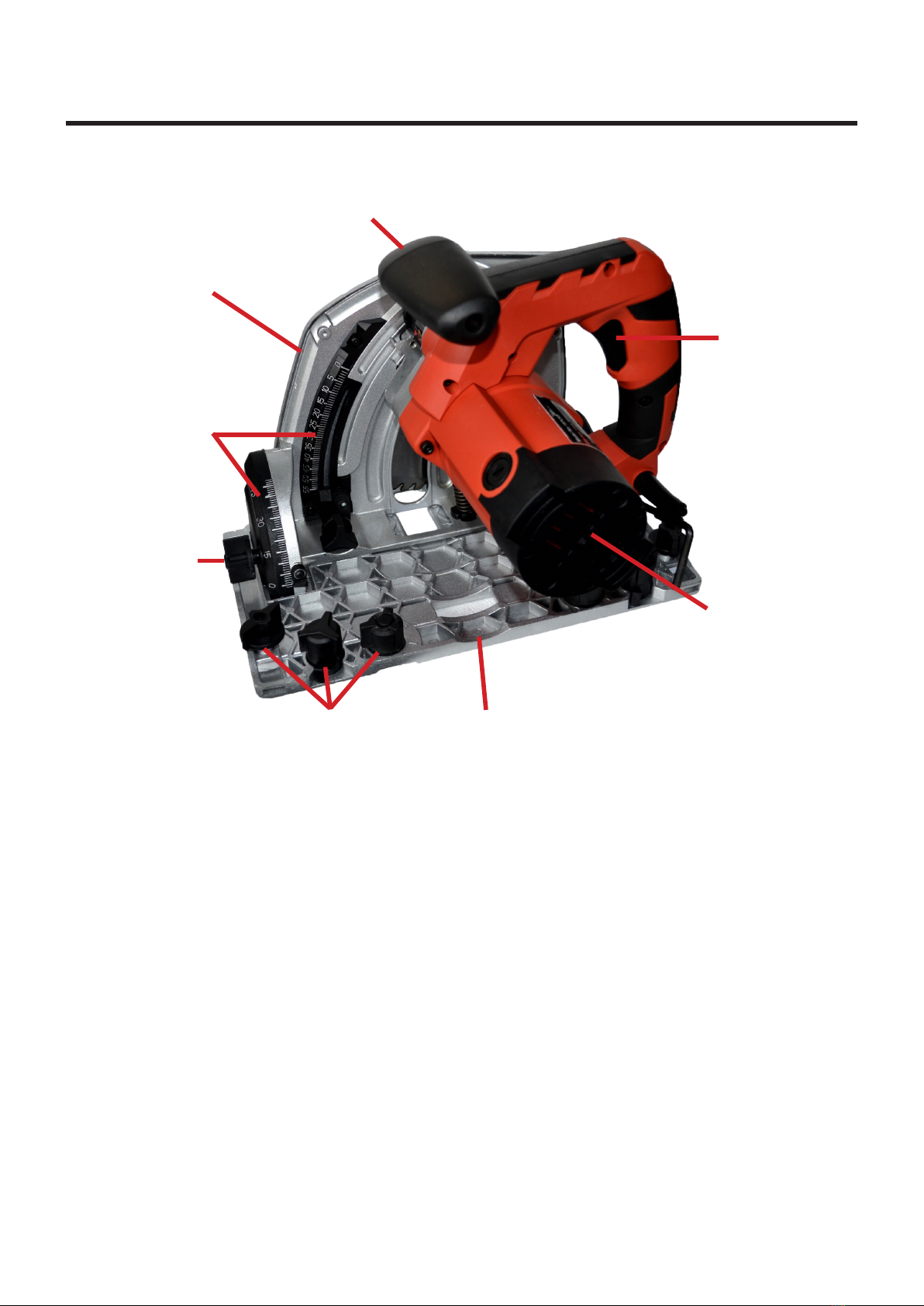
9
SAFETY GUIDELINES
to climb out of the kerf and jump back
towards the operator.
Kickback is the result of saw misuse and/
or incorrect operating procedures or
conditions and can be avoided by taking
proper precautions as given below:
- Maintain a rm grip with both hands
on the saw and position your arms to
resist kickback forces. Position your
body to either side of the blade, but not in
line with the blade. Kickback could cause
the saw to jump backwards, but kickback
forces can be controlled by the operator if
proper precautions are taken.
- When blade is binding, or when
interrupting a cut for any reason,
release the trigger and hold the saw
motionless in the material until the
blade comes to a complete stop. Never
attempt to remove the saw from the
work or pull the saw backward while the
blade is in motion or kickback may occur.
Investigate and take corrective actions to
eliminate the cause of blade binding.
