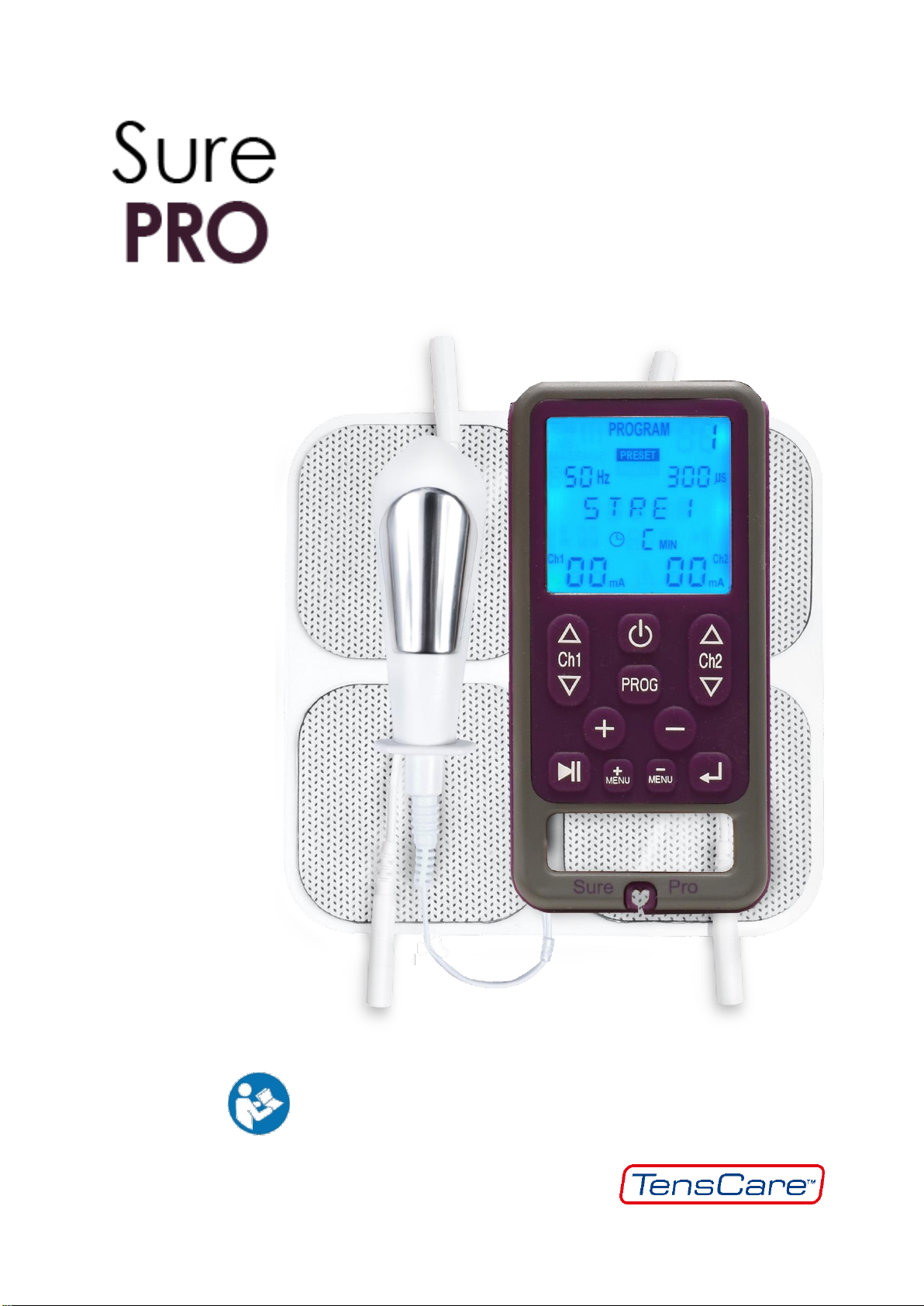
TensCare Sure PRO User manual
0
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
READ CAREFULLY BEFORE USE
1
QUICKSTART GUIDE
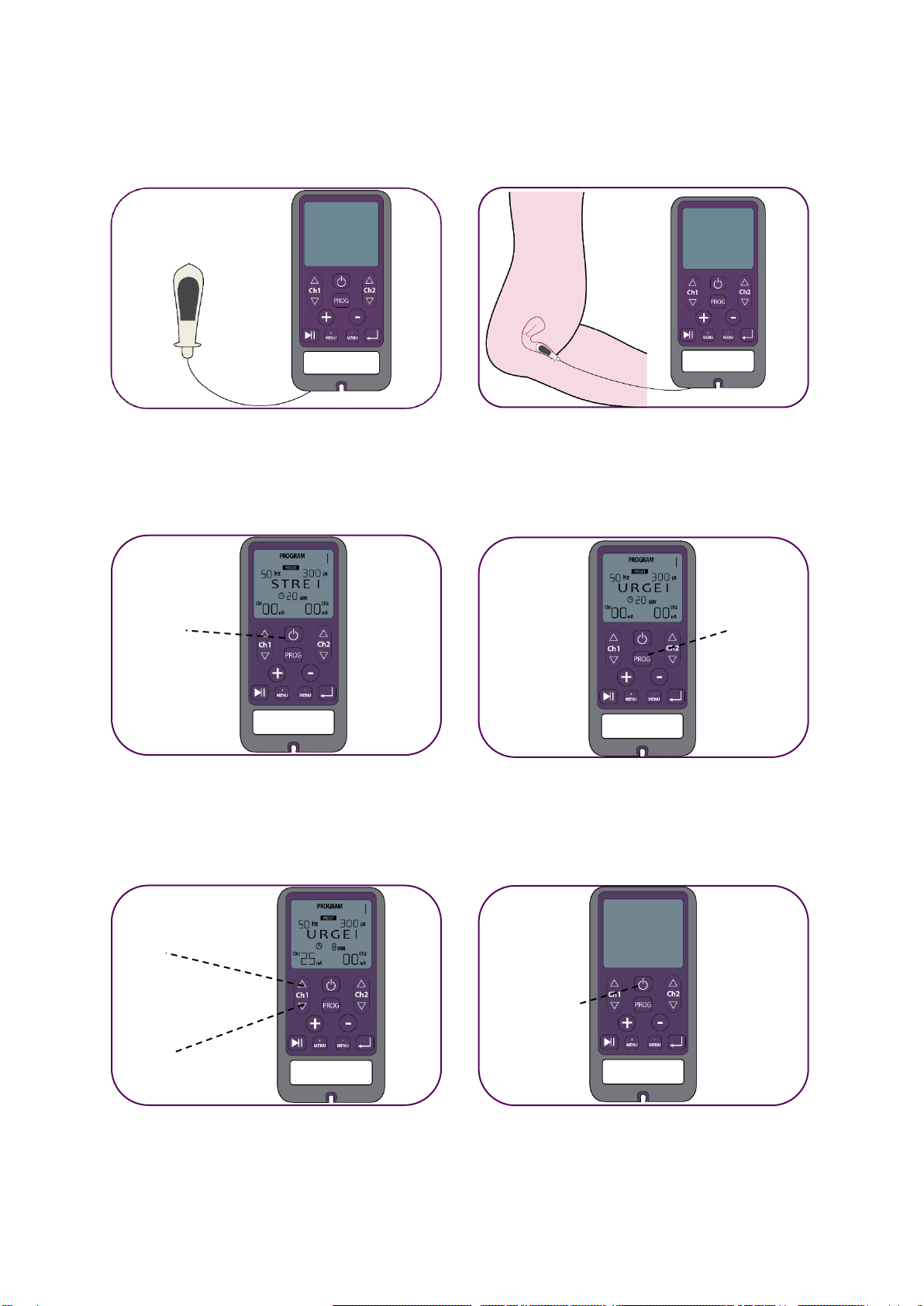
Connect the unit with the
vaginal probe
Insert the vaginal probe
Press the ON button to switch
the device on
Regulate the output intensity with
the buttons ▲and ▼
Press the OFF button to switch
the device off
ON
Button P
UP
DOWN
OFF
Select the programme by
pressing the button P
1
2
3
4
5
6

