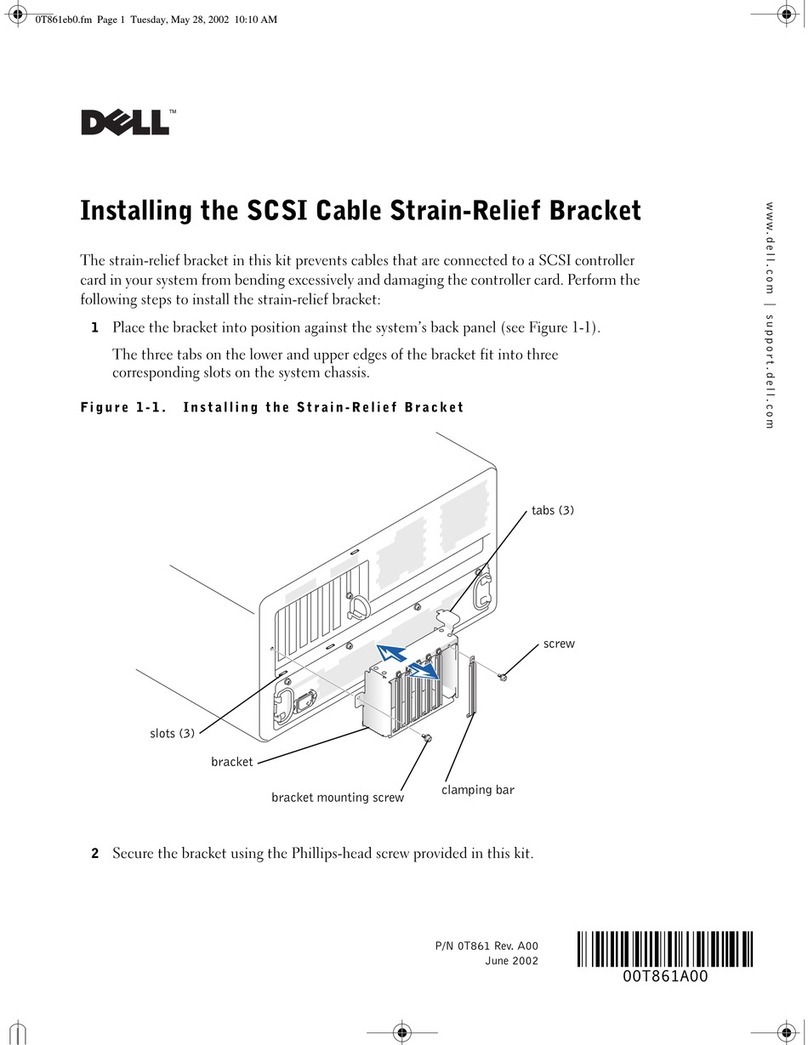
SnapTV 360GBPX-E Combo User manual

SYSTEM INSTALLATION GUIDE
Version 2.3.0
January 28, 2014

Contents
1 Introduction 1
1.1 Applicability ...................................... 1
1.2 Target audience .................................... 1
2 Getting started 3
2.1 First time power up .................................. 3
2.2 Console login ..................................... 3
2.3 Setting new passwords ................................ 4
2.4 Setting keyboard mapping .............................. 4
2.5 Network configuration ................................. 5
2.6 Assigning hostname .................................. 8
3 Accessing the web interface 9
3.1 Getting started continued ............................... 9
4 Software upgrade 11
4.1 About Software Upgrades ............................... 11
4.2 Upgrade using Web Interface ............................. 11
4.3 Upgrade using the terminal .............................. 12
5 Manage inputs 13
5.1 Numbering of the input sources ........................... 13
5.2 Satellite connection .................................. 13
5.3 Terrestrial and Cable connection ........................... 14
5.4 CA modules ...................................... 14
5.5 Analog sources .................................... 15
5.6 List inputs ....................................... 16
6 Manage live signals 17
6.1 List and edit channels ................................. 17
6.2 Add channel from input ................................ 20
6.3 Stream full transport stream from input ....................... 23
6.4 New external multicast ................................ 23
6.5 New looped file channel ................................ 24
i

