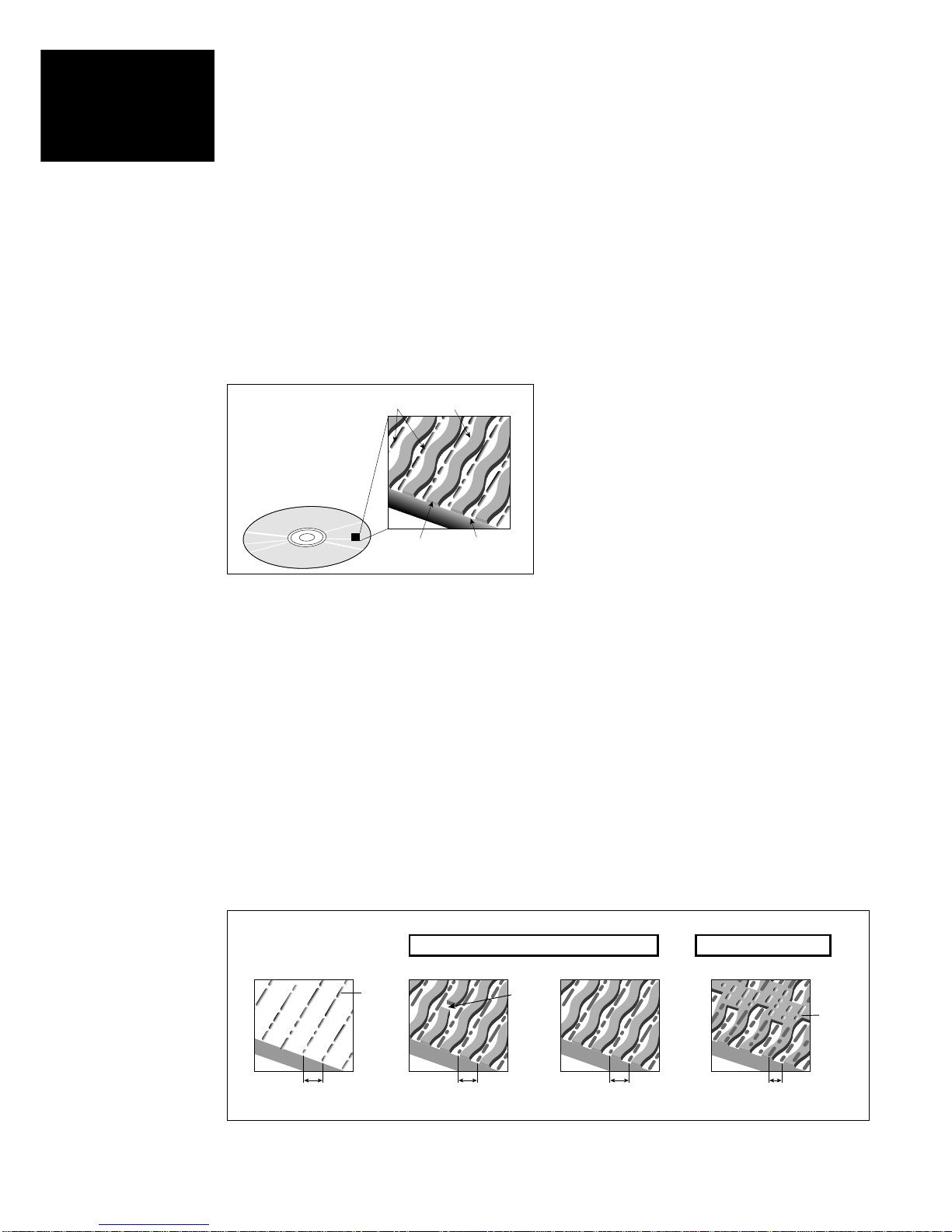
The Logical Format
The logical format is essentially the ‘file system’ used when
making a DVD recording. Data on hard discs, floppy discs, CD
ROM, and DVD ROM is recorded as ‘0’ and ‘1’ bit stream data.