2
Dear Customer,
Thank you for choosing Sure PRO. TensCare stands for high-quality,
thoroughly tested products for the applications in the areas of gentle
electrotherapy, muscle toning, continence management and pain relief
during labour.
Please read these instructions for use carefully and keep them for later
use and observe the information they contain.
Best regards,
Your TensCare Team

3
Contents
1. INTRODUCTION.................................................................................................5
2. INTENDED USE..................................................................................................5
3. SURE PRO FEATURES......................................................................................5
4. PELVIC FLOOR EXERCISES.............................................................................6
4.1. PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLES..........................................................................6
4.2. PERFORMING PELVIC FLOOR EXERCISES .............................................7
5. TYPES OF INCONTINENCE...............................................................................8
6. HOW EMS WORKS.............................................................................................9
7. HOW ‘TENS’ WORKS .......................................................................................10
8. CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS & CAUTIONS........................................11
9. INFORMATION ABOUT THE PROGRAMME SETTINGS ................................15
10. PROGRAMMES.............................................................................................16
10.1. PROGRAMME SETTINGS......................................................................16
10.2. PRESET PROGRAMMES.......................................................................17
10.3. TRANSCUTANEOUS TIBIAL NERVE STIMULATION............................20
10.4. MANUAL PROGRAMMES.......................................................................21
11. CONTENT......................................................................................................23
12. UNIT INFORMATION.....................................................................................24
12.1. CONTROLS & DISPLAY .........................................................................24
12.2. OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS................................................................25
13. SETTING UP AND USING THE SURE PRO.................................................28
13.1. CHARGING THEBATTERY ...................................................................28
13.2. INSTALLING THE BATTERY ..................................................................29
13.3. CONNECTING THE PROBE...................................................................29
13.4. PREPARING FOR SESSION ..................................................................29
13.5. TRAINING SESSION...............................................................................30
13.6. AFTER YOUR TRAINING SESSION.......................................................31
14. ANAL PROBE ................................................................................................32
14.1. CONDITIONS THAT MAY BE TREATED................................................32
14.2. HOW TO INSERT THE ANAL PROBE....................................................32
15. CLEANING.....................................................................................................33
16. EMC ...............................................................................................................33
17. DISPOSAL OF WASTE ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC PRODUCTS
(WEEE)....................................................................................................................34
18. ACCESSORIES .............................................................................................34
19. WARRANTY...................................................................................................35
20. TROUBLESHOOTING ...................................................................................37
21. GENERAL SPECIFICATION..........................................................................39

4
SYMBOLS USED
Attention! Please follow the instructions in the user’s instructions for use.
TYPE BF EQUIPMENT: Equipment providing a degree of protection against
electric shock, with isolated applied part. Indicates that this device has
conductive contact with the end user.
This symbol on the unit means “Refer to instructions for use”.
Temperature Limitation: indicates the temperature limits to which the
medical device can be safely exposed.
Lot Number: indicates the manufacturer’s batch code so that the batch or lot
can be identified.
Humidity Limitation: indicates the humidity limits to which the medical device
can be safely exposed.
Serial Number: indicates the manufacturer’s serial number so that a specific
medical device can be identified.
Do not dispose in household waste.
Catalogue Number: indicates the manufacturer’s catalogue number so that
the device can be identified.
Atmospheric Pressure: indicates the atmospheric limits to which themedical
device can be safely exposed.
Date of Manufacture: indicates the date which the medical device was
manufactured. This is included within the serial number found on the device
(usually in the battery compartment), either as “E/Year/Number”
(YY/123456) or “E/Month/Year/Number” (MM/YY/123456).
This medical device is indicated for home use.
This medical device is not water resistant and should be protected from
liquids.
The first number 2: Protected against access to hazardous parts with a
finger, and the jointed test finger of 12 mm ø, 80 mm length, shall have
adequate clearance from hazardous parts, and protected against solid
foreign objects of 12.5 mm ø and greater.
The second number 2: Protected against vertically falling water drops
when enclosure is tilted up to 15˚. Vertically falling drops shall have no
harmful effects when the enclosure is tilted at any angle up to 15˚ on either
side of the vertical.
LOT
S/N
REF
IP22