- When restarting the saw in the
workpiece, centre the saw blade in the
kerf and check that saw teeth are not
engaged into the material. If saw blade
is binding, it may walk up or kickback from
the workpiece as the saw is restarted.
- Support large panels to minimise the
risk of blade pinching and kickback.
Large panels tend to sag under their own
weight. Supports must be placed under
the panel on both sides, near the line of cut
and near the edge of the panel.
5
Kickback causes and related warnings
í kickback is a sudden reaction to a pinched, bound
or misaligned saw blade, causing an uncontrolled
saw to lift up and out of the workpiece toward the
operator;
í when the blade is pinched or bound tightly by the
kerf closing down, the blade stalls and the motor
reaction drives the unit rapidly back toward the
operator;
í if the blade becomes twisted or misaligned in the
cut, the teeth at the back edge of the blade can dig
into the top surface of the wood causing the blade
to climb out of the kerf and jump back toward the
operator.
Kickback is the result of saw misuse and/or incorrect
operating procedures or conditions and can be avoided
by taking proper precautions as given below.
9. Maintain a firm grip with both hands on the
saw and position your arms to resist kickback
forces. Position your body to either side of the
blade, but not in line with the blade. Kickback
could cause the saw to jump backwards, but
kickback forces can be controlled by the operator,
if proper precautions are taken.
10. When blade is binding, or when interrupting a
cut for any reason, release the trigger and
hold the saw motionless in the material until
the blade comes to a complete stop. Never
attempt to remove the saw from the work or
pull the saw backward while the blade is in
motion or kickback may occur. Investigate and
take corrective actions to eliminate the cause of
blade binding.
11. When restarting a saw in the workpiece, centre
the saw blade in the kerf and check that saw
teeth are not engaged into the material. If saw
blade is binding, it may walk up or kickback from
the workpiece as the saw is restarted.
12. Support large panels to minimise the risk of
blade pinching and kickback. Large panels tend
to sag under their own weight. Supports must be
placed under the panel on both sides, near the
line of cut and near the edge of the panel.
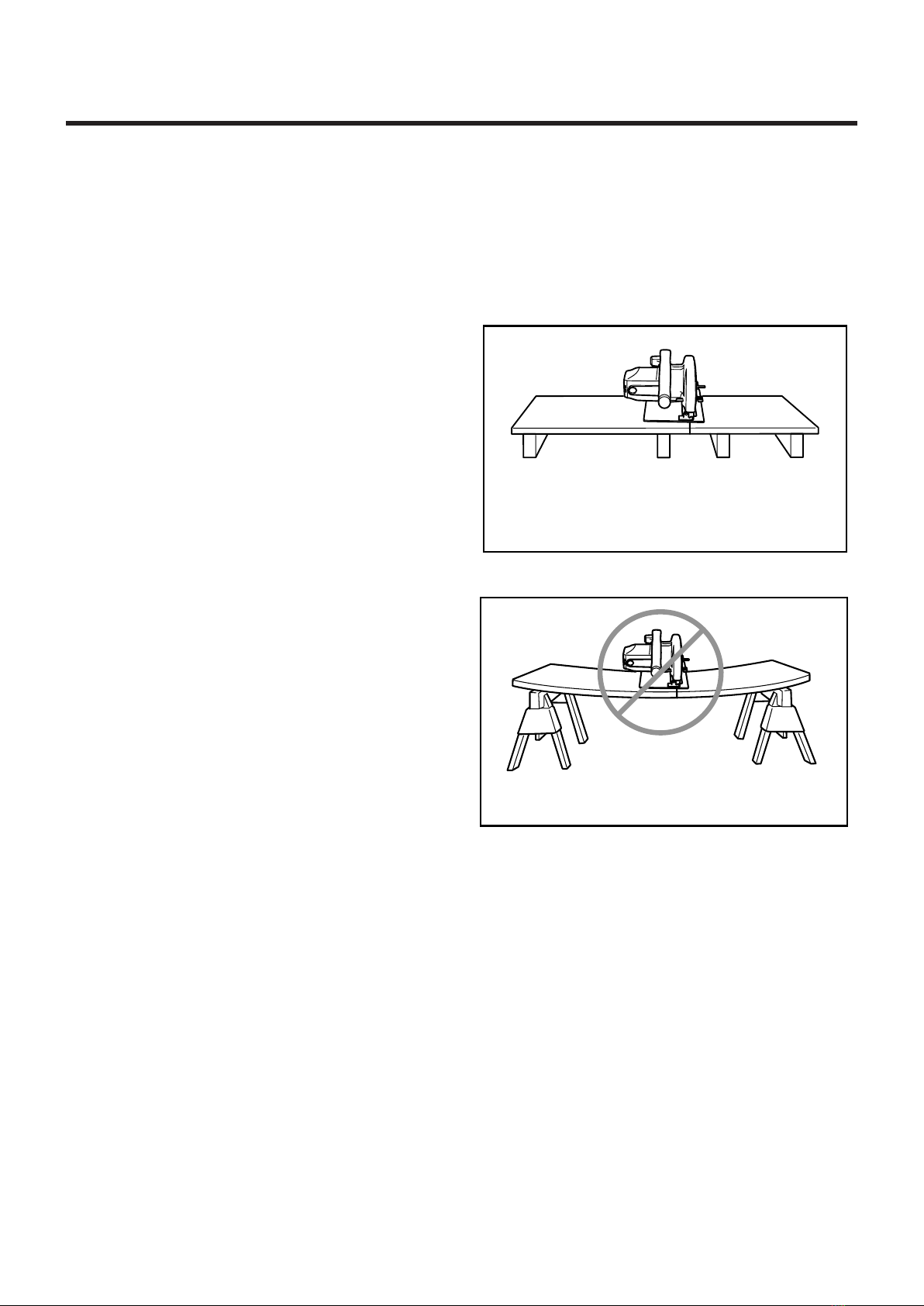
To avoid kickback, do support
board or panel near the cut.
