37
GB USER AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL
Translation of the original instructions
Reproduction, for any purpose, of parts of the text or of the
drawings is prohibited without prior written consent from the
manufacturer.
WARNING concerning machinery
Consult carefully before installing the machinery.
WARNING concerning partly completed machinery
Consult carefully before incorporating the partly completed machinery.
When reading, omit information relative to parts that are not present.
Comply with all applicable general safety criteria, to guarantee safe use of
the machinery in which the partly completed machinery is incorporated.
IMPORTANT
Themachineryandpartlycompletedmachinerydescribed hereinmustonlybe
usedbypersonswithappropriateknowledgeoftheiruse.Theymustnotbeleft
in a place accessible to children or to persons that might use them in an
inappropriate and, consequently, potentially dangerous manner. They must be
used exclusively in compliance with the intended use declared by the
manufacturer and in compliance with the safety specifications indicated in this
manual.Theymustalwaysbesupervisedduringuse.
Chapter 9 and relative subchapters, printed in italics, contain information for
maintenance exclusively for use by qualified technicians and must be
performedusingappropriate personal protectiveequipment.
This manual describes the use of the pump in compliance with the design
specifications and illustrates the technical specifications, methods of
installation, use and maintenance and information concerning residual
risks related to use. The manual must be considered part of the pump and
be kept for future consultation for the entire useful life of the pump.
The manufacturer shall not be held responsible in cases of improper use
of the pump, use contrary to specific national regulations, installation not in
conformity with the declared specifications, faults in the power supply,
unauthorized modifications and operations, use of non-original spare parts
or parts not relative to the specific model, total or partial failure to comply
with the instructions indicated herein.
CONTENTS
1 – DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS USED - GLOSSARY ...................37
2 – USE OFTHE MACHINERY/PARTLYCOMPLETED MACHINERY......37
2.1 – Specifications of pumped liquid .............................................37
2.2 – Environment of use .................................................................38
3 – TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION............................................................38
3.1 – Specifications...........................................................................38
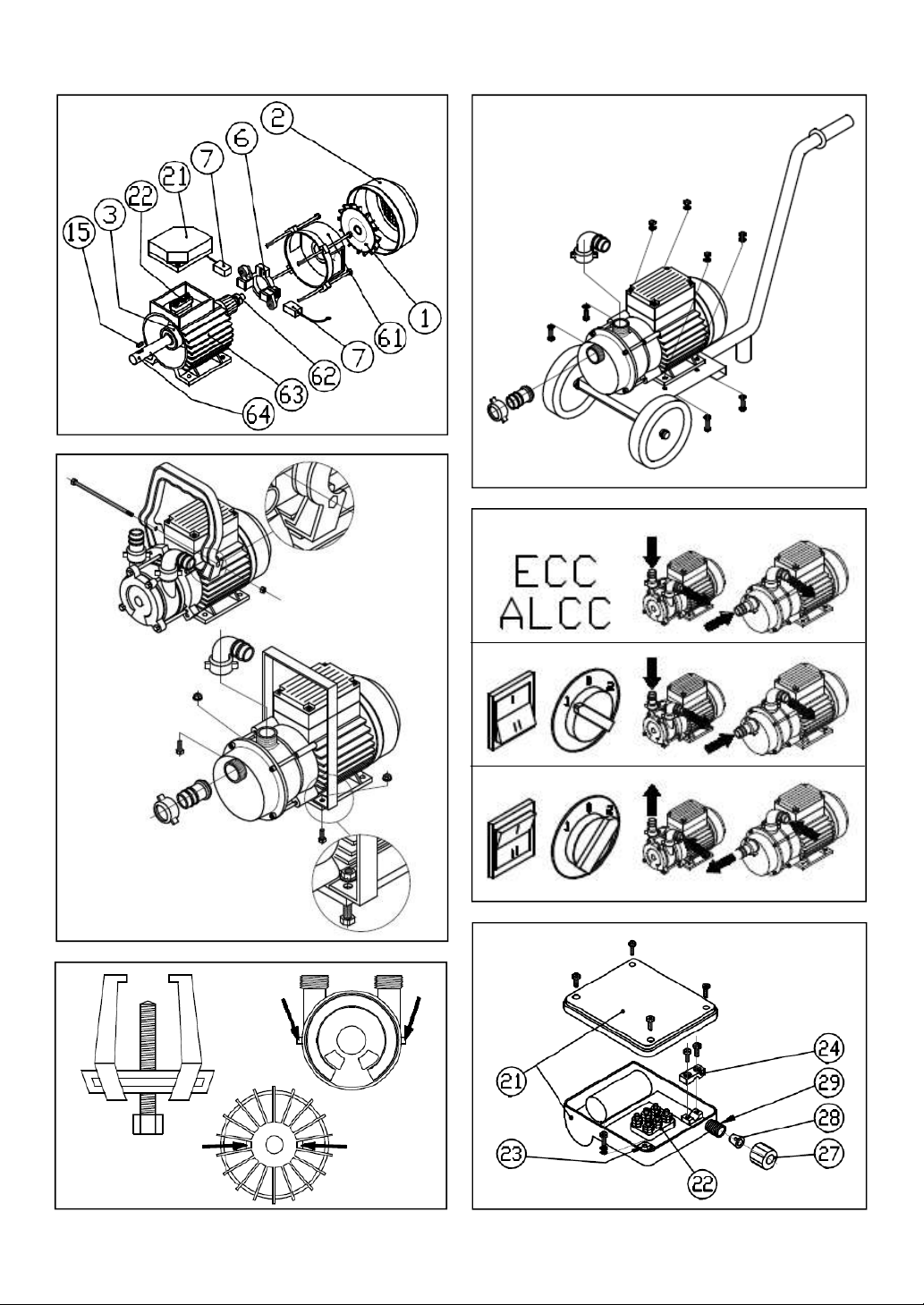
3.2 – List of components ..................................................................38
3.3 – Maximum priming height ........................................................39
3.4 – Pumping direction....................................................................39
3.5 – Shaft sealing devices ..............................................................39
3.6 – Optional accessories available ..............................................39
4 – INSTRUCTIONS FOR INSTALLATION AND USE .......................39
4.1 – Handling....................................................................................39
4.2 – Installation and use..................................................................39
4.2.1 – Preliminary operations............................................39
4.2.2 – Assembling the hoses.............................................40
4.2.3 – Electrical connection – general instructions ...........40
4.2.3.1 – Connection of single-phase and three-phase pumps 40
4.2.3.2 – Connection of direct current pumps................40
4.2.4 – Starting and stopping..............................................41
4.3 – Washing and storage..............................................................41
4.4 – Use of the by-pass (optional device).....................................41
4.5 – Demolition.................................................................................41
5 – INFORMATION ON RESIDUAL RISKS..........................................41