5
1. INTRODUCTION
Device Description & Principles of
Design
Bladder leakage and incontinence are
common problems for women and men,
affecting their long-term health.
Exercising the pelvic floor muscles is
recognised as the way of preventing
and treating symptoms of incontinence
and pelvic floor weakness.
The Sure PRO is a versatile
professional continence stimulator unit
that offers the latest technology in a
simple package that is equally suitable
for home use.
It has two independent stimulation
channels and can be used with vaginal
or anal electrodes, or for urge
incontinence and pain with four self-
adhesive electrode pads.
The Sure PRO has 12 preset and 3
manual programmes. In addition to the
standard settings, it has special
programmes for transcutaneous
stimulation of the tibial nerve for urge
incontinence.
The manual programmes can be
adjusted by healthcare professionals to
the specific needs of the patient.
The Sure PRO provides relief from
conditions such as:
•Urinary and faecal incontinence:
including stress, urge and mixed
types as well as post prostatectomy
urinary incontinence in men.
Additionally, it may help improve
sexual intimacy by toning the pelvic
floor muscles.
•Chronic pelvic pain: vulvodynia,
symphysis pubis or interstitial
cystitis.
•Treatment of erectile dysfunction
in men* and improvement of pelvic
strength (* requires an anal probe).
2. INTENDED USE
Sure PRO is a medical device
designed to be used in the
home healthcare environment
to treat symptoms of urinary and/or
faecal incontinence and is suitable for
use by all who can control the device
and understand the instructions.
Sure PRO may help to relieve
symptoms of chronic pelvic pain.
Do not use the device for any purpose
other than this intended use.
Warning: Not suitable for use
in children without medical
supervision.
3. SURE PRO FEATURES
•Dual channel
Two independent channels to treat
symptoms of all types of incontinence
via a tampon-shaped probe and/or
electrode pads.
•Comfortable Stimulation
Gentle stimulation with 99 small steps
of intensity, 1mA per step.
•12 Preset Programmes
EMS programmes including stress,
urge, mixed, endurance, pelvic floor
workout and a tone aftercare.
Additionally, dedicated TENS
6
programmes for Tibial Nerve
Stimulation and a Pelvic Pain Relief
programme.
•3 Manual Programmes
Choice of user defined programmes to
experiment and save favourite settings.
•Open Circuit Detection
Automatically resets the strength to
zero and flashes ‘LEADS’ if the
connection comes loose.
•Large Backlit Screen
Makes the screen easy to read under all
conditions as well as it clearly shows
the operation of the unit and the
parameters being used.
•Memory
Features choice of sophisticated
functions: exact history of daily usage
by programme and by time and
programme retention (automatically
starts in the last programme used).
4. PELVIC FLOOR
EXERCISES
4.1. PELVIC FLOOR
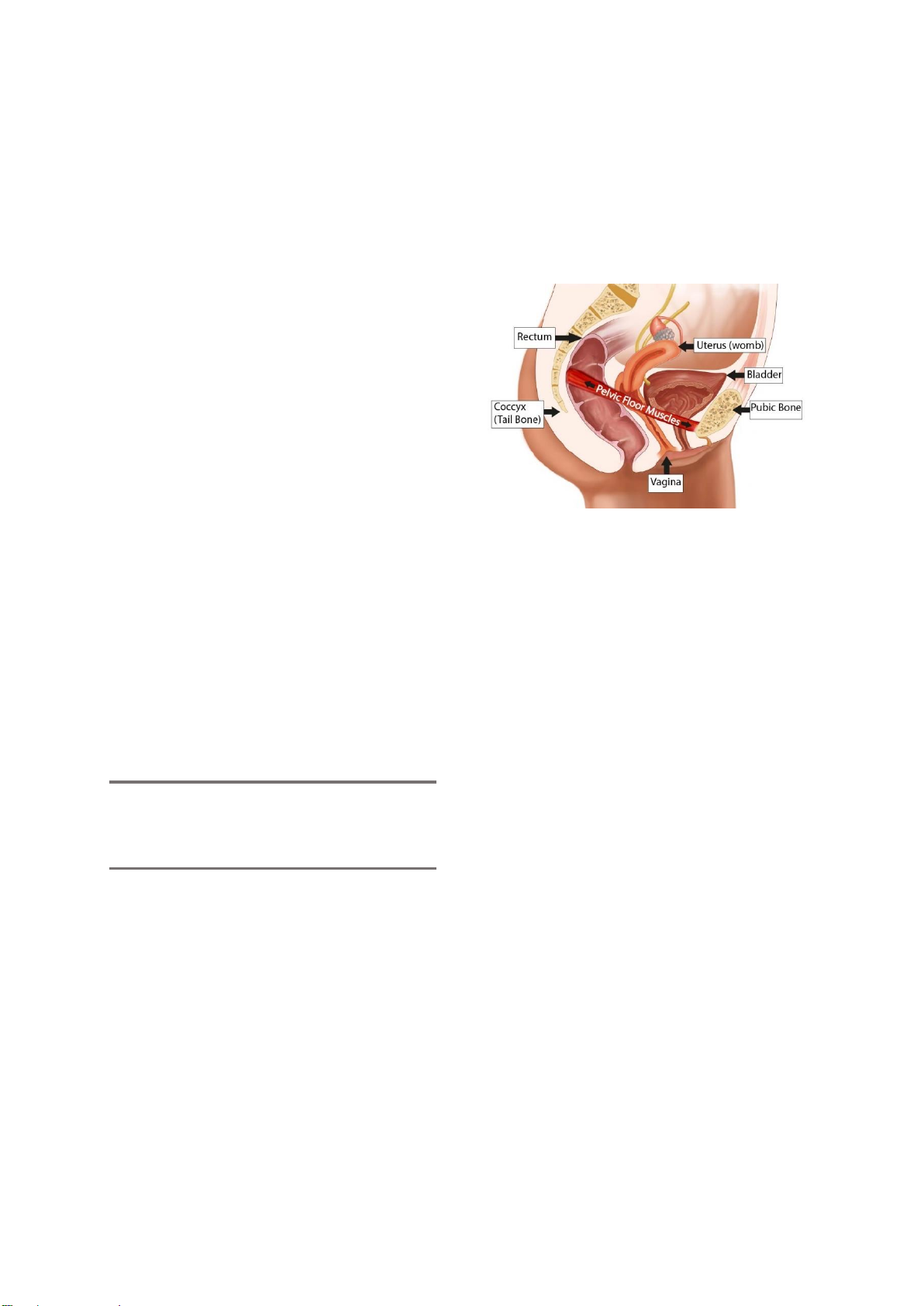
MUSCLES
The “FLOOR” of your pelvis is made up
of layers of muscles that support the
bowel, bladder, urethra and uterus.
These muscles are like a hammock, or
the bottom and sides of a bowl, in
shape. They run from the pubic bone in
the front to the end of the spinal column
(or tail bone) in the back.
The pelvic floor muscles:
•Assist in supporting the abdominal
and pelvic organs.
•Work with the abdominal and back
muscles to stabilise and support the
spine.
•In women, also
oprovide support for the baby
during pregnancy and
oassist in the birthing process
Pelvic floor muscles are also important
for sexual function in both men and
women:
•In men, it is important for erectile
function and ejaculation.
•In women, voluntary contractions
(squeezing) of the pelvic floor
contribute to sexual sensation and
arousal.
However pelvic floor muscles may
become weak. If your pelvic floor
muscles become stretched or
weakened, your pelvic organs may no
longer be fully supported and you may
lose control of your bladder or bowel
movements.
For some women, the pelvic floor
muscles can also become too tight.
This condition is less common, but it
can lead to pelvic pain and make it
difficult for you to empty your bladder or
bowel completely.

