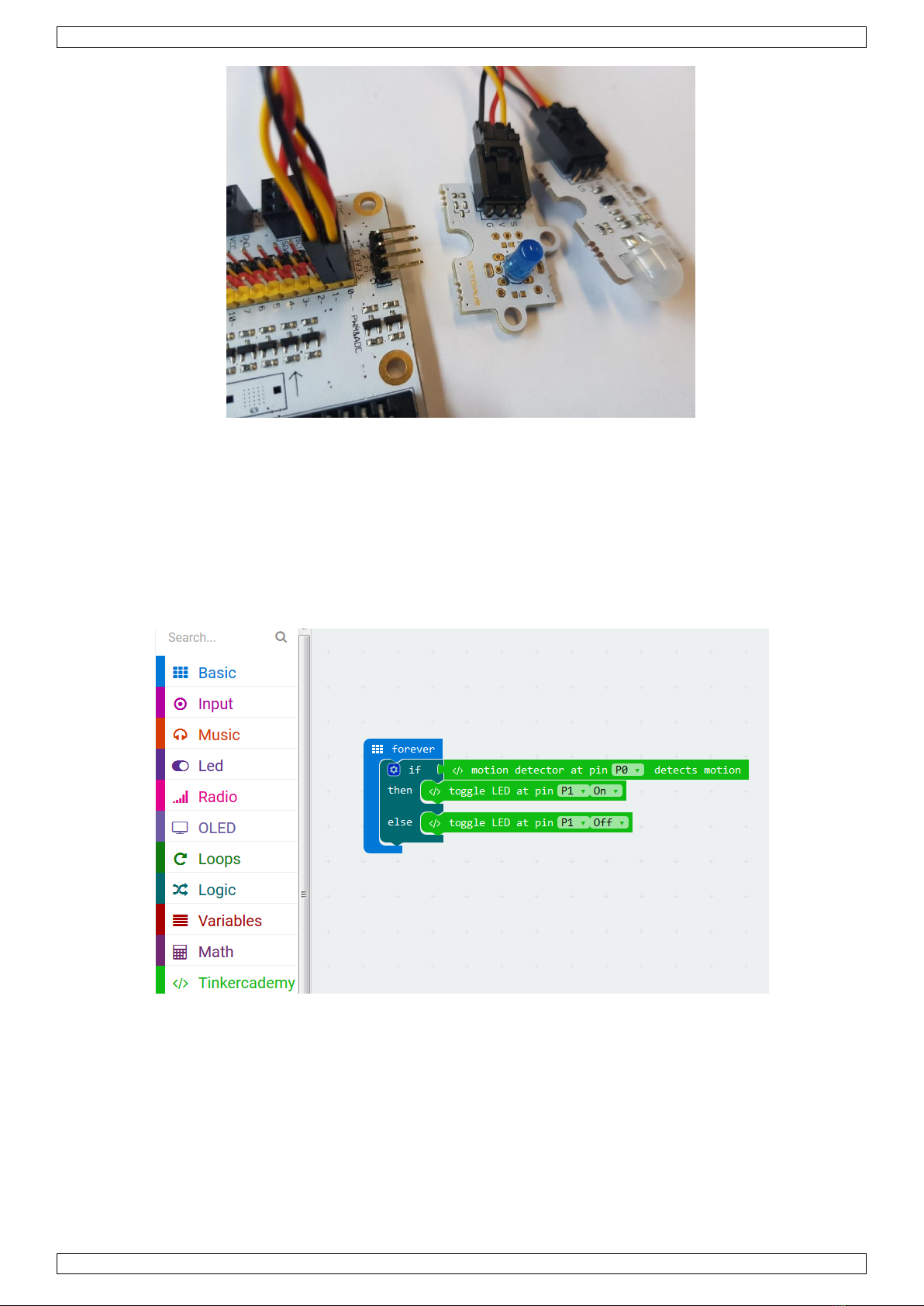