000154
Do not support board or
panel away from the cut.
000156
13. Do not use dull or damaged blades.
Unsharpened or improperly set blades produce
narrow kerf causing excessive friction, blade
binding and kickback.
14. Blade depth and bevel adjusting locking
levers must be tight and secure before making
cut. If blade adjustment shifts while cutting, it may
cause binding and kickback.
15. Use extra caution when sawing into existing
walls or other blind areas. The protruding blade
may cut objects that can cause kickback.
16. ALWAYS hold the tool firmly with both hands.
NEVER place your hand, leg or any part of
your body under the tool base or behind the
saw, especially when making cross-cuts. If
kickback occurs, the saw could easily jump
backwards over your hand, leading to serious
personal injury.
5
Kickback causes and related warnings
í kickback is a sudden reaction to a pinched, bound
or misaligned saw blade, causing an uncontrolled
saw to lift up and out of the workpiece toward the
operator;
í when the blade is pinched or bound tightly by the
kerf closing down, the blade stalls and the motor
reaction drives the unit rapidly back toward the
operator;
í if the blade becomes twisted or misaligned in the
cut, the teeth at the back edge of the blade can dig
into the top surface of the wood causing the blade
to climb out of the kerf and jump back toward the
operator.
Kickback is the result of saw misuse and/or incorrect
operating procedures or conditions and can be avoided
by taking proper precautions as given below.
9. Maintain a firm grip with both hands on the
saw and position your arms to resist kickback
forces. Position your body to either side of the
blade, but not in line with the blade. Kickback
could cause the saw to jump backwards, but
kickback forces can be controlled by the operator,
if proper precautions are taken.
10. When blade is binding, or when interrupting a
cut for any reason, release the trigger and
hold the saw motionless in the material until
the blade comes to a complete stop. Never
attempt to remove the saw from the work or
pull the saw backward while the blade is in
motion or kickback may occur. Investigate and
take corrective actions to eliminate the cause of
blade binding.
11. When restarting a saw in the workpiece, centre
the saw blade in the kerf and check that saw
teeth are not engaged into the material. If saw
blade is binding, it may walk up or kickback from
the workpiece as the saw is restarted.
12. Support large panels to minimise the risk of
blade pinching and kickback. Large panels tend
to sag under their own weight. Supports must be
placed under the panel on both sides, near the
line of cut and near the edge of the panel.
To avoid kickback, do support
board or panel near the cut.
000154
Do not support board or
panel away from the cut.
000156
13. Do not use dull or damaged blades.
Unsharpened or improperly set blades produce
narrow kerf causing excessive friction, blade
binding and kickback.
14. Blade depth and bevel adjusting locking
levers must be tight and secure before making
cut. If blade adjustment shifts while cutting, it may
cause binding and kickback.
15. Use extra caution when sawing into existing
walls or other blind areas. The protruding blade
may cut objects that can cause kickback.
16. ALWAYS hold the tool firmly with both hands.
NEVER place your hand, leg or any part of
your body under the tool base or behind the
saw, especially when making cross-cuts. If
kickback occurs, the saw could easily jump
backwards over your hand, leading to serious
personal injury.
- Do not use dull or damaged blades.
Unsharpened or improperly set blades
produce narrow kerf causing excessive
friction, blade binding, and kickback.
- Blade depth and bevel adjusting
locking levers must be tight and secure
before making a cut. If blade adjustment
shifts while cutting, it may cause binding
and kickback.
- Use extra caution when sawing into
existing walls or other blind areas. The