7
Common signs that can indicate a
pelvic floor problem include:
•Accidentally leaking urine when you
exercise, laugh, cough or sneeze
•Needing to get to the toilet in a hurry
or not making it there in time
•Constantly needing to go to the toilet
•Finding it difficult to empty the
bladder or bowel
•Accidentally losing control of the
bladder or bowel
•Accidentally passing wind
•Pain in your pelvic area
•Painful sex, or
•A prolapse
In women, this may be felt as a bulge in
the vagina or a feeling of heaviness,
discomfort, pulling, dragging or
dropping. This occurs when one or
more of the pelvic organs (bladder,
bowel or uterus) become displaced and
sag down into the vagina. It is very
common in the United Kingdom and
occurs in about 40% of women.
Symptoms tend to become
exacerbated towards the end of each
day and if left untreated, they will
generally worsen over time.
In men, this may be felt as a bulge in
the rectum or a feeling of needing to
use the bowel but not actually needing
to go.
Like other muscles in your body, the
pelvic floor can be strengthened with
regular exercise. Building pelvic floor
strength enables the muscles to better
support your pelvic organs, improves
your bladder and bowel control and can
stop accidental urine, faeces or wind
leakage.
It can also reduce your risk of prolapse,
improve your recovery from childbirth
and gynaecological surgery, and
increase your sexual pleasure. A
continence therapist can help you learn
how to exercise your pelvic floor.
Doing just a few pelvic floor exercises
every day will help to treat bladder
weakness or prolapse symptoms, and
will help to prevent problems later on.
4.2. PERFORMING PELVIC
FLOOR EXERCISES
It is recommended to make Pelvic Floor
Exercises (sometimes called Kegel
Exercises) part of your daily life.
1) Kegel exercises can be done at any
time and are verydiscreet so you can
do them almost anywhere; lying in
bed, sitting at the computer or
waiting for a bus. It is a good idea to
try and develop a routine which you
can repeat each day.
2) First, it is important to find your pelvic
floor muscles and feel them working.
So here are a couple of techniques
which might help:
Try inserting one or two clean fingers
into your vagina and then squeezing
the surrounding muscles, lifting up
and towards your belly button –a
squeezing and lifting sensation.
Another way is to try and stop the
flow of urine during urination. If you
are successful, then you know you
are exercising the correct muscles.
Note: These techniques are
just to help you confirm that you
are using the correct muscles. It is
important to have an empty bladder
before starting the exercises.

8
3) Try to remember the lifting and
squeezing sensation and when you
are ready try to recreate it just using
the muscles you identified earlier;
don't tense the muscles in your legs,
stomach or buttocks and remember
to breathe normally.
4) Aim to hold each squeeze or
'contraction' for three to five
seconds, then release and relax.
You should feel a ‘letting go’ of the
muscles. Rest for five seconds and
then repeat.
5) Try and do about ten squeezes in
this way.
6) Repeat the whole process three or
four times a day.
7) Over a period of time try to increase
the muscle contractions up to about
ten seconds, but remember to rest in
between each squeeze for longer
periods.
Note: It is important to aim for
quality contractions, not
quantity, so a few good hard squeezes
are better than a series of weak ones.
Do not worry if you find holding for 3
seconds difficult at first. Just
squeeze for as long as you feel
comfortable to do so. The more
exercise you do, the stronger the
muscles will become and the longer
you will be able to squeeze.
8) Using your Sure PRO pelvic floor
stimulator in conjunction with Kegel
exercises will give you a better
understanding of how they work and
how to get the greatest benefit from
them.
5. TYPES OF
INCONTINENCE
There are three types of incontinence:
Stress, Urge, and Mixed.
Stress Incontinence
If you leak urine when you cough,
sneeze, laugh, strain or make sudden
movements, this is called Stress
Incontinence.
It is particularly common in women who
have had a natural childbirth and occurs
when the bladder neck and the other
mechanisms that act to hold urine in the
bladder are not working properly. The
most common cause is a weak pelvic
floor.
Urge Incontinence
Describes an overactive bladder. A
person may experience a strong and
sudden urge to go to the toilet but are
not always able to hold on, or must go
so frequently that it becomes
inconvenient.
Mixed Incontinence
Is a combination of both Stress and
Urge Incontinence.
Faecal Incontinence
Faecal incontinence can be the result of
weakened or poorly functioning anal
sphincter muscles or damage to the
nerves controlling them. The purpose is
to re-educate the anal sphincter and
other muscles of the pelvic floor to
contract. The treatments aim to
progress towards graduated active

