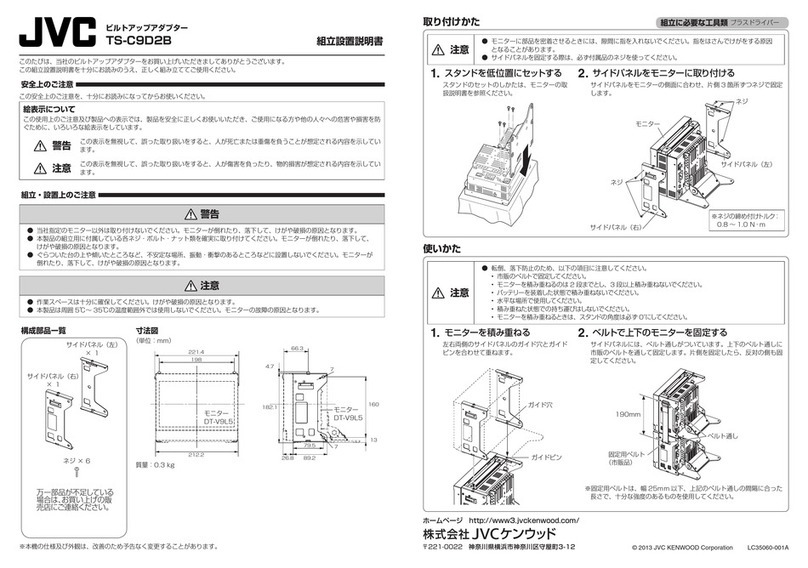
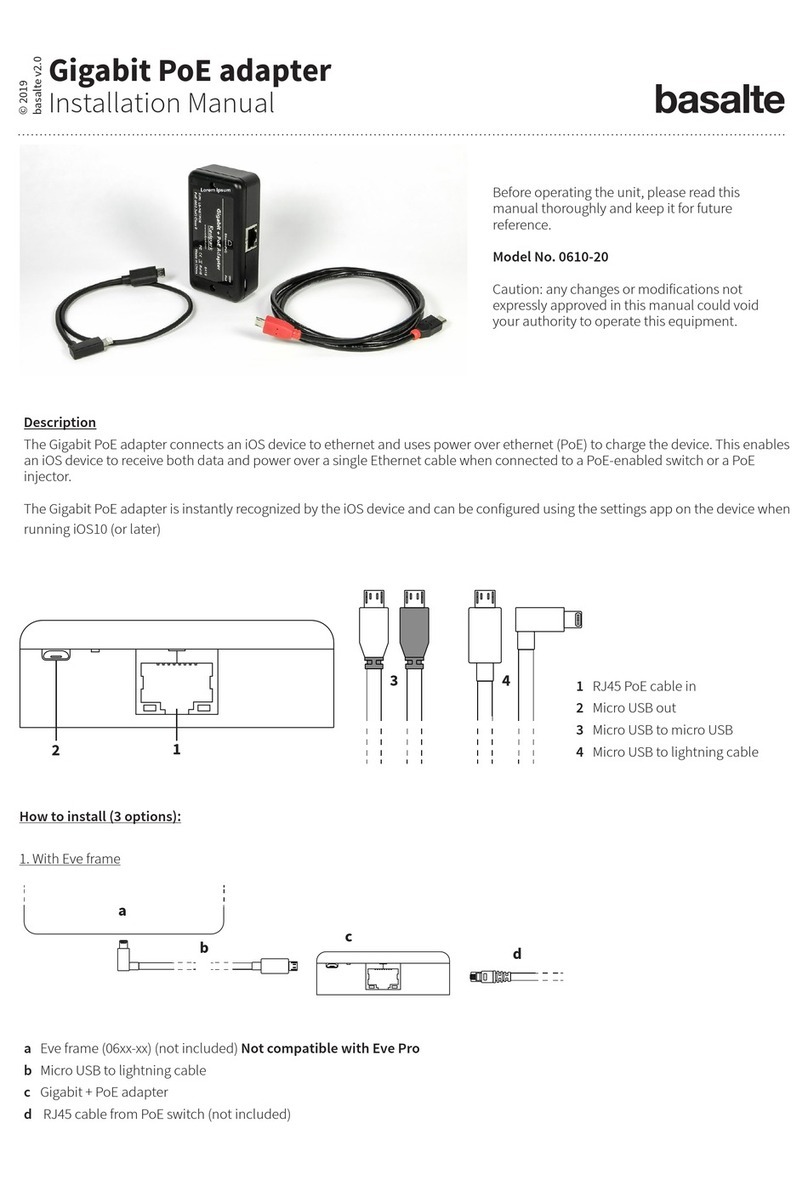
1
SLAU048I–August 2000–Revised October 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2000–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
MSP430™ Microcontroller Serial Programming Adapter
User's Guide
SLAU048I–August 2000–Revised October 2018
MSP430™ Microcontroller Serial Programming Adapter
This document describes how to use the MSP430™ Microcontroller Serial Programming Adapter
(MSP430-PRGS430). Instructions include how to install the software and hardware for the programmer
and how to use the programmer to read to and write from MSP MCUs.
Contents
1 Installation and Setup ....................................................................................................... 3
1.1 Installing the Software.............................................................................................. 3
1.2 Installing the Hardware............................................................................................. 3
2 Operation ..................................................................................................................... 5
2.1 Software and Hardware Layers of the PRGS430 Environment .............................................. 5
2.2 Programming MSP430 Devices With the GUI .................................................................. 6
2.3 Command Line Options .......................................................................................... 11
2.4 PRGS430.DLL Description....................................................................................... 14
3 Hardware.................................................................................................................... 26
3.1 Specifications ...................................................................................................... 26
3.2 Hints................................................................................................................. 26
3.3 Programming Adapter Target Connector Signals............................................................. 27
3.4 MSP-PRGS430 Circuit Diagrams............................................................................... 29
3.5 Location of Components on MSP-PRGS430.................................................................. 29
3.6 Interconnection of MSP-PRGS430 to OTP or EPROM-Based MSP430 Devices ........................ 30
3.7 Interconnection of MSP-PRGS430 to Flash-Based MSP430 Devices..................................... 31
4 Hex Object Format......................................................................................................... 32
4.1 Intel-Hex Object Format.......................................................................................... 32
4.2 TI-TXT File Format................................................................................................ 33
5 Schematics.................................................................................................................. 33
List of Figures
1 ADT430 Program Icons..................................................................................................... 3
2 Serial Programming Adapter............................................................................................... 4
3 Software and Hardware Layers............................................................................................ 5
4 MSP430 Programmer Dialog Box ......................................................................................... 6
5 Communication Error Box .................................................................................................. 9
6 Communication Error Box for Blown Fuse ............................................................................... 9
7 Erase Check Error Message ............................................................................................... 9
8 Data Error..................................................................................................................... 9
9 25-Pin Sub-D at Programming Adapter ................................................................................. 27
10 14-Pin Connector at End of Interconnect Cable ....................................................................... 27
11 MSP-PRGS430 Components............................................................................................. 29
12 MSP-PRGS430 Used to Program OTP or EPROM-Based MSP430 Devices..................................... 30
13 MSP-PRGS430 Used to Program Flash-Based MSP430 Devices.................................................. 31
14 Intel-Hex Object Format................................................................................................... 32
15 Schematics (1 of 2) ........................................................................................................ 34
16 Schematics (2 of 2) ........................................................................................................ 35