyright 2000-2022 Septentrio nv/sa. All rights reserved.
Septentrio
Greenhill Campus, Interleuvenlaan 15i
3001 Leuven, Belgium
http://www.septentrio.com
Phone: +32 16 300 800
Fax: +32 16 221 640
@septentrio

3
3
3
1Table of contents
1TABLE OF CONTENTS................................................................................................... 3
2DOCUMENT CHANGE LOG .......................................................................................... 7
3MOSAIC GNSS MODULE .............................................................................................. 8
3.1 Overview................................................................................................................... 8
3.2 Mechanical ............................................................................................................. 10
3.3 Absolute Maximum Ratings................................................................................. 10
3.4 Electrical Characteristics in Operational Conditions........................................ 11
3.4.1 Power Supply ........................................................................................................ 11
3.4.2 I/O .......................................................................................................................... 11
3.5 Power Consumption.............................................................................................. 12
3.6 Environmental ....................................................................................................... 12
4PINOUT AND I/O DESCRIPTION................................................................................ 13
4.1 Power Supply ......................................................................................................... 14
4.2 Antenna(s).............................................................................................................. 14
4.2.1 Main Antenna........................................................................................................ 14
4.2.2 Auxiliary Antenna ................................................................................................. 15
4.2.3 Typical Application................................................................................................ 16
4.3 COM Ports............................................................................................................... 17
4.3.1 Typical Application................................................................................................ 17
4.4 USB Device Interface............................................................................................. 18
4.4.1 Typical Application................................................................................................ 18
4.5 Ethernet.................................................................................................................. 19
4.5.1 Typical Application................................................................................................ 19
4.6 SD Memory Card .................................................................................................... 20
4.6.1 Typical Application................................................................................................ 21
4.6.2 Data Logging ......................................................................................................... 21
4.7 Clock Frequency Reference.................................................................................. 22
4.7.1 Using the internal TCXO ....................................................................................... 22
4.7.2 Using and external frequency reference ............................................................ 22

4
4
4
4.8 Event/TimeSync inputs ......................................................................................... 23
4.9 PPS output.............................................................................................................. 24
4.10 General Purpose Output (GPx) ............................................................................ 24
4.11 LEDs......................................................................................................................... 25
4.12 Standby................................................................................................................... 25
4.13 RTC........................................................................................................................... 27
5MOSAIC INTEGRATION.............................................................................................. 28
5.1 Minimal Design ...................................................................................................... 28
5.1.1 Single-Antenna Modules ...................................................................................... 29
5.1.2 Dual-Antenna Modules ........................................................................................ 30
5.2 Electrical Recommendations ............................................................................... 30
5.3 Decoupling.............................................................................................................. 31
5.4 Power States .......................................................................................................... 31
5.5 Layout Recommendations ................................................................................... 32
5.5.1 Coplanarity............................................................................................................ 32
5.5.2 Power..................................................................................................................... 32
5.5.3 Antenna Inputs ..................................................................................................... 32
5.5.4 Avoiding Self-Interference.................................................................................... 33
6PRODUCT HANDLING................................................................................................ 34
6.1 ESD Precautions..................................................................................................... 34
6.2 ROHS/WEEE NOTICE............................................................................................... 34
6.3 Packaging ............................................................................................................... 35
6.3.1 Packing List Label.................................................................................................. 36
6.3.2 MSL Level Label..................................................................................................... 36
6.4 Storage.................................................................................................................... 37
6.4.1 Note for Small Quantities .................................................................................... 37
6.5 Sticker and Identification..................................................................................... 37
6.6 Soldering................................................................................................................. 38
6.6.1 Solder Mask........................................................................................................... 38
6.6.2 Reflow Profile ........................................................................................................ 38
7DEVELOPMENT KIT .................................................................................................... 40

