ST Robotics ATHENA User manual

R19 robot manual page 1
R19man.doc 2021-01-11
ATHENA
R19 ROBOT SYSTEM
User manual

R19 robot manual page 2
System Components
A basic R19 robot system comprises the following -
1 R19 Robot arm
fitted with any options
Electric or pneumatic gripper
Quickstop sensor
Tool changer
1 Optional track
1 Controller K11R
1 Teach box
1 Cable 9-way D-type each end (M-M) - K11R to teach box
1 Motor cable - K11R MS connector to robot 25-way D-type
or for track, MS connector to track MS connector.
1 Sensor and encoder cable - 25-way each end (M-F)
1 Cable, D-type 25-way male to 9-way female - K11R to PC RS232
or USB converter, K11R to PC USB.
1 Power cable to K11R
1 Pack of CONNECTORS
1 output connector (unless already used for gripper)
1 input connector
1 stop circuit jack
1 Disk or USB drive with software and manuals.
1 optional USB/serial adaptor
1optional gripper pneumatics kit
1optional Quickstop pneumatics kit

R19 robot manual page 3
1. INTRODUCTION
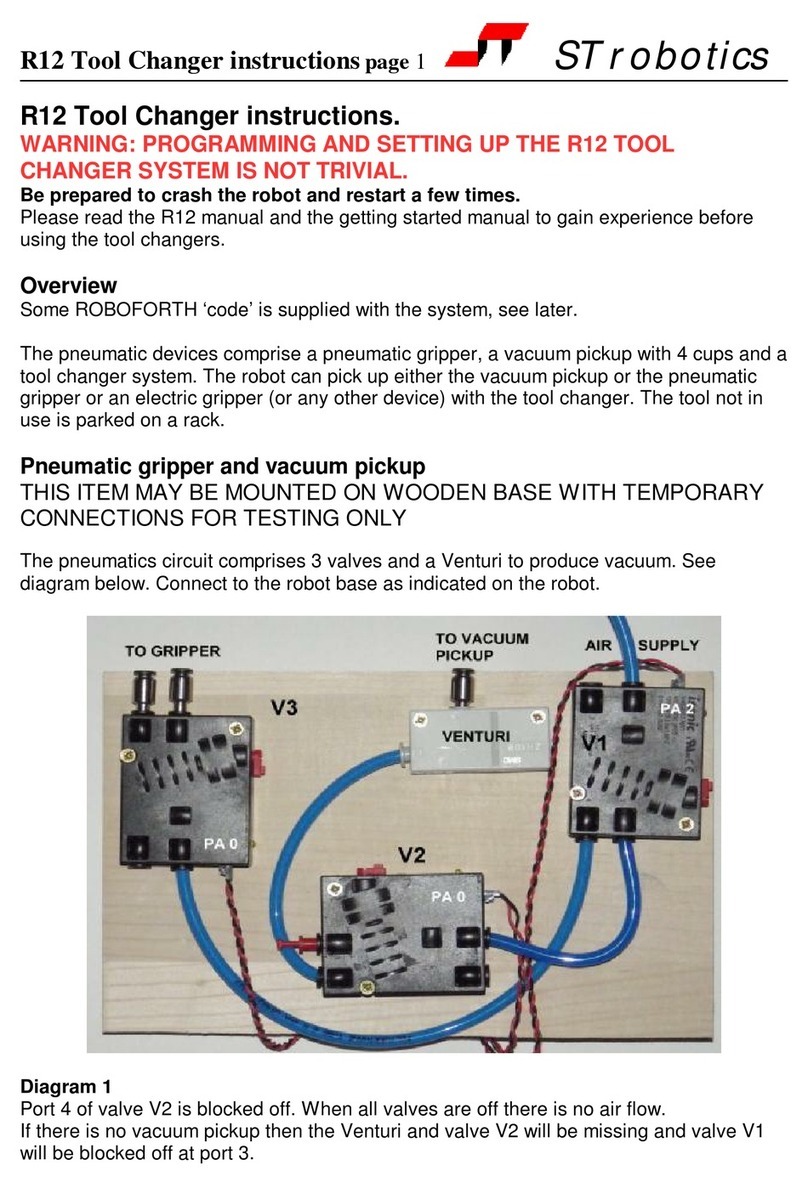
The R19, ATHENA is a robot arm of the cylindrical format i.e. its workspace is cylindrical.
It is hi hly suitable for bench top handlin and is more accurate than other formats.
Athena has a nominal reach of 550mm. Athena is driven by steppin motors controlled by
intelli ent micro-steppin MOS power drives with incremental encoder feedback. A choice
of rippers is available: pneumatic or electric. If fitted the pneumatic ripper is operated by
compressed air from 5 to 7 bar. This may be supplied by a compressor supplied with the
kit, or from another air supply.
The R19 robot system comprises 3 main units:- the robot, the controller, the computer or
terminal. The computer is used to pro ram the controller. Once pro rammed the controller
will run the robot independently without the need for the terminal or computer but it is a
ood idea to have a low cost terminal connected while the robot is in use.
OVERVIEW
All movement of the robot is controlled by the controller. As the controller may be both
readin sensors and si nals from and controllin associated equipment it follows that all
decisions about robot activity are usually made by the controller which is capable of
runnin without any host computer. The function of the computer is to (a) pro ram the
controller, (b) to copy (back up) the contents of controller RAM to disk and optionally (c) to
perform a supervisory role sendin commands to the controller throu h the RS232
interface. The function of a terminal is to display information or questions and for the
operator to enter answers or commands (e. . part type selection).
To pro ram the controller with a computer you need to run the utility ROBWIN.EXE.
When ROBWIN is executed it immediately opens a communications window. Once
communication is established all your commands o to the controller not to the computer
you are typin on. Pro rammin the controller involves pro rammin the robot and the
interaction with other equipment. The robot and interfacin are pro rammed usin
ROBOFORTH II © and FORTH. There are two HTML manuals, ROBOFORTH coverin
robot pro rammin and the system manual, which describes the controller and interfacin .
You can use the dynamic links to see connected concepts. There is also a lossary on
disk, which ives a brief description of every command. Some commands are used only
by ROBWIN or are not very useful and these are in the lossary but not in the
ROBOFORTH manual. In particular you should start off with the “ ettin started” manual
which is a pdf.
All FORTH and ROBOFORTH commands are in UPPER CASE (press caps lock). You
can add commands written in lower case but these would be different
commands from those spelled in upper case.
© RoboForth is copyri ht David N Sands