9
exercises, in order to improve pelvic
floor muscle strength and endurance
and to regain function.
You may benefit from the Sure PRO if
you either have no active anal sphincter
contraction, or a weak or poorly
sustained contraction. Use the STRES
or TONE programmes. Intensity should
be as strong as possible without being
painful. When possible, try to contract
the muscles at the same time as the
Sure PRO.
Post Prostatectomy Urinary
Incontinence
Electrical stimulation has been found to
help urinary incontinence in men after
radical prostatectomy in some trials.
Choose the programme depending on
the type of incontinence you are
suffering from and increase the
intensity to the highest tolerable.
Chronic Pelvic Pain
Pelvic pain can be due to several
causes such as:
Vulvodynia, Symphysis Pubis, or
Interstitial Cystitis.
Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic
pain syndrome: unexplained chronic
pelvic pain associated with irritative
voiding symptoms and/or pain located
in the groin, genitalia, or perineum in
the absence of pyuria and bacteriuria.
Low frequency stimulation stimulates
the release of Endorphins –your body’s
natural pain relief mechanism –to
reduce pain without side effects.
6. HOW EMS WORKS
E.M.S. stands for Electrical Muscle
Stimulation and has successfully been
used in medical rehabilitation and
training in competitive sports. EMS
produces intensive and effective
muscular contraction.
In rehabilitation, EMS is a well-
established method for treatment of a
broad field of musculoskeletal
diagnoses as well as pelvic floor
weakness. Electrical stimulation of an
intact peripheral nervous system may
create motor responses in patients with
impaired or lost ability for voluntary
muscle activity.
EMS is a complement to other physical
therapy and should always be
combined with active training such as
Kegel exercises (see section 4.2.).
Advantages of EMS
Use of EMS may lead to faster progress
in the patient’s treatment programme.
The method is simple and appropriate
for treatment in the clinical setting as
well as for self-treatment at home.
How EMS Works
Electrical Muscle Stimulators can play a
vital role in educating women and men
about their pelvic floor and the
sensation they should feel when doing
pelvic floor exercises. Electrical Pelvic
Floor Exercisers (PFE) offer a non-
invasive method of producing
contraction of muscles via a gentle
stimulation to the pelvic floor through a
discreet probe or electrode pads when
10
they are placed close to the nerve that
controls the pelvic floor muscles. This
current then passes into the nerve
fibres controlling that part of the muscle
stimulating it to contract. So, electrical
stimulation (EMS) artificially activates a
muscle for you enabling you to develop
your own muscle control. These
contractions exercise the muscles and,
as with any kind of exercise if
performed regularly, build strength and
tone.
In urge incontinence, pelvic floor
exercisers work in a slightly different
way. The electrical stimulation is
designed to soothe your bladder
muscles rather than exercise your
pelvic floor. Sure PRO uses a gentler,
low frequency setting which promotes
release of endorphins and reduces
involuntary contractions of the bladder
(detrusor) muscle.
Different frequencies have different
effects; low frequencies (1-10 Hz)
coupled with long impulse times, for
example, have a purifying and relaxing
effect through individual contractions,
whereby the circulation in the treated
muscle is simultaneously improved and
removal of metabolic end products is
supported (lymphatic drainage).
In contrast, by means of a rapid
succession of contractions (fibrillation),
medium frequencies (20-50 Hz) can put
a high level of strain on the muscle, thus
promoting the muscular structure.
Each preset programme has a specific
frequency and pulse width that will offer
the best results for the type of
incontinence treated.
7. HOW ‘TENS’ WORKS
T.E.N.S. stands for Transcutaneous
Electrical Nerve Stimulation. T.E.N.S.
stimulates your body’s own natural
defences against pain, namely the
release of endorphins. TENS is totally
safe and has been used successfully by
thousands of pain sufferers.
TENS sends a gentle stimulation
through the skin which works in
TWO ways:
Pain Gate
It stimulates the
sensory nerves,
which carry touch
and temperature
signals. These
nerves go to the
same connections
in the spine as the
nerves carrying pain. A strong sensory
signal will block the pain signal
travelling up the spine to the brain. This
is known as closing the “Pain Gate” and
takes effect quite quickly after the unit
is switched on. When the gate is open,
pain messages get through to the brain
and we feel pain. When the gate is
closed, these pain messages are
blocked and we do not feel pain.
Evidence suggests that TENS produce
pain relief in a similar way to ‘rubbing
the pain better’. The pain gate can be
closed by activation of
mechanoreceptors through ‘rubbing the
skin’.
Scientifically, the pain gate works by
release of chemical in the synapse at
spinal level that inhibits transmission of
pain signal.