This bit stream data is grouped in meaningful collections called
files, allowing the user to perform such operations as reading and
editing of this data by managing it through some type of file
system. The file system will vary depending upon the recording
media and the application. The following is an explanation of
some examples of specified file systems (file formats) used in
DVD.
■ UDF (Universal Disk Format)
This is a universally adopted file format proposed by OSTA*.
UDF is primarily intended for DVD, the specifications were
based on the concept of allowing the exchange of data between
other operating systems, including the common use of data
among various types of optical storage.
◆ UDF Version 1.02
This is a file format used for the DVD Video format. It is used to
enable playback compatibility of re recordable DVD.
◆ UDF Version 2.00
This is used in the DVD Video Recording format, a real time
video recording application format established by the DVD
Forum. It enables random write and read, as well as swapping
processing, so that the media can be used just like a floppy or
MO disc.
*The Optical Storage Technology Association is a group that has
established a worldwide standard file format for optical storage
applications.
■ ISO-9660
This universal file format is used in almost all CD ROM discs.
Its original form was the High Sierra format proposed by Apple,
DEC, Microsoft, Philips, Sony and other companies in 1986.
Later, ISO recognized this as a worldwide standard specification.
■ UDF Bridge
This format provides the access procedure for both ISO 9660
and the UDF Version 1.02, which is a logical format, created for
playback only discs. By adopting the access procedure for ISO
9660, a widely used file format for CD ROM, DVD discs can
even be used on systems, which do not support UDF.
The Application Format
DVD stands for “Digital Versatile Disc,” and as its name implies,
it can be used not only for moving video and sound, but also for
storing digital data. The various application formats have been
given detailed specifications to enable their respective
applications. For example, the DVD Video format was originally
established as an application format to record movies for
playback only. In addition, for music there is also the DVD
Audio format. DVD functions – what you can actually do and
what you can't do – vary greatly according to the application
format. The following is an explanation of three application
formats, which are presently used in DVD recording.
■ DVD-Video format
The DVD Video format was the first application format
established for ROM use in the DVD family. The objective of
establishing this format was to enable a single movie to be
recorded on a disc with high quality images and sound. Thus,
this format was used to enable commercial DVD Video software,
which could be played back on DVD players and other DVD
associated equipment. The MPEG2 digital coding format is used
to compress the video images, thereby achieving a resolution of
approximately 500 horizontal TV lines for a superior quality
image. In addition to linear PCM audio, other formats are also
used, such as the Dolby Digital format, which can offer up to 5.1
channels of surround sound. This enables the playback of
powerful soundtracks with a realistic soundstage and imaging.
Along with high quality images and sound there are a number of
interactive functions possible, for example, multi lingual, multi
story and multi angle features.
While this DVD Video format was originally established for
playback only discs, it is now also used as an application format
for DVD RW and DVD R recording in home use DVD
recorders. In this case, the biggest advantage is high
compatibility with legacy DVD players. This comes as no
surprise since this is the original playback format for DVD
players. However, it should be noted that at the stage during
recording (i.e. the un finalized condition), the data writing
required for playback of the DVD Video format may not be
complete. Therefore, in order to assure playback on other DVD
players, the finalization operation must then be performed.
■ DVD+RW Video format
The DVD+RW Video format, was established by Philips for
recording moving video content. Primarily in the PC application
field, this format is also called the “+VR” format. Essentially, the
DVD+RW format enables playback compatibility between
existing DVD players and DVD drives in personal computers. Its
biggest advantages are real time recording, additional recording
and re recording capabilities. Moreover, finalization, which
records a lead out to indicate the end of the data on the disc, has
been specified as automatic, so it does not need to be performed
by the user. Thanks to this feature, the disc taken directly out of
Chapter 2
Features of Recordable
DVD Formats
RDR GX7 Technical Notes