R19 robot manual page 4
2. IMPORTANT DOS AND DON'TS
(1) DON'T ever disconnect or connect the robot while the controller is switched on. This
will result in dama e to the electronics and the connectors themselves. Warranty claims
will not be accepted for dama e resultin from this.
(2) DON'T back-drive the 5th axis if fitted. It can dama e the earbox. Actually you can
backdrive it very slowly if the robot is dosconnected but be very careful.
(3) DO be very careful not to "crash" i.e. drive any joint a ainst a solid object so that it
stalls. Dependin on the speed dama e may result. At lower speeds the motors enerate
hi her torques so can do more dama e. DON'T drive the waist a ainst the stop.
(4) For the above reason DON’T use CALIBRATE unless you are sure the robot will not
crash into somethin in the workspace.
(5) DON'T use CALIBRATE unless you are sure the robot is in the valid position for
calibration includin takin into account any complex end effector fitted.
(6) DO have your hand poised over the emer ency stop button whenever testin a
pro ram. Remember that because of its eometry the arm may describe wide arcs from
far apart points, and may collide with objects within its reach.
(7) DO make a back-up of the computer disk supplied as soon as possible.

R19 robot manual page 5
SAFETY IS YOUR RESPONSIBILITY
Risks
Because steppin motors raise more torque at low speeds a substantial low speed force
can be brou ht to bear especially on fin ers, which may become trapped under or
between axes. Robot end effectors typically have sharp ed es or fin ers made of thin
metal, which can cause injury at the low speed hi h forces or at the hi her speeds.
The bi est risk comes from the element of surprise. If the system is active and receives
a command from a supervisin scheduler or a si nal from an associated machine the
robot will appear to move unpredictably. A human bein cau ht in the way can receive
injury.
However, because the robot is stepper motor driven, once stalled the system raises an
error and does not attempt further motion.
Safet measures
Where possible a robot system should be uarded. Any ate in the uardin can
be fitted with a switch, which is connected to the controller stop circuit.
If physical uards cannot be provided then li ht curtains are easily connected to the
robot controller
Where uardin is not appropriate and bench-top robots work closely with human
workers interlocks should be provided. For example if the user has access to the
workspace then he/she should be required to press a switch or keyboard key after
clearin the area.
A ood rule is that the robot should not be allowed to move outside an area
desi nated by the ed e of the bench on which it is mounted.
As an additional precaution the workin area should be marked out with painted
lines or black/yellow striped tape.
Statistically the hi hest incidence of contention between human and robot is when
both are accessin the same object. End effectors often have sharp ed es, which
can cause injury. This hazard can be minimized by fittin a collision sensor.
At the end of this manual you will find a form with which to do your own risk
assessment of the robot in your application. There are two concepts to consider:
hazard, which is the robot or robot fin ers or the product etc. and risk, which is the
probability of someone bein harmed by the hazard. The form enables you to
identify the hazards, the risks and ways of minimizin the risks. After completin
the form and carryin out any safety measures that the form has helped you
identify, do the assessment all over a ain.

R19 robot manual page 6
3. SETTING UP
Assembl :
The robot is packed with the extend axis (with hand) separated from the lift axis (with
waist). They are connected with a permanent cable hose.