11
Endorphin Release
At low frequency
settings, and
slightly stronger
outputs, TENS
drives the motor
nerves to produce
a small repetitive
muscle
contraction. This is seen by the brain as
exercise, and this promotes the release
of endorphins - your body’s own natural
pain killer. The relief builds up and
normally takes about 40 minutes to
reach a maximum level which can last
for hours after the machine is switched
off.
By using TENS, you can expect to
achieve a significant reduction in pain -
if not complete relief from pain.
•TENS is effective for pain from a very
wide range of causes.
•TENS machines can be used to help
reduce pain from problems in
muscles, joints and nerves.
•It can be also used for people with
musculoskeletal pain such as long-
term (chronic) back pain or knee joint
arthritis. They are also often used for
pain relief in the early stages of
labour (see perfect mamaTENS),
particularly whilst a pregnant woman
remains at home.
•TENS may also be used to treat
many types of pain, such as migraine
headaches, period pain and
endometriosis (see Ova+), cystitis,
sports injuries, fibromyalgia and
neuralgia, plantar fasciitis, post-
operative pain, TMJ disorder,
diabetic neuropathy, osteo-arthritis
and sometimes non-painful
conditions such as travel sickness.
•You can use low frequency (<10 Hz)
programmes on acupuncture points,
to achieve similar effects to
acupuncture.
•With neurogenic pain (caused by
inflamed nerves) such as shingles
and neuralgia, TENS may start by
increasing the pain. We recommend
that you only use TENS for these
conditions under medical
supervision.
•You can safely use TENS as long as
it gives you pain relief. The effect
may wear off after a few hours (this
is called “accommodation”). If this
happens, take a break of an hour or
so before trying again. If you use
settings that cause muscle
movement for more than 40 minutes,
you may experience aching muscles
a few hours later.
8. CONTRAINDICATIONS,
WARNINGS &
CAUTIONS
In this manual:
A Warning is used when failure
to follow the instructions may
result in serious injury or death.
A Caution is used when failure
to follow the instructions may
result in a minor or moderate injury, or
damage to the device or other property.
Notes are used to provide
clarification or
recommendation.
12
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
•Do NOT use if you are or may be
pregnant. It is not known whether
TENS may affect foetal
development.
•Do NOT use with optional electrode
pads if you have a pacemaker (or if
you have a heart rhythm problem) or
with any electronic medical devices.
Using this unit with electronic
medical devices may cause
erroneous operation of the device.
Stimulation in the direct vicinity of an
implanted device may affect some
models. Stimulation on the front of
the neck can affect your heart rate.
Very strong stimulation across the
chest may cause an extra heartbeat.
•Do NOT use in the first 6 weeks
following a pelvic surgery or vaginal
childbirth. Stimulation may disrupt
the healing process.
•Do NOT use if you have symptoms
of active urinary tract infection,
vaginal infections, or localized
lesions. Introducing the probe may
irritate sensitive tissue.
•Do NOT use if you have poor
sensation in the pelvic region. You
may not be able to control the
intensity of stimulation safely.
WARNINGS:
Do NOT use if you are unable
to properly insert the vaginal or
anal probe. If you have a severe
prolapse, or if any discomfort occurs
when inserting the probe, consult your
healthcare professional before use.
Do NOT use when driving,
operating machinery, or similar
actions needing muscular
control. Loose electrode pads,
damaged leads, or sudden changes in
contact may cause brief involuntary
muscle movements.
Do NOT use to mask or relieve
undiagnosed pain. This may
delay diagnosis of a progressive
condition.
Do NOT use if you have, in the
area being treated: active or
suspected cancer or undiagnosed pain
with a history of cancer. Stimulation
directly through a confirmed or
suspected malignancy should be
avoided as it may stimulate growth and
promote spread of cancer cells.
CAUTIONS:
Caution should be used if you
have a bleeding disorder as
stimulation may increase blood flow to
the stimulated region.
Caution should be used if you
have suspected or diagnosed
epilepsy as electrical stimulation may
affect seizure threshold.
Caution should be observed
when using the device at the
same time as being connected to
monitoring equipment with body
worn electrode pads. It may interfere
with the signals being monitored.
Caution: Simultaneous
connection to high frequency
surgical equipment may result in burns
and damage to the stimulator.
Caution: Strong
electromagnetic fields (electro-
surgery/ microwave cookers/ mobile
phones) may affect the correct
operation of this unit. If it appears to
behave unusually, move it away from
these devices.
13
Caution Do not permit use by
persons unable to understand
the instructions or persons with
cognitive disabilities, i.e.; Alzheimer’s
disease or dementia.
Caution: Insertion of the
vaginal or anal electrode
makes it unsuitable for use in children
without clinical supervision
Caution: Keep away from
children under 5 years of age.
Long cord - risk of strangulation in
infants.
Caution should be observed
when using the Sure PRO at
high strength settings. Prolonged use at
high settings may cause muscle injury
or tissue inflammation.
Note: No serious or long term
adverse effects have been
reported. Mild adverse reactions are
very rarely reported, but these have
included muscular pain and cramps,
vaginal tenderness, irritation and
bleeding, mild or short term urge or
faecal incontinence, and tingling
sensation in legs. If you experience any
of these, stop use. When symptoms
have gone, try resuming at a lower
intensity setting.
PROBE CAUTIONS:
Caution: The Sure PRO
vaginal probe is intended for
single patient use only. Do not share
yourSure PRO probe with anyone else.
Improper treatment or cross-infection
may occur.
Caution: This probe is
intended for single orifice use
only (intra-vaginal or intra-anal use).
Improper treatment or cross-infection
may occur.
Caution: It is important that the
vaginal probe is cleaned after
each use. Ineffective cleaning may lead
to irritation or infection.
Caution: Never insert or
remove vaginal probe unless
the control unit is powered OFF as
insertion or removal when stimulation is
active may cause discomfort or tissue
irritation.
Caution: If tissue irritation
occurs, discontinue treatment
immediately. Ask your healthcare
professional for advice before
continuing further treatment to prevent
injury.
Caution: Do not use a silicone
based lubricant on the metal
plates of the probe as it may decrease
the effectiveness of Sure PRO’s
muscle stimulation.
Caution: The stainless steel in
the probe’s metal plates contain
some Nickel. This could cause a
reaction if you have a Nickel allergy.
Alternative gold probe specially made
without Nickel is available (see X-VPG).
Use with caution if you have a
copper IUD. If discomfort
occurs, discontinue treatment
immediately and ask your healthcare
professional for advice. There is a small
risk of stimulating the uterine wall if the
IUD is not correctly positioned.
Caution: Do not use this
device with vaginal probe, anal
probe or electrode pads other than
those recommended by the
manufacturer in section 18. Electrodes
with smaller surface area may cause
tissue irritation.
14
DO NOT PLACE THE ELECTRODE
PADS:
•On skin, which does not have normal
sensation. If the skin is numb too
great a strength may be used, which
could result in skin inflammation.
•On broken skin. The electrode pads
could encourage infection.
•On the neck/throat. This could cause
respiratory closures and discomfort
in breathing. This could also cause
blood pressure to drop (vagal
discomfort).
•Over the eyes. This can affect sight
or cause headaches.
•Across the forehead. The effects on
patients subject to stroke and
epilepsy are not known.
ELECTRODE PADS CAUTION:
Caution: Do not ignore any
allergic reaction to the
electrode pads: If a skin irritation
develops, stop using TENS, as this type
of electrodes may not be suitable for
you. Alternative electrode pads
specially made for sensitive skin are
available (see E-696-SS).
Caution: Do not use this
device with leads or electrode
pads other than those recommended
by the manufacturer. Performance
may vary from specification. Electrodes
with smaller surface area may cause
tissue irritation.
TO KEEP YOUR DEVICE IN GOOD
WORKING ORDER, OBSERVE THE
FOLLOWING ADDITIONAL
CAUTIONS:
Caution: Do not immerse your
device in water or place it close
to excessive heat such as a fireplace or
radiant heater or sources of high
humidity such as a nebulizeror kettle as
this may cause it to cease to operate
correctly.
Caution: Keep the device
away from sunlight, as long-
term exposure to sunlight may affect
the rubber causing it to become less
elastic and crack.
Caution: Keep the device
away from lint and dust, as
long-term exposure to lint or dust may
affect the sockets or cause the battery
connector to develop a bad contact.
Caution: Temperature &
Relative Humidity of storage: -
25°C to + 70°C, up to 93% RH.
Temperature & Relative Humidity of
transportation: -25°C to + 70°C, up to
93% RH.
Caution: Do not attempt to
open or modify the TENS unit.
This may affect the safe operation of
the unit and will invalidate the warranty.

