1. INTRODUCTION
TP series adjustable DC power supply are designed to be used in applications such as powering operational
amplifier, push pull stages, logic circuit and definition systems where plus and minus voltages are required to
track with an insignificant error, and in any application where three independent power supplies housed in a
single package represent an operating convenience.
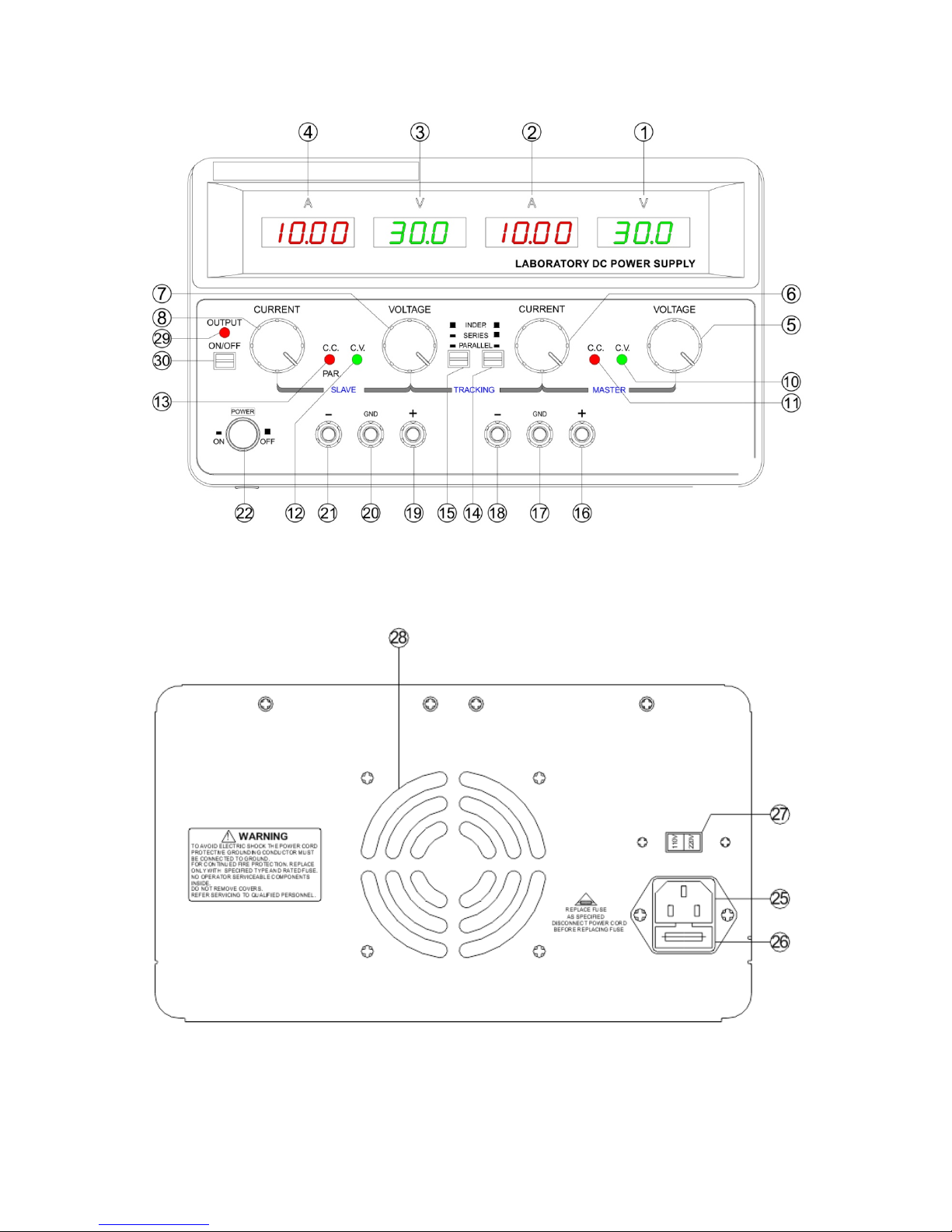
The instruments consist of two identical, independently adjustable and one fixed 5V/3A DC power supplies. A
front panel switch selects one of three modes of operation: independent, series and parallel. In the
independent mode, the output voltage and current of each supply are controlled separately, and each supply
is isolated up to 300V from output to chassis or output to output. In the tracking mode, both outputs are
automatically connected in series or parallel, and the controls of the left supply adjust the magnitudes of both
the positive and negative output voltages. Because the outputs are connected in a tracking configuration, any
internal disturbance in the master supply (such as drift or ripple) will cause an equal percentage change in the
outputs of both the supplies.
Each power supply is a completely transistorized, well-regulated, constant voltage/constant current supply
that will furnish full rated output voltage at the maximum output current or can be continuously adjusted
throughout the output range. The front panel current controls can be used to establish the output current limit
(overload or shout circuit) when the supply is used as a constant voltage source (independent or tracking
modes) and the voltage controls can be used to establish the voltage limit (ceiling) when the supply is used as
a constant current source(independent mode only).The supply will automatically cross over from constant
voltage to constant current operation(current limited operation in the tracking mode) and vice versa if the
output current or voltage exceeds these preset limits. Each supply had its own front panel meter that can
measure output voltage and current. One power supply may be used as a master supply controlling, one
slave supplies furnishing various voltages or current for a system. When operated with the front panel mode
switch in the tracking position, the instrument is automatically internally connected in auto-tracking
configuration.
Another feature of this instrument is its output ON/OFF key.
a. For model TP-2303E/2305E/2303K/2305K/2303/2305, it is only the key to cut off or resume the output as
other similar instrument.
b. For model TP-2303TK/2305TK, it is not only the key to cut off or resume the output, but also be endowed
with a new function which its kindred has not. This function is that when the output has been cut off, the both
intending voltage and current can be preset, though in model TP-2303K/2305K/2303/2305 condition, only the
intending voltage can be adjusted. It means that CC preset is very easy as CV preset. Also in this way, an
over current by any unknown load can be avoided. So the new function of the key is a safety design.
Especially this feature is very important to the student use.