7
8 007 487/10-10-99 Technical Description • LGT © SICK AG • Safety Systems • Germany • All rights reserved
5 Installation and Commissioning
5 Installation and Commissioning
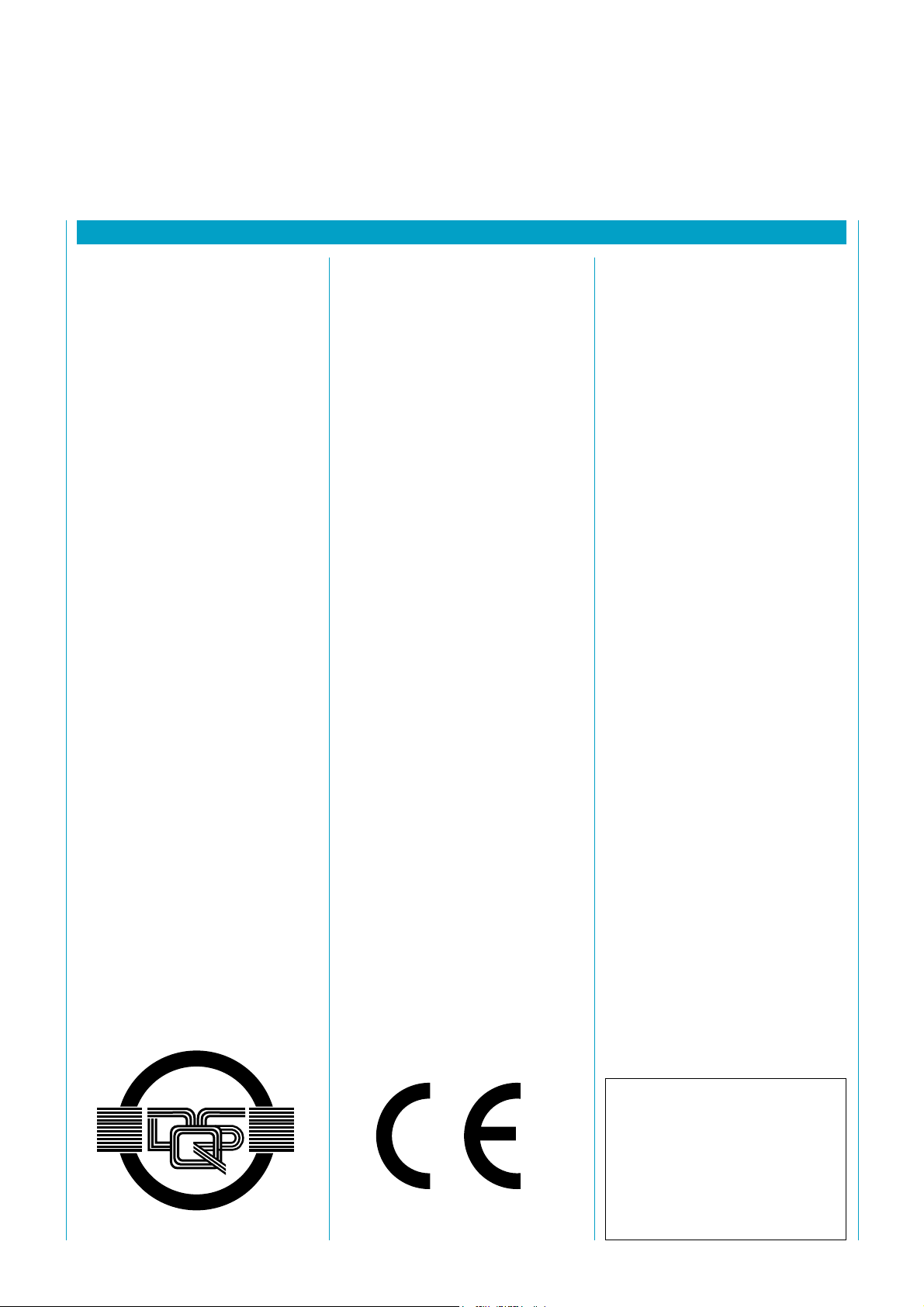
Fig. 7. Determining the coasting time and the safety clearance
For S < 500 mm
S = 2000 .....T + 8 (d - 14)
greater (S = > 500 mm)
S = 1600 .....T + 8 (d - 14)
S Safety distance
T Total response time in s
(stopping time of the machine
+ response time LGT)
d Resolution
The LGT must be commissioned in
accordance with the following steps
1 Clarify and carry out mechanical
mounting
2 Connect the sender and re-
ceiver strips to the control unit
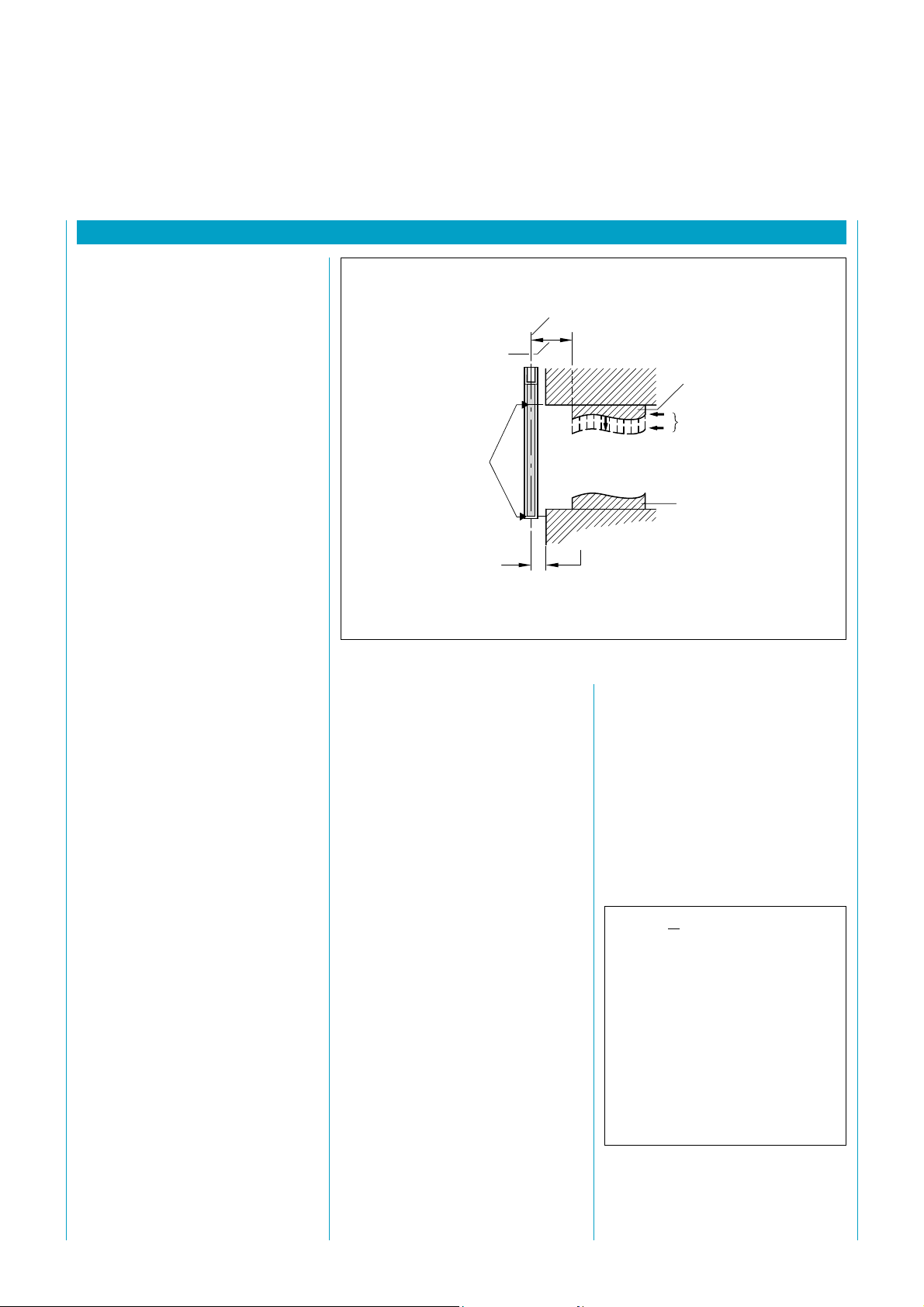
3 Set the DIP switches "With ...”
or "Without restart interlock"
(preset at factory), fig. 15
4 Connect the "machine control"
input (jumper or terminal)
5 Set the DIP switch: either 1 or
2 LGT connected to control
unit (fig. 15)
6 Connect or jumper the contac-
tor monitor
7 Perform blanking in accordance
with Section 5.3.8 if required
8 Set the sender power in ac-
cordance with 5.3.7
9 Insert the output elements in
the switch-off control line of the
machine
The individual measures for this
purpose are described in the fol-
lowing chapters.
5.1General
The LGT can be operated in any
position as long as the specified
safety distances and sufficient pro-
tective height are provided
(see 11 selection table).
Before the unit is installed, check
the components to ensure that
they are complete:
The LGT Light Grid comprises 5
individual parts. These must always
be available before starting the in-
stallation:
1 control unit LGTN
1 sender strip LGTS
1 receiver strip LGTE
2 connecting leads (preassembled)
Test rod (30 mm) as accessory
available.
Two sensor pairs (sender and re-
ceiver) can be connected to each
control unit.
5.1.1 Safety Distance from
Hazardous Point
The protective device requires a
certain minimum distance to the
hazardous point to ensure that the
point can only be reached once the
machine or system has come to a
standstill (Fig. 7). The safety dis-
tance (as per EN 775, 999 and
294) depends on the
‡stopping time of the machine,
‡response time of the protective
device,
‡resolution of the light grid
and the reach speed.
The stopping time is a measured
value of the machine. The reach
speed is equal to
at (short distances) up to 500 mm
safety distance 2 m/s
greater than this 1.6 m/s
The safety distance S is calculated
using the formula:
Mean protection field depth
S = Safety clearance Boundary of hazardous site
Protection field boundary
Upper edge of tool
Coasting time of machine
Lower edge of tool
This value must be strictly observed
in order to prevent access behind
the protection field.
≤ 75 mm