15
9. INFORMATION ABOUT
THE PROGRAMME
SETTINGS
Each programme has its own
combination of Frequency and Pulse
Width settings which allow for different
sensations through the probe or
optional electrode pads and help
treating the different types of
incontinence.
•Frequency (measured in Hz -
pulses per second)
Low frequencies (1-10 Hz) have a
purifying and relaxing effect through
individual contractions.
Medium frequencies (20-50 Hz) can put
a high level of strain on the muscle, thus
promoting the muscular structure
Endorphin release (programme PAIN
only): A low frequency of 4 or 10 Hz
allows for the release of endorphins, the
body’s natural morphine-like
substances.
•Pulse Width (measured in μs -
millionths of a second)
The Sure PRO unit has pulse widths of
50 to 500 μs. Generally speaking, the
higher the pulse width, the more
"aggressive" the stimulation feels, if the
pulse width is set high enough, it will
usually elicit a muscle contraction,
which is required for an effective toning
of the pelvic floor muscles.
16
10. PROGRAMMES
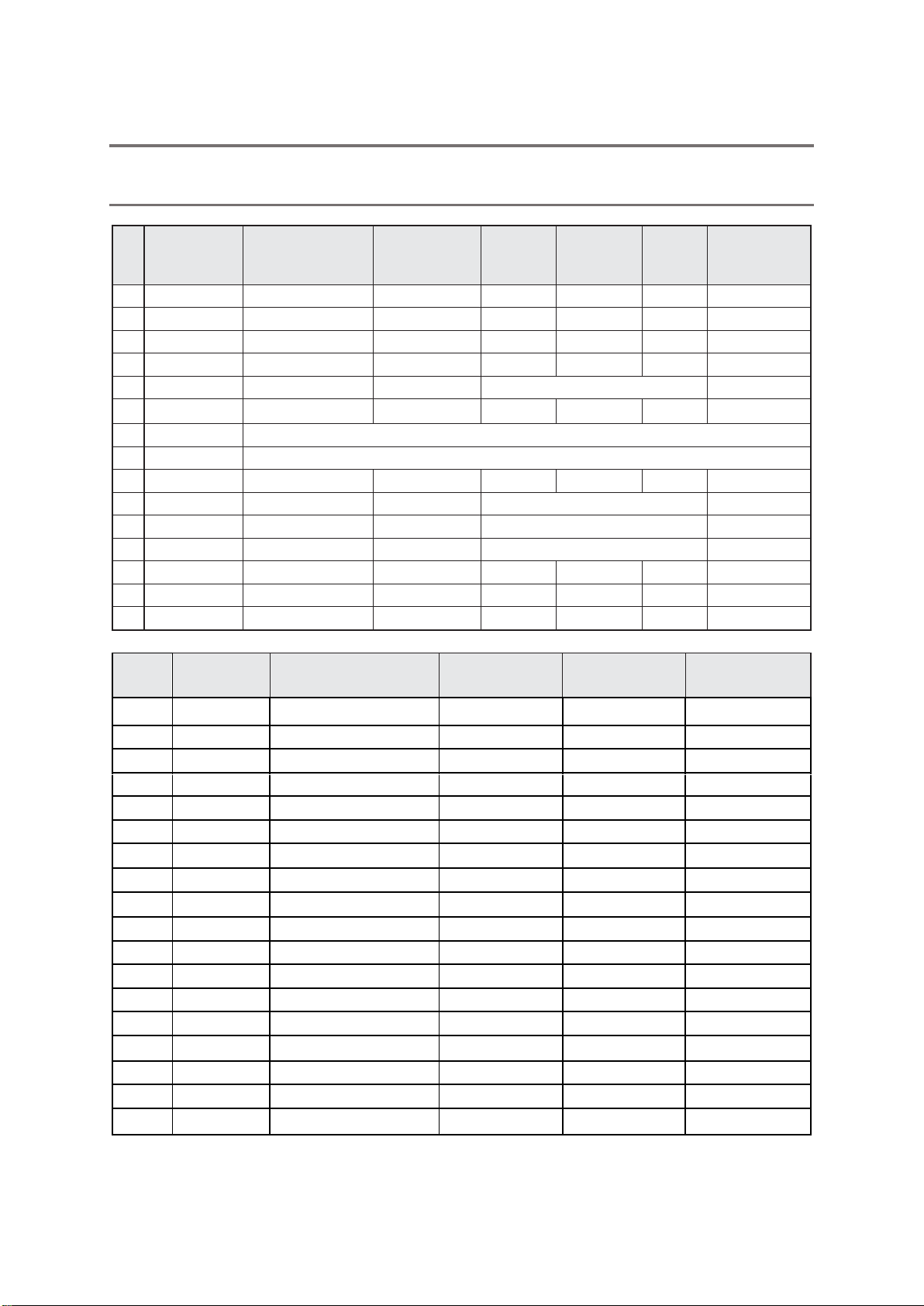
10.1. PROGRAMME SETTINGS
Programme
Frequency
(Hz)
Pulse Width
(µs)
Ramp
(sec)
Work
(sec)
Rest
(sec)
Default
duration
(min)
1
STRE 1
50
300
1
5
10
20
2
STRE 2
35
250
2
3
6
20
3
URGE
10
200
1
5
10
20
4
MIXED
10/50
200/300
30
5
URGE 2
10
200
Constant
Continuous
6
SENS
3/10/20/30/40
250/200
25
7
PFW A
See the table below
8
PFW B
See the table below
9
ENDUR
20
250
2
5
10
20
10
PAIN
4
200
Constant
20
11
TIBN 1
10
200
Constant
20
12
TIBN 2
20
200
Constant
20
13
CSTM 1
4-90
50-400
1-10
1-20
0-30
5-60
14
CSTM 2
4-90
50-400
1-10
1-20
0-30
5-60
15
CSTM 3
4-90
50-400
1-10
1-20
0-30
5-60
.
PFW
Frequency
(Hz)
Pulse Width (µs)
Work(sec)
Rest (sec)
Default
duration (min)
A
20
250 µs fixed
4
6
2
20
250 µs stepped
4
6
5
3
250 µs fixed
4
4
5
10
500 µs fixed
4
4
15
20
250 µs stepped
4
6
10
35
250 µs stepped
4
8
5
45
250 µs stepped
4
8
5
10
500 µs fixed
4
4
5
Total
52 min
B
20
250 µs fixed
6
8
2
20
250 µs stepped
6
8
5
3
250 µs fixed
6
6
5
10
500 µs fixed
6
6
15
20
250 µs stepped
6
8
10
35
250 µs stepped
6
12
5
45
250 µs stepped
6
12
5
10
500 µs fixed
6
6
5
Total
1. min
In PFWA the Pulse Width increases from 175µs to 250 µs in 4 secs - 25 µs per sec. This stepping up
occurs during Output ON time.
In PFWB the Pulse Width increases from 170 µs to 250 µs in 8 secs - 10 µs per sec.