5
5
5
7.1 Header Types ......................................................................................................... 40
7.2 Powering the DevKit ............................................................................................. 40
7.3 Antenna Connectors ............................................................................................. 41
7.4 LEDs and General Purpose Output Pins ............................................................. 42
7.5 COM Ports............................................................................................................... 43
7.6 PPS Out and Event Inputs..................................................................................... 44
7.7 Ethernet.................................................................................................................. 44
7.8 USB Dev................................................................................................................... 44
7.9 USB Host ................................................................................................................. 44
7.10 REF IN ...................................................................................................................... 45
7.11 Buttons ................................................................................................................... 45
7.12 SD Card Socket ....................................................................................................... 45
8EVALUATION KIT: MOSAIC-GO.................................................................................. 46
8.1 Interfaces ............................................................................................................... 46
8.1.1 USB......................................................................................................................... 46
8.1.2 RSV USB ................................................................................................................. 46
8.1.3 RF_IN1 and RF_IN2................................................................................................ 46
8.1.4 TF Card................................................................................................................... 47
8.1.5 6-pin Connector .................................................................................................... 47
8.1.6 4-pin Connector .................................................................................................... 47
8.2 Accessories............................................................................................................. 47
8.2.1 6-pin COM1 Open-Ended Cable .......................................................................... 48
8.2.2 4-pin COM2 Open-Ended Cable .......................................................................... 48
8.3 LEDs......................................................................................................................... 48
8.4 Powering the mosaic-go ....................................................................................... 48
APPENDIX A LED STATUS INDICATORS......................................................................... 49
APPENDIX B SYSTEM NOISE FIGURE AND C/N0.......................................................... 51
APPENDIX C MOSAIC-H RF GAIN ADJUSTMENT.......................................................... 52
APPENDIX D EMC CONSIDERATIONS ........................................................................... 54

7
7
Document Change Log
7
2Document Change Log
Document
Release
Release
Date
Main Changes
1.1.0
Oct 2019
First published version
1.2.0
Jun 2020
Extended the description of the standby mode
Added description of the MODULE_RDY pin
Added power state diagram
Extended and clarified the “Product Handling” section
1.3.0
Jul 2020
Added a note that the RTC_XTALI pin must be tied to ground
1.4.0
Dec 2020
Added description of the dual-antenna mosaic-H
Added complete pad list in appendix
1.5.0
Sep 2021
Added frequency plan in the “Overview”section
Added description of the mosaic-go evaluation kit
Added “mosaic-H RF Gain Adjustment” appendix
1.6.0
Mar 2022
Added documentation of the GPLED2 pin (pin #M3)
Added mosaic-CLAS frequency plan
1.7.0
Sep 2022
Extended and clarified the “Product Handling”section (packaging,
storage and soldering recommendations)

8
8
mosaic GNSS Module
8
3mosaic GNSS Module
3.1 Overview
Septentrio’s mosaic modules are low-power multi-band multi-constellation GNSS receiver
packaged in a 31x31mm LGA module. The internal block diagram is shown below.
The module operates from a single 3V3 power supply (VDD_3V3).
The ANT_1 input pad receives the RF signal from the main antenna. On dual-antenna
modules (mosaic-H), a second antenna input is available (ANT_2) for the auxiliary antenna.
A 3V to 5.5V DC voltage can be applied to the main antenna from the VANT pin, obviating
the need for an external antenna supply. The internal bias control circuit detects
overcurrent conditions (>150mA) and protects the module in case of short circuit. See
section 4.2.
The module can use its internal TCXO as frequency reference, but also accepts an external
frequency reference on the REF_I pin (mosaic-T only). See section 4.7.
Two event timer pins and a PPS output are available (1.8V LVTTL). See section 4.8.
The module features a rich set of communication interfaces:
•Four serial ports (3.3V LVTTL), three of them with hardware flow control. See
section 4.3.
•USB. See section 4.4.

9
9
mosaic GNSS Module
9
•Ethernet (the PHY is external to the module). See section 4.5.
•SDCard interface for logging to an external SD card. See section 4.6.
•GPIO and LEDs output. See section 4.10.
The table below summarizes the main differences between the mosaic models in terms
of hardware features. The frequency bands in blue are supported.
mosaic
model
#Ants
Time &
Freq sync
Supported Frequency Bands per Antenna
mosaic-X5
1
No
mosaic-Sx
1
No
mosaic-T
1
Yes
mosaic-
CLAS
1
No
mosaic-H
2
No
mosaic-H can be configured in two different band plans,
applicable to both antennas:
By default, mosaic-H operates in band plan #1, with the
E5b/B2b/B2I band enabled. Band plan #2, with B3 enabled
instead of E5b/B2b/B2I, is selected when the BDSB3I signal is
enabled with the setSignalTracking user command.