7 Manage content 25
7.1 VoD ........................................... 25
7.2 Infopage ........................................ 26
7.3 Mini Browser Pages .................................. 26
8 Manage recording 29
8.1 Configure Recorder Manager ............................. 29
8.2 Configure recording of TV and Radio channels ................... 30
9 Content Provisioning Server 33
10 Client provisioning 35
10.1 Amino .......................................... 35
10.2 Standard ........................................ 36
11 System configuration 39
11.1 Network ......................................... 39
11.2 Cluster ......................................... 43
11.3 Mini browser server .................................. 44
11.4 EPG service ...................................... 45
11.5 Monitoring ....................................... 47
11.6 Portal .......................................... 50
11.7 Set time zone ..................................... 53
11.8 Unicast radio services ................................. 54
11.9 Manage administrators ................................ 54
11.10Configuration profiles ................................. 56
11.11Setting up SSL ..................................... 57
12 System information 59
12.1 License ......................................... 59
12.2 List versions ...................................... 60
12.3 System status ..................................... 60
13 Console: Advanced configuration 63
13.1 Working in a text-based console ........................... 63
13.2 Using the Nano editor ................................. 63
13.3 EPG: Importing XMLTV data into the SnapTV EPG server Configuring the gate-
way for using an XMLTV EPG source ........................ 64
13.4 EPG: Importing XMLTV data ............................. 65
13.5 Resetting the System Passwords .......................... 65
14 AMT - Active Management Technology 67
14.1 Overview ........................................ 67
14.2 Connection ....................................... 67
14.3 Tools for accessing AMT from a PC in the network ................. 67
15 PAGA Mute 73
15.1 Network based I/O switch ............................... 73
15.2 Serial cable ....................................... 74
16 UPS Shutdown 75
16.1 Serial cable ....................................... 75
ii

17 Audio Media Player 77
17.1 Play radio channels on your Audio Media Player .................. 77
18 SnapCast 79
18.1 SnapCast administration pages ........................... 79
18.2 Enabling SnapCast .................................. 80
18.3 Channels ........................................ 80
18.4 Items .......................................... 82
18.5 Schedule ........................................ 83
18.6 Configuration ...................................... 84
18.7 Offline import ...................................... 84
19 Final Notes 87
20 Indices and tables 89
Index 91
iii

iv

CHAPTER 1
Introduction
Dear Customer, thank you for selecting SnapTV equipment for your IPTV operation. Please
follow this installation manual carefully during installation of your equipment.
1.1 Applicability
This Installation Guide is applicable to
• SnapTV 360GBPX-E Combo
• SnapTV 360GBPX-E GW Maxi
• SnapTV 360GBPX-E GW Classic
• SnapTV Maxi Express
• SnapTV Mini Streamer
• Software version: 2.3.0
Some sections are only applicable to some products.
1.2 Target audience
The target audience of this installation manual is personnel who install SnapTV server prod-
ucts. The reader of this manual is required to have a basic command line user experience on
Linux and preferably basic knowledge about Linux networking.
For specifics on the SnapTV Linux distribution (Ubuntu 12.04 LTS), the following is a good
starting point
•http://community.ubuntu.com/help-information/
•http://help.ubuntu.com/
Also, man pages are part of the SnapTV Linux distribution whenever you need detailed infor-
mation on the command syntax of relevant utilities.
1

System Installation Guide, Release 2.3.0
2 Chapter 1. Introduction

CHAPTER 2
Getting started
2.1 First time power up
Connect both power cables to the unit and to 220VAC wall outlets. Switch both switches on the
power supplies to the 1position. Thereafter, switch the unit on by pressing the toggle switch
on the front panel.
2.2 Console login
Attach a VGA cable to a monitor and a standard PS/2 or USB keyboard.
3