1. Set the robot up in the desired location.
2. Remove all from the case. Place the waist unit on a level surface with the lift axis
vertical.
3. You can see where the extend axis carria e plate mounts to the lift axis carria e plate
with 4 holes. Offer the extend axis up to the lift axis with the slot and the carria e plate
uppermost.
4. Line up the 4 holes and insert the 4 screws provided. Make sure the steel cones are
between the axes. Use nuts and washers accordin to this dia ram.
5. Ti hten the four screws. An Allen key (wrench) and 8mm spanner (wrench) are
provided.
6. Make sure the robot is bolted down so it can’t slip or fall over. Rotate the waist by hand
to feel out the limits of rotation and set the waist in it’s mid position
Assembl to track
7. Mount the robot on to the track carria e plate. Orient it so that the connector plate of
the robot should be nearest to the drive box of the track. Use the four lar e bolts provided
with flat washers under the heads. Ti hten usin the Allen key (wrench) provided.
8. Connect the two cables which emer e from the track on to the connectors at the read
of the robot arm.

R19 robot manual page 7
Setting up for use
Connect up all cables - their positions should be self-evident. Cables to the robot connect
to the rear of the controller.
There are 5 basic cables:
Motor power – the metalized cable from rear of controller to robot base, 26wMS to
26wMS.
When there is a track this cable oes to the connector plate of the track.
Sensor cable – from rear of controller to robot base (25wD male to 25wD female)
When there is a track this cable is doubled i.e. two cables end to end for extra len th.
Connect it to the 25-w D connector on the end of the track.
Gripper cable (if supplied) - from rear of controller to ripper valve (9wD to DIN)
Serial cable – from front of controller to computer (usually 25wD male to 9wD fem) or
USB adaptor.
Teach pad cable – from front of controller to teach pad (9wD to 9wD male to male).
There is also a Stop Jack for connectin an external stop circuit. Even if there is no
external stop circuit the jackplu must be plu ed in at the rear of the controller. The plu
has a shortin link, which is removed when connectin an external circuit.
The serial (RS232 null modem) cable from a computer to the controller should plu into
the 25-way D connector on the front of the controller. The other end (usually 9wD)
connects to the rear COM1 serial connector of the computer. If COM1 is already in use
you can use any COM port or the USB serial adaptor (usually COM3). The serial speed is
19200 Baud, 8 bits, 1 stop bit.
DOS utilities only work with COM1.
Pneumatic connections
Connect the air line by pushin it into the push-fit connectors on the air valve and two from
the valve to the rear of the robot. If there is no compressor supplied then connect the shop
air supply to the air valve. The air supply must have a bowl filter and a pressure re ulator.
Pneumatic gripper or vacuum pickup
If a pneumatic ripper or vacuum pickup is fitted the robot will have two airlines fitted
throu h it, emer in on the forearm on two push-fit connectors. Two external lines
loop to the ripper/vacuum pickup. The control valve is usually external. The valve is
controlled from port PA bit 0.
The pneumatic ripper or vacuum is optionally fitted with a sensor to detect if the ripper
is holdin an object or has closed completely without an object or if there is no
vacuum because no object is held.. This sensor usually connects to port PB bit 5.
Electric gripper
If the electric ripper is fitted this is wired throu h the robot and requires no installation by
the customer. The ripper is controlled from port PA bit 0. Therefore you can not use
this output line for any other purpose.