10
10
mosaic GNSS Module
10
3.2 Mechanical
All dimensions in millimeters.
Weight = 6.8g
LGA Details
Specification
Land pitch
1.27 mm
Land diameter
0.6 mm
Pin 1 mark
Bottom: the A1 pad is missing
Top: A1 marked by the hole in the shield
Land plating
Nickle/Gold
Array
23 x 23, three outer rows
Number of terminals
239
3.3 Absolute Maximum Ratings
The following conditions should never be exceeded, even momentarily, as it may cause
permanent damage to the module.
Parameter
Comment
Min
Max
Units
VDD_3V3 voltage
See 4.1
-0.3
3.6
V
VDD_BAT voltage
See 4.12
-0.3
3.6
V
VANT voltage
See 4.2
-0.3
5.5
V
3V3_LVTTL input pin voltage
-0.3
VDD_3V3+0.3
V
A1
AC1

11
11
mosaic GNSS Module
11
EVENT input voltage
See 4.8
-0.3
1V8_OUT+0.3
V
RF input power at ANT_1
See 4.2
20
dBm
RF input power at ANT_2
See 4.2
10
dBm
REF_I level
See 4.7
1.7
Vp-p
Output pins drive current
10
mA
Storage temperature
-55
+85
°C
Operational temperature
-40
+85
°C
3.4 Electrical Characteristics in Operational Conditions
3.4.1 Power Supply
Parameter
Comment
Min
Typ
Max
Units
VDD_3V3 voltage
See 4.1
3.135
3.3
3.465
V
VDD_BAT voltage
See 4.12
3.135
3.3
3.465
V
VANT voltage
See 4.2
3.0
3.3
5.5
V
USB_VBUS1 voltage
See 4.4
4.4
5.0
5.5
V
1V8_OUT output voltage
1.764
1.8
1.836
V
2V8_OUT output voltage
2.744
2.8
2.856
V
VDD_3V3 current
160
210
500
mA
VDD_BAT input current
0.03
1
mA
USB_VBUS1 input current
See 4.4
10
50
mA
1V8_OUT output current
120
mA
2V8_OUT output current
100
mA
VANT input current
150
mA
3.4.2 I/O
Parameter
Comment
Min
Typ
Max
Units
VIH, 1.8V inputs
0.7*1V8_OUT
V
VIL, 1.8V inputs
0.3*1V8_OUT
V
Input capacitance
1.8V inputs
2.0
pF
Pull-down, 1.8V inputs
80
210
515
kOhm
VOH, 1.8V outputs
7.2 mA
0.75*1V8_OUT
V
VOL, 1.8V outputs
7.2 mA
0.4
V
VIH, 3.3V inputs
0.7*VDD_3V3
VDD_3V3
V
VIL, 3.3V inputs
0
0.3*VDD_3V3
V
Pull-up, 3.3V inputs
Except nRST_IN
68
100
150
kOhm
Pull-up, nRST_IN
9.6
9.8
10
kOhm
VOH, 3.3V outputs
1 mA
VDD_3V3-0.15
V
VIL, 3.3V outputs
1 mA
0.15
V
REF_I input level
0.5
1.7
Vp-p
REF_I input capacitance
8
pF
REF_I input frequency
10
MHz
REF_O output level
See 4.7.1
1.2
Vp-p

12
12
mosaic GNSS Module
12
3.5 Power Consumption
The module is powered through the VDD_3V3 pins, see section 4.1.
The power consumption depends on the set of GNSS signals enabled and on the
positioning mode. The following tables list the average power consumption for some
configurations, while tracking all satellites in view from an open sky, and with the module
at room temperature. The current is applicable to a supply voltage of 3.3V.
Single-Antenna Modules
GNSS Signals
Positioning
Mode
Power
(mW)
Current
(mA)
GPS L1 C/A
Stand-Alone (1Hz)
550
167
GPS L1/L2
RTK (1Hz)
670
203
GPS/GLONASS L1/L2
RTK (1Hz)
695
211
GPS/GLONASS L1/L2+GALILEO L1/E5a
+BeiDou B1C/B2a (phase 3)
RTK (1Hz)
850
258
GPS/GLONASS L1/L2+GALILEO L1/E5a
+BeiDou B1C/B2a (phase 3)
RTK (100 Hz)
930
282
GPS/GLONASS L1/L2 + L-band
PPP (1Hz)
760
230
All signals from all GNSS constellations
Static (1Hz)
910
276
All signals from all GNSS constellations
+L-band
Static(1Hz)
980
297
All signals from all GNSS constellations
+L-band
Static (100Hz)
1080
327
Dual-Antenna Modules
GNSS Signals
Positioning
Mode
Power
(mW)
Current
(mA)
GPS L1 C/A
RTK+heading (10Hz)
680
206
GPS L1/L2
RTK G +heading
(10Hz)
900
273
All signals from all GNSS constellations
RTK+heading (10Hz)
1060
321
Enabling wideband interference mitigation with the setWBIMitigation command adds 70
mW.
Note that the currents given in the above tables are average values. To account for peak
currents, the minimum power supply drive capability should be 500 mA.
3.6 Environmental
Operational: -40 to +85 °C
Storage: -55 to +85 °C

