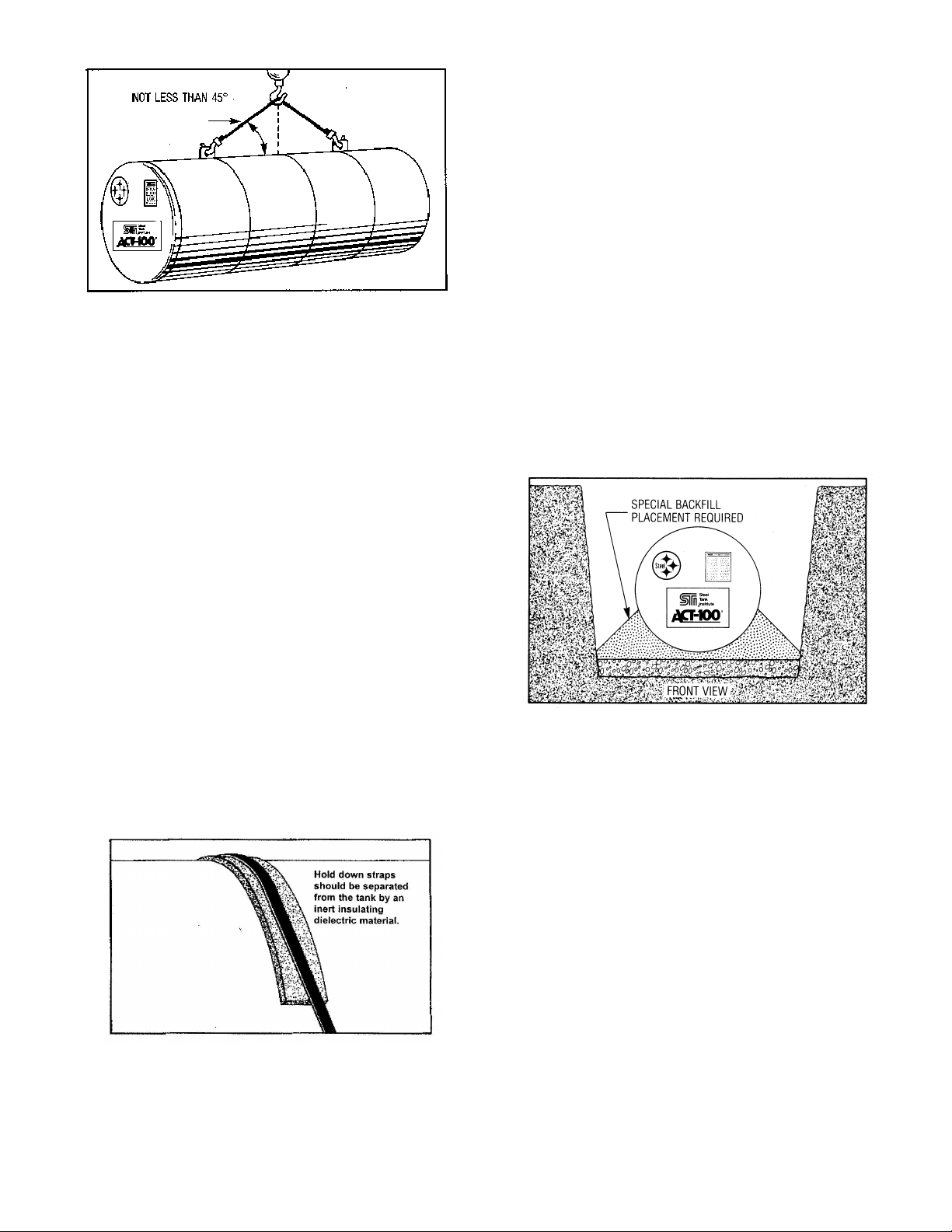
all other grounded electrical devices.
8.1.1 Prior to backfilling to top of tank, all openings
shall be visually inspected to assure that the
di-electric isolation (nylon bushings or flange
gaskets), where furnished, remains in place.
Where flanged openings have been used,
isolation of the flange gaskets shall be
confirmed with a continuity tester. Contact
with the tank shall be made with the inside of
the tank, or possibly at the lift lug, if steel is
exposed, prior to application of the lift lug
cover. No current shall pass through the
factory installed flange gaskets. Isolation of
the fittings is required to assure tank integrity.
8.2 If the tank is to be installed near an
impressed current system, the effect of the
system must be considered on the ACT-100®
tank. The corrosion consultant must consider
including the ACT-100®tank into the design
of the impressed current system.
9.0 SEALING OF PIPE CONNECTIONS,
LIFTING LUGS AND REPAIRS
9.1 Clean areas to be repaired through removal
of surface rust, dirt, contaminants, and
disbonded laminate. The laminate and
surface coat surrounding all holidays,
laminate flaw areas, lift lugs and/or exposed
steel areas shall be surface prepared by
using a coarse grit sandpaper or grinder.
(Refer to SSPC SP-2 "Hand Tool Cleaning"
or SP-3 "Power Tool Cleaning" for additional
guidance). This process shall remove all
glossiness from the surface surrounding the
repair area within 6 inches (152 mm) of the
holiday. Repair the area by using the repair
kit supplied by the manufacturer.
9.2 During the installation process, steel can
become exposed at the lift lugs due to
handling of the tank or at the interface
between the steel tank and either the nylon
bushing or gasket. These areas must be
repaired by one of the following methods.
9.2.1 A di-electric cap, if supplied by the
manufacturer, shall be placed over each lift lug.
First, prepare the surface of the tank to be
bonded to the cap in accordance with
paragraph 9.2. Apply the cap to the tank in
accordance with paragraph 9.2.1.1 or 9.2.1.2).
9.2.1.1 Place cap over lifting lug. Pre-mix resin with
catalyst and apply around the cap and the
tank surface immediately adjacent to the cap.
Bond the cap to the tank with two layers of
fiberglass mat previously saturated with resin.
Roll out all air bubbles and air pockets, or as
an alternative, see paragraph 9.2.1.2.
9.2.1.2 Pre-mix resin with filler material and catalyst.
Apply generously to tank surface at lift lug
and to bottom of FRP cap. Place cap over lift
lug. Apply additional resin with filler and
catalyst around edges of cap to seal. Allow to
cure.
9.2.2 As an alternative to Paragraph 9.2.1, exposed
steel at the lift lugs may be covered with the
laminate via the repair kit supplied by the
manufacturer.
9.2.2.1 Follow the manufacturer’s instructions given
in the repair kit.
9.3 After application, the installer shall verify that
the repair work has cured (adequate
material hardness and solidification) prior to
backfill.
9.4 After an air test has established tightness,
tank fittings shall receive a coat of resin prior
to backfill. (Refer to Section 9 for surface
preparation). Resin coating shall include the
entire plug on unused fittings.
9.5 Follow temperature guidelines supplied by the
manufacturer for proper catalyst/resin ratios
and recommendations. Ideally, exterior
temperature shall be within the 60-80oF (15.5-
26.6oC) range. Temperatures below 50oF
(10oC) shall require an external heat
source to enable a chemical reaction to
proceed.