R19 robot manual page 8
Pneumatic Gripper connections
Programming the confirmation sensor.
The confirmation sensor is normally connected to PB 5. There is a RoboForth word
GRIPCHECK which checks to see that the ripper has closed on a part. This is best
used after the robot has withdrawn from the active area, for example insert this word
at a suitable place for the robot to check it has a valid pick e. .
JIG GRIP WITHDRAW GRIPCHECK
Adjusting the optional grip sensor.
It has already been set at the factory but should it require further adjustment proceed as
follows. Disconnect the air supply so you can move the ripper jaws by hand.
1. Type PP to display the input port. You should see 11111111
2. As you close the jaws you should see the sensor o from 11111111 to 11011111 and
back to 11111111 a ain.
3. Put the object to be handled in the jaws and close the jaws by hand. The screen
should show 11011111
4. Adjust the sensor by slackenin the small screw on the side and slidin it up and down
the slot as necessary until you see the 11011111. The objective is that you only see
the zero on the object but with no object (jaws fully closed) or with the jaws fully open
the screen should show 11111111
If you wish to move the rip sensor to another port, for example to PB 7 then you can
patch the definition of GRIPSENSE. Check the existin value with
‘ GRIPSENSE 2+ ? (answer shoul be 5)
Patch with
7 ‘ GRIPSENSE 2+ !

R19 robot manual page 9
Vacuum pick-up connections:
Programming the vacuum sensor.
The vacuum switch is connected to PB 5. You can quickly check this with
GRIPCHECK
Insert this word at a suitable place for the robot to check it has a valid pick e. .
JIG GRIP WITHDRAW GRIPCHECK
If there is no vacuum (object not picked) you will et “Grip fail” error.
Adjusting the vacuum sensor.
It has already been set at the factory but should it require further adjustment proceed as
follows:
1. type GRIP (remember that this consumes a reat deal of air and you may need to
UNGRIP then allow the compressor to rechar e before tryin a ain.
2. Type PP to display the input port. You should see 11111111
3. Adjust the sensor usin the 1.5mm Allen key supplied until you see 11011111 then
back off a ain until you see 11111111.
4. Cover the vacuum cups and the display should chan e back to 11011111