13
13
Pinout and I/O Description
13
4Pinout and I/O Description
The module provides 239 LGA pads, configured as follows.
The following sections describe all the non-reserved pads. Pads are grouped by functions.
A complete pad list can be found in Appendix E.
Conventions:
•Pin Type: I=Input, O=Output, P=Power, Ctrl=Control, Clk=Reference clock
•PU: pulled up
•PD: pulled down
•K: keeper input type

14
14
Pinout and I/O Description
14
4.1 Power Supply
The module is powered through the VDD_3V3 pins.
Pin Name
Type
Level
Description
Comment
VDD_3V3
P,I
3.3V +/-5%
Main power supply input
All VDD_3V3 pins must be tied
together.
GND
Gnd
0
Ground
All GND pins must be connected to
ground.
VDD_BAT
P,I
3.3V +/-5%
“Always-on” supply.
Must be tied to VDD_3V3 unless an
external power switch is available.
See section 4.12.
nRST_IN
Ctrl,PU
3V3_LVTTL
Reset input, active negative. Module is in reset when low. Short
low pulses of less than 1 µs are ignored.
Internally debounced, can be directly
connected to a push-button.
MODULE_RDY
O
3V3_LVTTL
Level is high when module is operating, and low when in standby
or reset.
Level becomes high about 300
milliseconds after powering /
unresetting the module.
1V8_OUT
P,O
1.8V
1.8V output, see below
SYNC
I
1V8_LVTTL
Reserved. Must always be connected to 1V8_OUT.
Note that the 2V8_OUT and 2V8_IN pins are exclusively reserved to power the internal
TCXO. See section 4.7.
The 1V8_OUT pin is a DC output (120mA max current) which can, for example, be used to
power level-shifters for the 1V8_LVTTL signals (EVENT and PPS), see for example section
4.8.
The module can also control an external power switch, to enable standby mode. See
section 4.12 for details.
See also the power state diagram in section 5.4.
4.2 Antenna(s)
4.2.1 Main Antenna
The main antenna (which is the only antenna on single-antenna modules) is directly
connected to the ANT_1 pad. The ANT_1 input is ESD-protected in the module and carries
a DC-voltage to power the antenna, avoiding the need for an external bias-tee. This DC-
voltage is imposed to the module via the VANT pad.
In case of an overcurrent condition (e.g. short circuit in antenna cable), the module will
first limit the current to about 150 mA and then switch off the antenna supply in about 10
ms. It will periodically retry to switch on the antenna supply until the overcurrent
condition has disappeared.
Pin Name
Type
Level
Description
Comment
ANT_1
RF
RF input for main antenna
VANT
P,I
3–5.5V
DC supply to the ANT_1 antenna. Max current 150mA. DC supply
is turned off if overcurrent is detected.
If those pads are not connected or if they are tied to GND, there
is no DC voltage at the ANT_1 pad.
The two VANT pads should be tied
together.