System Installation Guide, Release 2.3.0
You will need to log in to your equipment in order to define network specific information. Enter
username snap and password as indicated on the factory settings sheet or defined during the
installation phase if you installed the software yourself.
Example:
localhost login: snap
password: ******
If the password is correct, you will have a bash prompt:
localhost ~#
2.3 Setting new passwords
It’s recommended to define new passwords for your product.
2.3.1 Setting new password for the default user (snap)
Example:
~# passwd
New UNIX password:
Retype new UNIX password:
passwd: password updated successfully
For more details about the passwd command, type man passwd at the shell prompt.
2.3.2 Creating admin user for accessing the web interface
In case the current web interface user/password is forgotten, a new user and password can be
defined using this command.
Example:
~# sudo /opt/snaptv/bin/create_admin_user.pm <username> <password> (<real name>)
Creating user <username> (admin)with password <pasword>
2.4 Setting keyboard mapping
Keyboard mappings for the console are stored in the ascii text file /etc/conf.d/keymaps. Use
the nano text editor to change the value called KEYMAP into a value suitable for you. Valid
values for the KEYMAP variables are found in subfolders of /usr/share/keymaps/i386:
~# nano /etc/conf.d/keymaps
Use the arrow keys to navigate in the file, change the value of the KEYMAP parameter, then
save and exit with Ctrl+X →Y→ENTER. In order to change the keyboard mapping without
having to do a reboot of your system, use the command-line utility loadkeys to load the selected
keyboard mapping. If your keryobard mapping is se to no-latin1 , type:
4 Chapter 2. Getting started

System Installation Guide, Release 2.3.0
~# loadkeys no-latin1
Loading /usr/share/keymaps/i386/qwerty/no-latin1.map.gz
2.5 Network configuration
2.5.1 Default settings
Your unit has two network interfaces, named eth0 and eth1 as labeled at the rear of the server.
In a typical configuration, eth1 will be used for external connection, providing Internet access,
while eth0 is connected to the local network where the radio and TV channels are to be multi-
casted.
By default, eth0 has it’s IP address set to 10.0.0.5 with netmask set to 255.255.255.0. eth1 is
by default set to get its address, netmask, default gateway and name server using the DHCP
protocol.
You may use the ifconfig command to check the IP addressing details associated with each
interface.
Example:
~# ifconfig eth0
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:18:7d:2b:43:5d
inet addr:10.0.0.5 Bcast:10.0.0.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::218:7dff:fe2b:435d/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:1277066 errors:0 dropped:33493259 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:530222399 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:364621269 (364.6 MB)TX bytes:721189228250 (721.1 GB)
Interrupt:16 Memory:f7e40000-f7e60000
~# ifconfig eth1
eth1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:18:7d:2b:42:db
inet addr:192.168.1.205 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::218:7dff:fe2b:42db/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:899720 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:292126 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:106295691 (106.2 MB)TX bytes:69399912 (69.3 MB)
Interrupt:20 Memory:f7f00000-f7f20000
In case the default setup is insufficient for your needs, the following sections describe how to
change the configuration. All changes are made by editing /etc/network/interfaces. More exam-
ples for network setup can be found here https://help.ubuntu.com/12.04/serverguide/network-
configuration.html.
Example: Default content of /etc/network/interfaces:
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
auto eth0
2.5. Network configuration 5

System Installation Guide, Release 2.3.0
iface eth0 inet static
address 10.0.0.5
netmask 255.255.255.0
up ip route add 224.0.0.0/4 dev eth0
auto eth1
iface eth1 inet dhcp # This blank configuration will automatically use DHCP for any net.*
Note that no default gateway is assigned to eth0. This is because a default gateway will be
assigned to eth1 if eth1 is used to connect to an external network with automatic configuration
via DHCP.
2.5.2 Changing network address in /etc/network/interfaces
In the file /etc/network/interfaces, the network interfaces are configured with the format:
iface <interface> inet static
address 10.0.0.5
This can, for example, be:
iface eth1 inet dhcp
or
iface eth1 inet static address 192.168.1.112 netmask 255.255.255.0
Setting the option to dhcp causes the interface to retrieve its IP address, netmask, default
gateway address and name server from a DHCP server (if available). In order to manually
specify the interface address, use the static syntax in order to replace dhcp with an IP address
and netmask.
2.5.3 Changing default gateway in /etc/network/interfaces
The default gateway is specified by route -n, where gateway address is the IP address of your
gateway. Note that the gateway only needs to be set for one of the network interfaces.
Example: If you need to assign a default router to eth0, enter the command:
localhost ~#route add default gw x.y.z.w
Where you substitute x.y.z.w with the IP address of the default gateway.
If you need to delete a default route, use:
localhost ~# route del default gw x.y.z.w
And if you assign an explicit default gateway as a part of the boot sequence, add a line in
/etc/network/interface in the iface section of your choice (eth0 or eth1)
gateway 192.168.1.112
6 Chapter 2. Getting started