R19 robot manual page 10
4. COMPUTER
Note: Commands to computer or controller are in the form of a strin of characters
followed by the enter key. In all my examples of dialo between man and machine I will
underline text typed in by the user. I won't keep mentionin the need for the enter key. A
machine response will be in upper case but not underlined. My comments will be in lower
case.
Before switchin on the controller switch on the terminal or computer and proceed as
follows:-
WINDOWS
1. Create a directory (folder) ROBOT on C: drive
2. Copy all the files to your ROBOT directory
3. If you have a USB-serial converter first install its software. It should install itself.
4. Plu in the USB converter and use either the serial cable or the adaptor to connect
to the controller. Windows 7 will probably want to o online for the drivers, select
skip for both drivers, USB serial converter and USB serial port. Once installed it
should tell you what port number it has selected. If less than 10 then skip step 5.
5. Go to control panel, system, hardware, device mana er, ports. You will see USB
serial port - note the port COM number.
6. RobWin will only work up to com9 so if your converter has been mapped to hi her
than com9 then double-click that port, then o to settin s, advanced. You will see
COM Port Number click the drop-down. You will see a lot of COM ports marked "in
use". It's not so. Pick com3 anyway (or up to 9 as indicated in the device mana er).
It will say it's in use do you want to continue, click Yes.
Whatever com number you choose, make a note. When you run RobWin7 click
comm at the top, then confi ure and make that the same number.
7. Find robwin7.1.20.msi (or later) and install RobWin 7. You may also use earlier
versions robwin6x.exe on the CD
8. Double-click robwin.exe to run.
9. RobWin defaults to COM1. If you need to chan e the port number (for USB port,
see step 5) click Comm, confi ure. Baud rate should be 19200
10.Click Settin s, Open file then enter R19.cf
Also click settin s > joint names and settin s > Cartesian axes and make sure both are
set to 4. For the 5-axis version set them to 5. See RobWin7 manual for more information.
You are now ready to use RobWin7
Note:
If usin RobWin6 please ensure that in settin s, confi uration, bank memory is checked.

R19 robot manual page 11
5. POWERING UP THE CONTROLLER
To power up the controller, connect the power cord at the rear and operate the power
switch, which is inte ral with the power connector. You may have all other cables
disconnected if you wish. However be sure to turn off the power before you connect any
rear cable, especially the motor cable. When power is switched on the front TX li ht
should flash which means it has sent the openin messa e to the computer, which you
should see, in the communications window of ROBWIN. If the li ht flashes but nothin
appears on the screen then this indicates a problem with the computer. Try clickin
comms and select another COM port. If you have a USB-serial converter make sure the
COM port selected matches the port shown in the device mana er. Also make sure the
baud rate is 19200.
The Mk5 controller utilizes the EZ80L92 microprocessor with Flash ROM and static RAM
on the same PCB. Cold/warm/start selection is a front panel key switch. The memory
ima e is in flash ROM which is loaded to RAM when you power up (or press reset). When
powerin up for the first time select COLD start before you switch on. You will see a
herald on screen that should include the words COLD START.
Front panel designations:
Fail: indicates power supply problem e. . low mains volta e. When power is turned on it
stays lit until power supply is secure. Also li hts when reset is pressed.
OK: opposite of fail, indicates ood power supply.
TX: li hts when serial data is passin from controller to computer
RX: li hts when serial data is passin from computer to controller
STOP: stops robot motion (provided CPU is in control – see software manual)
RESET: resets CPU, DSP and other lo ic.
TEACH: teach pad input
COLD/WARM/AUTO switch – selects start-up mode when power is turned on or reset is
pressed. (see section 7)
RS232 – connects to computer.

R19 robot manual page 12
If there is no messa e on screen press the reset button on the front panel and watch the
li hts. The red led should li ht as you press the button. As you release the button the red
led oes out, the reen li ht comes on and the yellow TX li ht should flash. If it flashes
the controller has sent characters up to the computer. Check the screen. If there is
nothin there check com port and baud rate.
Assumin you have the herald press the enter key and you should see
> OK
Press caps lock and you should now be able to type commands into the communications
window, for example START
Rear Fuses
Viewed from the rear of the controller from ri ht to left:
Power connector has 2 fuses. These should be 6.5A anti-sur e for 110v power and 3.5A
ant-sur e for 220-240 power.
12v unre ulated DC fuse. This should be 3 amp quick blow. The 5v lo ic (and lower) all
comes from the 12v re ulated supply so if this fuse blows the whole controller is dead.
This supply emer es from the 9 way input and 15 way output connectors for users
sensors etc so if you are blowin 12v fuses the fault would be there.
24v unre ulated DC fuse. 24v is an alternative for users external circuitry as most
industrial contactors etc are all 24v DC. Pneumatic valves can be 12v or 24v.
Also on the rear panel is a jack plu . This is for the external stop circuit and has it’s
terminals linked inside the plu . If the jack plu is removed the robot will not run.