15
15
Pinout and I/O Description
15
4.2.1.1 ANT_1 Electrical Specifications
Never inject an external DC voltage into the ANT_1 pad as it may damage the module. For
instance, when using a splitter to distribute the antenna signal to several GNSS receivers,
make sure that no more than one output of the splitter passes DC. Use DC-blocks
otherwise.
4.2.2 Auxiliary Antenna
In dual-antenna modules, the auxiliary antenna is connected to the ANT_2 pad. In single-
antenna modules, ANT_2 is not used and must be tied to ground.
Pin Name
Type
Level
Description
Comment
ANT_2
RF
RF input for auxiliary antenna
To be tied to ground in single-antenna
modules
Contrary to the ANT_1 pad, ANT_2 is not ESD-protected and it carries no DC voltage. ESD
protection and biasing must be performed externally. See section 4.2.3.2.
4.2.2.1 ANT_2 Electrical Specifications
1
The pre-amplification gain is the total gain of the distribution network in front of the module. Typically, this
equals antenna active LNA gain minus coax losses in the applicable GNSS bands. The pre-amplification gain
can be computed from the AGC gain reported by the module in the ReceiverStatus SBF block and shown
in the web interface or the RxControl GUI. The conversion formula from the reported AGC gain to the pre-
amplification gain is:
Pre-amp gain[dB] = 65 - AGCgain[dB]
So, if the receiver reports an AGC gain of 30dB, the pre-amplification gain is 35dB.
2
The listed noise figure is at room temperature. Add 2 dB for the noise figure at the worst temperature corner
(85°C)
DC bias
DC level provided with the VANT pad
Equivalent DC series impedance at
the ANT_1 pin
2.5 Ohms typical, 3.0 Ohms max
Antenna current limit
150 mA
ANT_1 pre-amplification gain range1
Single-antenna modules: 15-50 dB (AGC gain: 15-50dB)
Dual-antenna modules: 15-35dB (AGC gain: 30-50dB)
ANT_1 receiver noise figure2
(NFrx, see Appendix B)
8.5 dB with 15 dB net pre-amplification
18 dB with 25 dB net pre-amplification
26 dB with 35 dB net pre-amplification
35 dB with 45 dB net pre-amplification
RF nominal input impedance
50 Ohms
VSWR
< 2:1 in all the supported frequency bands
DC bias
None, ANT_2 is AC-coupled
ANT_2 pre-amplification gain range1
15-35 dB (i.e. AGC gain: 30-50dB)
ANT_2 receiver noise figure
(NFrx, see Appendix B)
6 dB with 15 dB net pre-amplification
14.5 dB with 25 dB net pre-amplification
21 dB with 35 dB net pre-amplification
RF nominal input impedance
50 Ohms
VSWR
< 2:1 in all the supported frequency bands

16
16
Pinout and I/O Description
16
4.2.3 Typical Application
4.2.3.1 Single Antenna Modules
The ANT_1 input is DC-biased and ESD-protected, so that no external component is
needed. Make sure to connect the ANT_2 pad to ground.
Refer to 5.5.3 for RF-routing recommendations.
4.2.3.2 Dual-Antenna Modules
The main antenna connects to ANT_1 and the auxiliary antenna to ANT_2. ANT_1 is DC-
biased and ESD-protected, while ANT_2 is AC-coupled and unprotected. A recommended
application circuit is shown below. With this circuit, the DC bias from the ANT_1 pad is
shared between the two antennas. Note that the combined current drawn by both
antennas must not exceed 150mA in that case.
Refer to 5.5.3 for RF-routing recommendations.
If the pre-amplification gain is higher than 35dB, it is recommended to put attenuators in
the RF path. See Appendix C for instructions.
In addition, the ANT_1 and ANT_2 pre-amplification must not differ by more than 5dB. It
is recommended to use the same antenna type for the main and auxiliary antennas, and,
as much as possible, to use antenna cables of the same type and length. In case this is
not possible, the strongest signal needs to be attenuated, as also described in Appendix
C.

17
17
Pinout and I/O Description
17
4.3 COM Ports
The module provides four serial COM ports. Three of them (COM1 to COM3) support
RTS/CTS hardware flow control:
Pin Name
Type
Level
Description
Comment
TXD1
O
3V3_LVTTL
Serial COM1 transmit line (inactive state is high)
RXD1
I, PU
3V3_LVTTL
Serial COM1 receive line (inactive state is high)
RTS1
O
3V3_LVTTL
Serial COM1 RTS line.
The module drives this pin low when
ready to receive data
CTS1
I, PU
3V3_LVTTL
Serial COM 1 CTS line.
Must be driven low when ready to
receive data from the module.
TXD2
O
3V3_LVTTL
Serial COM2 transmit line (inactive state is high)
RXD2
I, PU
3V3_LVTTL
Serial COM2 receive line (inactive state is high)
RTS2
O
3V3_LVTTL
Serial COM2 RTS line.
The module drives this pin low when
ready to receive data
CTS2
I, PU
3V3_LVTTL
Serial COM3 CTS line.
Must be driven low when ready to
receive data from the module.
TXD3
O
3V3_LVTTL
Serial COM3 transmit line (inactive state is high)
RXD3
I, PU
3V3_LVTTL
Serial COM3 receive line (inactive state is high)
RTS3
O
3V3_LVTTL
Serial COM3 RTS line.
The module drives this pin low when
ready to receive data
CTS3
I, PU
3V3_LVTTL
Serial COM3 CTS line.
Must be driven low when ready to
receive data from the module.
TXD4
O
3V3_LVTTL
Serial COM4 transmit line (inactive state is high)
RXD4
I, PU
3V3_LVTTL
Serial COM4 receive line (inactive state is high)
Unused COM-port signals can be left floating. Flow control is disabled by default.
The COM port settings (baud rate, flow control, etc) are set with the setCOMSettings user
command. The maximum baud rate is 4Mbits/s.
The LVTTL RXD and CTS inputs of the module shall not be driven while its VDD_3V3 input
supply is not present.
4.3.1 Typical Application
An example of a circuit to convert the COM1 signals to RS232 level is shown below. In
green, the signals to be connected to the mosaic pins. The RTS1 and CTS1 signals can be
left unconnected if hardware flow control is not required.
It is recommended to use the same 3V3 source to supply the RS232 transceiver and the
VDD_3V3 pins of the module, to ensure that the transceiver outputs are not driven when
the module is not powered.