System Installation Guide, Release 2.3.0
2.5.4 Changing multicast routes in /etc/network/interfaces
Multicast traffic is routed to the interface selected by the multicast route. By default this is eth0.
The default multicast route then looks like the following:
up ip route add 224.0.0.0/4 dev eth0
2.5.5 Checking the routing tables
Use the command route to check the routing table of your SnapTV gateway.
Example:
~# route -n
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
0.0.0.0 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 UG 100 0 0 eth1
10.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0
192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth1
224.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 240.0.0.0 U 0 0 0 eth0
Tip: It’s a good idea to use the -n option to route if DNS has not been configured yet, as
the route command without the -n option will attempt to do reverse DNS look-up for the IP
addresses, which may cause long delays before eventually timing out.
The above is a typical routing table after initial setup from default configuration files. A de-
fault gateway has been defined on eth1 by DHCP, at 192.168.1.1. Multicast routing has been
defined for eth0.
2.5.6 Assigning NTP server
In order for some of the SnapTV services (notably the Electronic Program Guide (EPG) and
nPVR), the system needs to keep accurate time. This is done through the Network Time
Protocol. As long as the SnapTV unit has access to the Internet, this will work transparently.
Should this option not be available, an NTP server should be made available to the SnapTV
unit on the local network. In this case, the following steps must be taken to make the unit aware
of the local network NTP server.
• In the file /etc/conf.d/ntp-client replace pool.ntp.org with the address of your local NTP
server: NTPCLIENT_OPTS=”-s -b -u pool.ntp.org”→NTPCLIENT_OPTS=”-s -b -u
<LAN ntp address>“
• In /etc/ntp.conf the value server pool.ntp.org must be changed to server <LAN ntp ad-
dress>.
Where <LAN ntp address> is the IP address of the local network NTP server.
2.5.7 Using new network settings
To make new network settings take effect, restart the network interface. For eth0, the command
would be:
2.5. Network configuration 7

System Installation Guide, Release 2.3.0
~# sudo ifdown eth0 && sudo ifup eth0
2.6 Assigning hostname
Note: If you change the hostname and the new hostname does not have a valid entry in
the configured DNS, you have to add an alias for it in the file /etc/hosts, or the SnapTV web
interface will not work.
Use the nano editor to modify the line 127.0.0.1 localhost to something like this (See sec-
tion Using the Nano editor for more help on using nano):: 127.0.0.1 localhost snapreceiver-
myhotel01
The hostname is a convenient way of identifying the various SnapTV units in a network. The
hostname is always shown in the web interface and at the console, so that one can know
which unit is being configured. The server should come with a sensible default hostname
based on the order documents, but it is possible to change if the default does not suit you. We
recommend using the following syntax for the host name:
<unit-type>-<location><number>
E.g.: snapreceiver-myhotel01
The hostname is stored in the file /etc/hostname. The syntax is:
<hostname>
E.g.: snapreceiver-myhotel01
8 Chapter 2. Getting started

CHAPTER 3
Accessing the web interface
Administration of the SnapTV units is primarily done through the web interface available on the
unit. Now that we have done the basics in a terminal window, we can move on and set up the
rest of the services. There are still some things that can only be done in a terminal. These are
described in chapter 11.
To access the web interface:
Open a web browser from a computer in the network and point it to the IP address of your
SnapTV unit. (e.g.: http://10.0.0.5) and log in to the web interface using the username and
password from the factory settings sheet or the password you set during installation. If you
changed the password for the admin user as described in Creating admin user for accessing
the web interface, use this password instead.
3.1 Getting started continued
The first things you want to do in the web interface is the following:
• Setting time zone, see section Set time zone
9