R19 robot manual page 13
6. PREPARING FOR USE
1. Now switch off the controller and wait 10 seconds. Connect up the sensor/encoder
cable to the robot – this is the cable with a 25w D each end. Do not connect the screened
(braided sheath) cable at this time. Switch on the controller.
2. Enter the followin :
ROBOFORTH <enter>
This invokes the RoboForth dictionary. This is only necessary after a cold start and you
need to type it every time you switch on with the key set to ‘cold’.
START <enter>
ENCTEST <enter>
A row of numbers appears. As you move each joint by hand the numbers will chan e.
This shows the encoders are workin . Press escape key to exit this mode.
3. Enter PP <enter>
A row of 1s and 0s appears. Initially this should be 11111111
These represent the calibration sensors on the robot. Set the robot up in an approximate
home position, which is with the arms bolt upri ht. From ri ht to left the di its are: waist,
shoulder, elbow, left hand, wrist.
4. Now move the joints 1 – 4 very slowly towards the sensors. Don't move axis 5. You
should find these with the lift fully up, extend fully extended and waist a few de rees
CCW/ACW.
For example if you move the waist counter-clockwise to its sensor you will see:
11111111 chan e to 11111110 then back to 11111111
Press escape to exit the PP command.
5. You are now ready to connect the motors. SWITCH OFF THE POWER FIRST and wait
10 seconds before connectin the motor cable from controller to robot.

R19 robot manual page 14
7. GETTING STARTED
WARNING
Before tr ing an of the following commands be sure to
KEEP OUT OF THE ROBOT ENVELOPE
Note: ALL FORTH and ROBOFORTH COMMANDS ARE IN UPPER CASE.
Assumin ROBWIN is loaded and runnin :
1. Press caps lock and you should now be able to type ROBOFORTH commands into the
communications window.
2. Type
ROBOFORTH <enter>
(if the key was set to ‘cold’)
3. In the communications window type
START <enter> or click the button
A herald will appear announcin ROBOFORTH and it’s version.
Even thou h you have not yet calibrated the arm you can check out the axes with the
teach pad.
4. To start movin the arm click the button or type
TEACH then press <enter> two times. I nore any “FN=” messa e.
The red “TEACH” and reen “ON” li hts should be on.
With this method pressin a key on the teach box moves the arm. Since you mi ht let o
of the key at any time and expect the robot to stop it is not possible to accelerate to hi h
speed. Moreover a slow speed is more desirable to achieve precision, and the teach
speed is determined by the value of CREEP-FACTOR, which is requested after you enter
TEACH. At this sta e just hit the return key.
After enterin TEACH you are now in "TEACH mode". To move the arm first select the
joint to move, J1 for waist, J2 for lift, J3 for extend, J4 for hand or wrist pitch, J5 for track
or wrist roll. On selectin a joint the terminal/computer will beep. Then press either + or -
for motion in a positive or ne ative direction. To test the ripper press the key marked
'GRIP', then to close the ripper press the + key and to open the ripper press the - key.
Do not try other keys for the moment. Use TEACH mode to test all the joints and finally
drive the robot to an approximate home position. Exit TEACH mode by pressin the
escape (ESC) key on the terminal.