18
18
Pinout and I/O Description
18
4.4 USB Device Interface
The following pins are used for accessing the module over USB in USB-device mode.
Pin Name
Type
Level
Description
Comment
USB_VBUS1
P,I
4.40V to
5.5V
USB VBUS input.
This pin cannot be used to power the module.
Maximal current drawn by the module is 50 mA.
Note: if USB is unused, this pin shall be left floating
This pin powers the integrated PHY of
the USB interface.
USB_DEV_N
I/O
USB
USB data signal, negative
USB_DEV_P
I/O
USB
USB data signal, positive
USB is configured in USB 2.0 mode (high speed, 480Mbps max).
4.4.1 Typical Application
An example of an USB application circuit with ESD protection is shown below. The user
shall make sure to use an ESD-protection and common mode choke compatible with high-
speed USB if this is desired, for instance the USBLC6-2 from ST and DLP31SN121ML2L
from Murata.

19
19
Pinout and I/O Description
19
4.5 Ethernet
The module supports full duplex 10/100 Base-T Ethernet communication. The Ethernet
PHY and magnetics are to be implemented on the host board. Connection with the PHY
is through the RMII interface available on the following pins:
Pin Name
Type
Level
Description
Comment
RMII_CLK
O
3V3_LVTTL
LAN PHY Clock
MDIO
I/O
3V3_LVTTL
LAN PHY control data
MDC
O
3V3_LVTTL
LAN PHY control clock
RMII_RXD1
I, PU
3V3_LVTTL
LAN PHY receive data 1
RMII_RXD0
I, PU
3V3_LVTTL
LAN PHY receive data 0
RMII_CRSDV
I, PU
3V3_LVTTL
LAN PHY CRS
RMII_RXER
I, PU
3V3_LVTTL
LAN PHY RX error
RMII_TXEN
O
3V3_LVTTL
LAN PHY transmit enable
RMII_TXD0
O
3V3_LVTTL
LAN PHY transmit data 0
RMII_TXD1
O
3V3_LVTTL
LAN PHY transmit data 1
nRST_LAN
O
3V3_LVTTL
LAN reset (low to reset the PHY)
When connecting this pin to enable an
Ethernet PHY, add a 10k pull-down.
If Ethernet is not used, all these pins should be left unconnected.
Hostname: the module hostname is based on the last seven digits of the serial number.
For example, the hostname of the module shown below is mosaic-X5-3054938.
4.5.1 Typical Application
An application circuit using the KSZ8041NLI PHY and a Würth 74990111217 RJ45
connector with integrated magnetics is given below. In green, the signals to be connected
to the mosaic pins.

20
20
Pinout and I/O Description
20
It is recommended to use the same 3V3 source to supply the PHY and the VDD_3V3 pins
of the module, to ensure that the PHY output pins are not driven when the module is not
powered.
The module also supports other PHYs. An up-to-date list of supported PHY’s can be found
in Septentrio’s Knowledge Base pages :
https://customersupport.septentrio.com/s/article/which-ethernet-phy-does-mosaic-support
4.6 SD Memory Card
The module can interface to an external SD memory card through the pins listed in the
table below.
Pin Name
Type
Level
Description
Comment
SD_CLK
O
3V3_LVTTL
SD card CLK line
SD_CMD
O
3V3_LVTTL
SD card CMD line
SD_DAT0
I/O
3V3_LVTTL
SD card DAT0 line
LOGBUTTON
I, PU
3V3_LVTTL
Toggle logging on/off or mount/unmount the disk. See below
This manual suits for next models
5
Table of contents
Other SEPTENTRIO Control Unit manuals