CHAPTER 4
Software upgrade
4.1 About Software Upgrades
If your system is connected to the Internet, new software updates will be available regularly.
We recommend updating the system to the latest version before it is put to use.
The server operating system is based on Ubuntu 12.04 LTS (Long Term Support) a debian
based Linux distribution sponsored by Canonical Ltd. Software updates are downloaded from
an online service by SnapTV, while some security patches will be downloaded directly from
Canonical servers.
It is recommended to backup your configuration before upgrading your system.
The upgrade will typically take only a few minutes and there is usually no need to reboot the
system after the upgrade. You might experience minor disturbances to TV signals, recording
and other services during software upgrade.
4.2 Upgrade using Web Interface
• Click on System information and Software upgrade
• Press the Check for updates button
• Press the Upgrade now button to upgrade your system
11

System Installation Guide, Release 2.3.0
If you get error messages or experience other problems during upgrade, please try upgrading
using the terminal or contact SnapTV support.
4.3 Upgrade using the terminal
The SnapTV server uses Aptitude to keep software up to date. Log into the server using ssh
or use an attached keyboard and monitor.
First update the list of available updates:
~# sudo aptitude update
Start the upgrade:
~# sudo aptitude dist-upgrade
Note: See the Operation And Maintenance Guide for a description of advanced up-
grade methods.
12 Chapter 4. Software upgrade

CHAPTER 5
Manage inputs
In this section we will explain how to connect various input sources and configure them to
become TV channels.
5.1 Numbering of the input sources
The input devices will be identified by an port identifier like for instance 9:1 or 5:a-1. The
number before the colon is the slot number which has the range 1 to 12. The number or string
after the colon distinguishes between multiple functionality of the same slot. dvb-s2-cards have
two fully independent ports. They are identified from the bottom of the slot. The slot positions
at the back of the cabinet is shown in the figure.
5.2 Satellite connection
Each DVB-S/S2 input card has two standard F connectors. Each input connector can be
configured individually with regard to selecting band/polarity and up to four different satellite
positions using DiSEqC multiswitches.
13

System Installation Guide, Release 2.3.0
5.3 Terrestrial and Cable connection
Each DVB-T/DVB-C input has a standard IEC 169 connector (also called Belling-Lee or TV
Aerial Plug). The connector at the top is for antenna input to both DVB-T/DVB-C tuners of the
two port input card. The bottom connector is a loop through connector.
5.4 CA modules
All DVB-CI ports will be visible in the input page and identified like x:ci-y, where x is a slot num-
ber and y the Common Interface port number within the slot. The CI ports may be accessable
from the back of the cabinet or the front of the MAXI cabinet. A CI port can be connected to
any transponder. To ease operation, there is a default setup. When tuning a transponder, the
nearest neighbour CI is auto connected if available, limited to the same slot or the next slot.
When there is a link between an input transponder and a CI port, an associated CAM will be
able to descramble pay TV channels. Most EN 50 221 compatible CA modules may be used,
but ask your sales contact for verification whether a given module type works.
14 Chapter 5. Manage inputs

System Installation Guide, Release 2.3.0
Insert your program card into the CAM and then insert the CAM into its port. Note that it may
take some time from the channel is first tuned until it works as expected when the program
card is new or have been unused for a while.
All reconfiguration of transponders to CI ports can be done in via the tuning page.
5.5 Analog sources
Each analog input slot has a number of different connectors, but only one video and one audio
can be used at once. The inputs normally available are stereo RCA audio connectors, S-video,
5.5. Analog sources 15
This manual suits for next models
4
Table of contents
Other SnapTV Server manuals
Popular Server manuals by other brands

Supermicro
Supermicro X5DPR-iG2 Plus Specifications

Alcatel-Lucent
Alcatel-Lucent 9130 BSC Evolution Maintenance handbook

Lenovo
Lenovo ThinkServer TS430 warranty and support information

Lenovo
Lenovo ThinkSERVER TS130 warranty and support information
Sonnet
Sonnet XMac Pro server user guide

7starlake
7starlake SCH-401 user manual