R19 robot manual page 15
7. continued
Next the robot should be calibrated. Before tryin the CALIBRATE feature check as many
of the five proximity detectors as you can as follows:
First un-power the arm with
DE-ENERGISE or DE-ENERGIZE
Next display the sensors with:
PP
A row of 1s will appear on the screen thus:
11111111
This is a binary representation of the sensor input port. Hold a steel item a ainst the waist
sensor (which is visible just under the skirt) and the least si nificant di it should chan e to
zero
11111110
The next di it is the lift sensor,
11111101
Next the extend sensor, next the hand sensor then wrist twist sensor. Only the waist
sensor is accessible on the R19 but the other sensors can be checked by movin the
joints by hand - move shoulder ne ative and move elbow positive. Press ESC to exit PP
function then type
START
Use TEACH mode a ain to set an approximate home position then press escape (ESC
key). If the proximity detectors checked out OK then enter:
CALIBRATE
which drives all the joints to the proximity detectors and corrects the motor and encoder
counts
It is possible that the lift axis will not calibrate in one o and you need to repeat the
command. It is worth typin
TELL LIFT 8000 MOVE
then
CALIBRATE
HOME
drives the whole arm to the calibrated HOME position.
Track
The track appears as a 5th axis. It should calibrate alon with the other axes.
You can calibrate the track alone like this:
TELL TRACK REVERSE DATUM
then
LIMITS 8 + @ 4 GLOBALS ! ENCSET
If the calibrate count for the track is zero then just enter
TELL TRACK REVERSE DATUM
SETHOME

R19 robot manual page 16
8. CONTROLLER SETTINGS
Changing default values
All the robot parameters revert to their ori inal values when the controller is powered up or
the reset is pressed. To make these values permanent you need to write them to flash
ROM with the command
PSAVE
Be very sure you have not made a mistake before you use this command because if the
flash ROM is corrupted it is very difficult to recover (see below).
FLASH ROM
Cold start mode
When power is switched on, or the reset button is pressed all RAM contents are refreshed
from flash ROM. All the user pro rammin , whether entered in immediate mode or usin
ROBWIN will be lost.
After you see the herald and the words ‘cold start’ enter
ROBOFORTH
Warm start mode
If power oes off/on or the reset button is pressed all RAM contents are refreshed from
flash ROM includin the user pro ram area. Therefore your user pro ram will be over-
written with any older pro ram previously saved. To ensure that the new pro ram is
reloaded after a power-up or reset type the command
USAVE
Or click USAVE in ROBWIN.
If you for et to do this and accidentally lose power or press reset (or are forced to press
reset because of a bu ) then in ROBWIN save the project and re-open it.
Changing default values
All the robot parameters revert to their ori inal values when the controller is powered up or
the reset is pressed. If you wish to chan e any values and make them permanent there
are commands to write memory back to flash – see software manuals.

R19 robot manual page 17
9. ROBOT PARAMETERS
WARNING – there should be no reason to alter these constants unless some
change has been made to the robot.
These parameters are particular to your robot, sometimes called a ‘si nature’. They are
embedded into the ROBOFORTH, which is in protected memory.
RAM memory is loaded from flash ROM on each power-up or reset. If you chan e
somethin you will need to update the flash ROM so test thorou hly before you do this.
If you are supplied with a new version of ROBOFORTH you will need to transfer the
parameters to a disk file, load the new ROBOFORTH as described above then overlay the
parameters file.
To save the parameters (signature)
1. Click file – save binary. Chan e parameters to start 9C00, len th 100 (bank should
be 0).
2. Save as e. . R19D123.SIG – this is the serial number of the robot. The actual
filename will be R19D123.SIG.ram
3. Enter PSAVE to save to the flash ROM.
To reload (overla ) the parameters.
1. Click file – load binary. Chan e parameters to start 9C00, len th 100 (bank should
be 0).
2. Choose file name you used to save above.
3. When loaded enter PSAVE to save the new ROBOFORTH and the overlaid
parameters to flash ROM.