5.1 – Contact with moving parts......................................................41
5.2 – Temperature of accessible surfaces......................................41
5.3 – Risks caused by spattering and leakage of fluids................41
5.4 – Residual risks caused by faulty operation ............................42
6 – TROUBLESHOOTING ......................................................................42
7 – DECLARATIONS ...............................................................................43
8 – WARRANTY........................................................................................43
9 – NOTES FOR THE SERVICE TECHNICIAN (reserved for qualified
technicians) ...............................................................................................43
9.1 – Disassembling the hydraulic part of the pump.....................43
9.2 – Assembling the hydraulic part of the pump ..........................43
9.2.1 – Replacing the lip seal (brass models type 20 and 50)..........43
9.2.2 –Replacing the lipseal (brass models type 25-30-35-40).......44
9.2.3 – Replacing the mechanical seal ....................................... 44
9.3 – Replacing the brushes ........................................................... 44
1–DESCRIPTIONOFSYMBOLSUSED-GLOSSARY
Safety hazard
Danger of electric shock
Danger of damaging the pump
• The series of products EEMQ, ENMQ, ALMQ, ENTQ and ALTQ are
partly completed machinery identical, respectively, to the machinery of
series EEM, ENM, ALM, ENT and ALT, except for the fact that they are
supplied without the switch and cable for connection to the power
supply but provided with an electrical terminal block. In the rest of the
manual, reference will only be made to the series without the suffix –Q.
When switch and cable are mentioned this refers to the completed
machinery, while when terminal block is mentioned this refers to the
corresponding partly completed machinery.
• The term “series ALCC” refers to the pumps AL 12/20, AL 24/20, AL
12/25, AL 24/25, AL 24/40.
• The type of power supply is indicated in the box identified by the word
“Motor” in the pump ratings plate. 1~ means “single-phase alternating
current”, 3~ means “three-phase alternating current” and
means “direct current”.
2 – USE OF THE MACHINERY/PARTLY COMPLETED
MACHINERY
The machinery or partly completed machinery is a self-priming pump of
“side channel” type. It has been designed and manufactured specifically
for transferring and handling liquids, thanks to some important features:
very rapid self-priming capacity, i.e. suction of air contained in the suction
hose to start pumping;
no damage to the pump if the liquid in the suction tank finishes;
possibility of reversing the flow of liquid (for models supplied with
alternating current).
Although it has been designed for professional use, it can also be used in
a domestic environment, providing the user has become acquainted with
its use, by carefully reading the instructions contained in this manual.
2.1 – PROPERTIES OF PUMPED LIQUID
the liquid to be pumped:
- must have no hard suspended particles (sand, gravel, etc.) which can
cause rapid wear of internal parts. If the liquid to be pumped has this risk
factor, install a suitable filter in the suction hose.
- must not be aggressive towards the materials with which it comes
into contact, i.e.:
1) the material forming the pumping body (brass for series EEM, ENM,
ENT, ECC - AISI 316 stainless steel for series AL);
2) the material of which the shaft is manufactured (AISI 316 stainless
steel);
3) the materials of which the gasket and the sealing device are
manufactured (see Chapter 3.5).
4) (only for models with by-pass) acetalic resin.
- must have suitable viscosity: these pumps are not suitable for very
viscous liquids (such as honey). For series ENM, ENT, ALM, ALT pumps,
consider as an indication of maximum viscosity a mineral oil type SAE 30
at a temperature of 40° C; all other series are suitable for liquids with
viscosity similar to water.
- must have a maximum fluid density of: for series ENM, ENT, ALM,
ALT pumps: 1.1 g/cm3; for other series: density similar to water.
- must have a minimum temperature of: -15°C, in any case above the
freezing temperature of the liquid to be pumped.
WARNING
WARNING