17
10.2. PRESET PROGRAMMES
The Sure PRO has 12 preset
programmes, with programmes for
each type of incontinence (STRESS,
URGE and MIXED), as well as other
programmes for conditions including
loss of sensation and pelvic pain .
1) STRE1-Stress Incontinence
The STRESS incontinence programme
strengthens the muscles of the pelvic
floor using gentle stimulation. Once
muscular strength has been improved
these muscles are better able to resist
urinary leakage caused by external
pressure being applied to the bladder
such as with a cough, sneeze or
physical exertion. The stimulation
causes the muscles to contract and
work thereby building their strength.
Successful treatment requires
stimulation once a day for one to three
months. Improvement starts becoming
apparent after about four weeks. It
helps to keep a record of leakage
problems so that you have an objective
measure of your progress.
The sensation is like a strong drawing
in of the muscles of the vagina, pulling
up the pelvic floor. Your natural reaction
will be to pull your muscles in and up,
and this exercises and strengthens
them.
It is necessary that the pelvic floor
muscles contract. Increase the intensity
level as high as you can tolerate, then
reduce by 1 mA.
2) STRE 2 - Stress Incontinence,
aftercare
Having restored your pelvic floor
muscles to an excellent condition with
STRE 1, you will want to keep them
toned and strong.
Regular use of this programme, about
twice a week, will ensure that your
muscles remains fit and toned.
May also be used as an alternative
treatment for STRE 1.
The sensation is a mixture of a strong
drawing in of the muscles and then
releasing. The programme repeats this
sensation.
It is necessary that the pelvic floor
muscles contract. Increase the intensity
level as high as you can tolerate, then
reduce by 1 mA.
A strong and fit pelvic floor muscle may
increase sexual health and enjoyment.
3) URGE –Urge Incontinence
The URGE incontinence programme
reduces the involuntary contractions of
the bladder (detrusor) muscle. This
prevents the unwanted and unexpected
emptying of the bladder.
Successful treatment will require daily
stimulation and improvements can be
seen in as little as two weeks.
The sensation is of a longer and softer
pulling in of the pelvic floor than the
STRESS programme.
It is important to feel this sensation
throughout the programme, so you may
need to increase the intensity duringthe
treatment session. However, it is not
necessary to contract the muscles
4) MIXED –Mixed Incontinence
This programme is ideal if you suffer
both stress and urge incontinence. This
programme is a combination of 15
minutes of the URGE programme,

18
followed by 15 minutes of the STRE 1
programme.
During the first part, the sensation in the
pelvic floor is soft, like a vibration. It is
important to feel this sensation
throughout the programme; you may
need to increase the intensity duringthe
treatment session. However, it is not
necessary to contract the muscles.
In the second part, the sensation is like
a strong drawing in of the muscles of
the vagina, pulling up the pelvic floor.
Your natural reaction will be to pull your
muscles in and up, and this exercises
and strengthens them.
It is necessary that the pelvic floor
muscles contract. Increase the intensity
level as high as you can tolerate, then
reduce by 1 mA.
5) URGE2 –Urge Incontinence,
aftercare
Similar to the programme 3, but the
sensation is continuous (there is no
work/rest period), which you may find
more comfortable.
The sensation in the pelvic floor is soft,
like a vibration. It is important tofeel this
sensation throughout the programme,
so you may need to increase the
intensity during the treatment session.
However, it is not necessary to contract
the muscles.
6) SENS - Lack of Sensation
After surgery or childbirth, you may find
that you have good muscle control, but
experience a lack of sensitivity. This
can be due to nerve damage and is a
problem that may be helped with the
programme.
The sensation is like a strong drawing
in of the muscles of the vagina, pulling
up of the pelvic floor. Your natural
reaction will be to pull in and up your
muscles, thereby exercising and
strengthening them.
It is necessary that the pelvic floor
muscles contract. Increase the intensity
level as high as you can tolerate, then
reduce by 1 mA.
7) PFW A - Pelvic Floor Workout
A multiphased programme for Mixed
incontinence. The smaller steps in
frequency are believed to be less likely
to aggravate the Urge component.
The sensation is like a strong drawing
in of the muscles of the vagina, pulling
up of the pelvic floor. Your natural
reaction will be to pull in and up your
muscles, thereby exercising and
strengthening them.
It is necessary that the pelvic floor
muscles contract. Increase the intensity
level as high as you can tolerate, then
reduce by 1 mA.
8) PFW B - Pelvic Floor Workout,
aftercare
Having restored your pelvic floor
muscles to an excellent condition with
PFW A, you will want to keep them
toned and strong with this programme
which has a longer Work time
(contraction time).
The sensation is the same as PFW A.
It is necessary that the pelvic floor
muscles contract. Increase the intensity
level as high as you can tolerate, then
reduce by 1 mA.

19
9) ENDUR- Endurance
Choose this programme if you feel like
you can contract your pelvic floor
muscles quite easily, but can’t keep
them contracted for very long. ENDUR
programme will help to build up muscle
strength and improve muscle
endurance.
The sensation is like a strong drawing
in of the muscles of the vagina, pulling
up of the pelvic floor. Your natural
reaction will be to pull in and up your
muscles, thereby exercising and
strengthening them.
It is necessary that the pelvic floor
muscles contract. Increase the intensity
level as high as you can tolerate, then
reduce by 1 mA.
10) PAIN –Pelvic pain
The PAIN programme helps treat pain
in the pelvic area. It is particularly useful
for treating vulvodynia, a condition that
can cause burning, stinging, irritation
and rawness in the female genital area.
The sensation in the pelvic floor is soft,
like a vibration. It is important tofeel this
sensation throughout the programme;
you may need to increase the intensity
during the treatment session. However,
it is not necessary to contract the
muscles.
11) TIBN 1 –Transcutaneous tibial
nerve stimulation
External stimulation of the ankle with
self-adhesive electrode pads. It is
particularly effective for urge and faecal
incontinence. Uses 10Hz
See Section 10.3. for more information
about this programme.
12) TIBN 2 - Transcutaneous tibial
nerve stimulation
Same as 11, but at 20 Hz.
For the programmes that cause muscle
contractions, it is advisable not to
‘overdo’ it early on, as the resulting
aches may not be felt until the next day.
As long as you can feel the contraction,
it is working. You can build up slowly
over a number of days.
Most of the programmes cycle between
Work and Rest to allow your muscles
to recover in between contractions.
For best results in the programmes that
cause muscle contractions try to
contract the pelvic floor muscles along
with the Sure PRO, and to sustain the
contraction into the rest interval. If
possible, link the contraction to your
breathing to get into a gentle rhythm.
When you change the strength setting,
this cycle stays on Work until you stop
pressing the buttons Ch1▲ or Ch2▲
for more than 5 seconds
Once the pelvic floor has been
strengthened using the Sure PRO,
continue to exercise the pelvic floor
muscles regularly.
The uses mentioned above for each
programme are indicative only, it is
possible to adapt the use according to
your needs.
Treatment Time and Treatment
Interval
Current clinical evidence indicates that
there should normally be no need to
exceed the default treatment time
settings in all but the URGE, URGE 2
and PAIN programmes. These may be
used continuously if required.
Table of contents
Other TensCare Fitness Equipment manuals

TensCare
TensCare Sports TENS 2 User manual

TensCare
TensCare Sports TENS 2 User manual

TensCare
TensCare Unifit User manual

TensCare
TensCare Unipro User manual

TensCare
TensCare Ova User manual
TensCare
TensCare Perfect PFE User manual
TensCare
TensCare Perfect PFE User manual

TensCare
TensCare iTouch Tone User manual
TensCare
TensCare Elise 2 User manual
TensCare
TensCare MT9000 User manual