R19 robot manual page 18
10 CALIBRATION
When the robot calibrates it seeks out proximity detectors on each axis and corrects the
counts to values seen in the array LIMITS which you can view with VIEW LIMITS
You can, if absolutely necessary, chan e these values by directly addressin the element
in the array, for example to chan e the value for the waist enter
(new value) LIMITS ! for the waist (that last character is the exclamation mark and it
means ‘store the value’)
(new value) LIMITS 2 + ! for the lift axis
(new value) LIMITS 4 + ! for the extend
(new value) LIMITS 6 + ! for the hand
Next time you power up or press reset these value will revert to the ori inal.
The accuracy of these fi ures affects the home position, and is particularly important in
Cartesian transformations i.e. calculations of joint positions from Cartesian coordinates. If
you wish to chan e these fi ures, for example if you reset or replaced a proximity
detector, then the values in LIMITS can be chan ed as described above and under
'calibration' in the ROBOFORTH II manual.
GEAR RATIOS
The followin constants are the numbers of motor half steps for 90 de rees of joint
movement:-
Joint: WAIST LIFT EXTEND WRIST(yaw)
Constant: B-RATIO L-RATIO E-RATIO W-RATIO
To print the current value enter
B-RATIO . (that last character is a full stop or dot and it means print)
Or L-RATIO . for the lift etc.
ENERGIZING CURRENT
Althou h the hi h power motors will accept 4.7 amps we ener ize at less for two reasons:-
(1) At low speeds the torque at the final drive can be very hi h so the reduced current
reduces this torque for safety. (2) At a certain low speeds the rotor of a steppin motor
can resonate resultin in vibration. This effect is eliminated by reducin the current. This
also reduces low speed torque, which can be dama in when mistakes are made.
IDEAL GECKO 203V MOTOR DRIVE CURRENT SETTINGS. RESISTOR VALS
AXIS
NO.
JOINT NAME LOGIC
CHAN.
AMPS RESISTOR
VALUE
MICRO-
STEP
SETTINGS
VALUE
OF
MICROS
1 WAIST 0 3.0 36k 10 4
2 LIFT 1 3.0 36k 10 4
3 EXTEND 2 2.5 27k 10 4
4 HAND 3 1.6 15k 10 4
5 TRACK 4 3.0 36k 10 4

R19 robot manual page 19
11. CONNECTIONS-R19
Connections to the rear panel are identical with the controller as follows:-
Robot Motor Drives (Ba onet) Sensor (datum) inputs (25wa D)
A motor 1 coil 1 1 sensor 1 (PB 0)
B motor 1 coil 1 2 sensor 2 (PB 1)
C motor 1 coil 2 3 sensor 3 (PB 2)
D motor 1 coil 2 4 sensor 4 (PB 3)
E motor 2 coil 1 5 sensor 5 (PB 4) ( track)
F motor 2 coil 1 6 encoder 1 up
G motor 2 coil 2 7 encoder 1 down
H motor 2 coil 2 8 encoder 2 up
J motor 3 coil 1 9 encoder 2 down
K motor 3 coil 1 10 encoder 3 up
L motor 3 coil 2 11 encoder 3 down
M motor 3 coil 2 12 encoder 4 up
N motor 4 coil 1 13 encoder 4 down
P motor 4 coil 1 14 encoder 5 up (track)
R motor 4 coil 2 15 encoder 5 down (track)
S motor 4 coil 2
T motor 5 coil 1 17 di ital 0volts (sensors)
U motor 5 coil 1 18 15-20v for sensors
V motor 5 coil 2 19 di . 0v (encoders)
round to robot
W motor 5 coil 2 20 +5v for encoders
X motor 6 coil 1 21 Grip feedback sensor (PB 5)
Y motor 6 coil 1 22
Z motor 6 coil 2 23
a motor 6 coil 2 24
b electric 25
c ripper
FCC declaration – please see certificate contained in the transit case.
CE declaration – please see certificate contained in the transit case.
The equipment conforms to:
2006/95/EC The Low Volta e Directive
2004/108/EEC The Electroma netic Compatibility Directive
CE technical file – please see appendix on the CD.

R19 robot manual page 20
RISK ASSESSMENT
This form must be completed by a competent Assessor for any procedure using the robot system before
an attempt is made at the procedure by any orker or visitor.
For further information on hazards and risks please refer to the section SAFETY IS YOUR
RESPONSIBILITY on page 5 of this manual.
Name and Status of the Assessor: Date:
Activity being assessed:
Kno n or expected hazards associated ith the activity:
The risk of injury and its severity likely to arise from these hazards:
Who is at risk?
Measure to be taken to reduce the level of risk:
Training prerequisites:
Level of risk remaining:
Emergency action:
References if any:
Signature of Assessor Revision date
This manual suits for next models
1
Table of contents
Other ST Robotics Robotics manuals