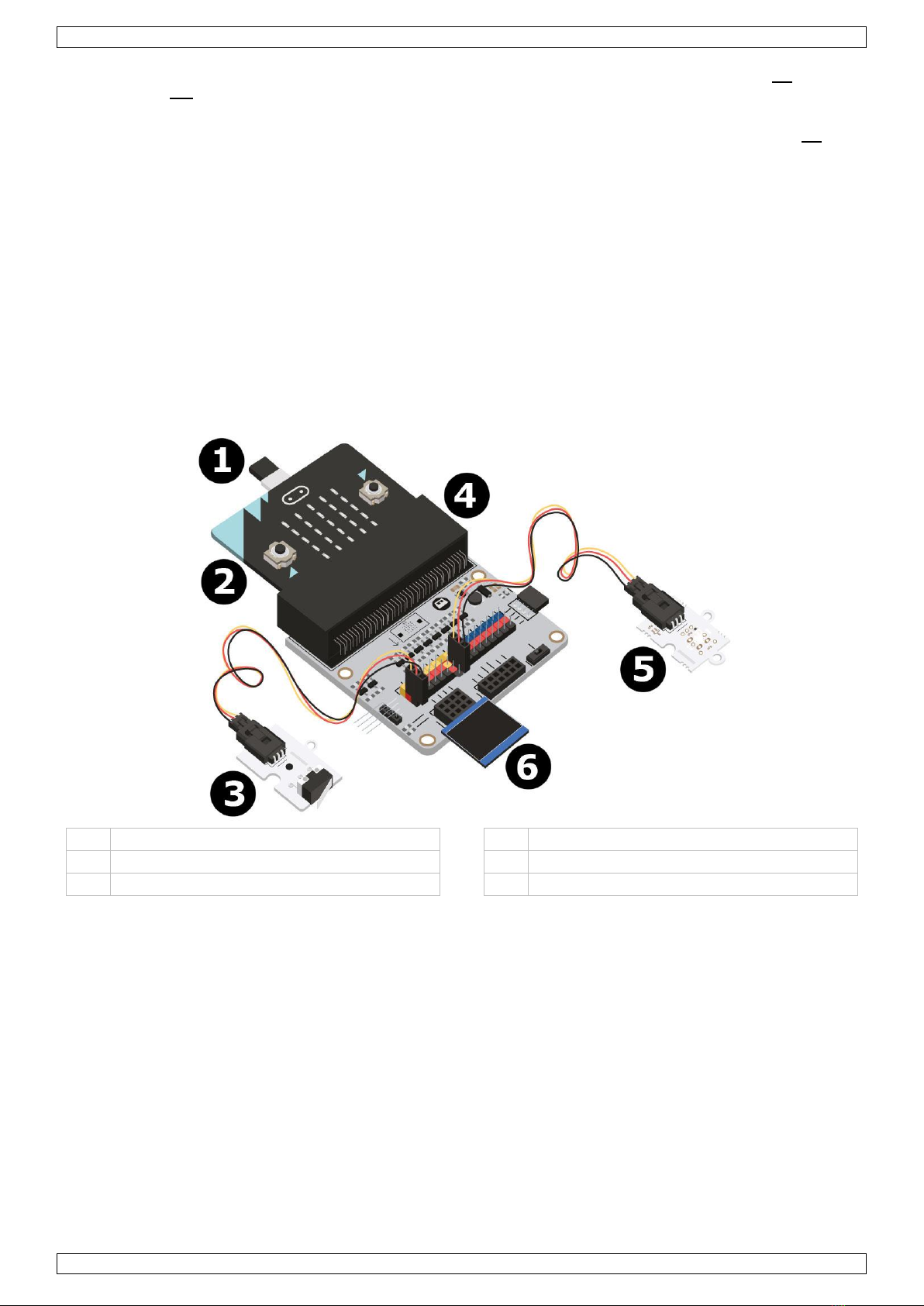
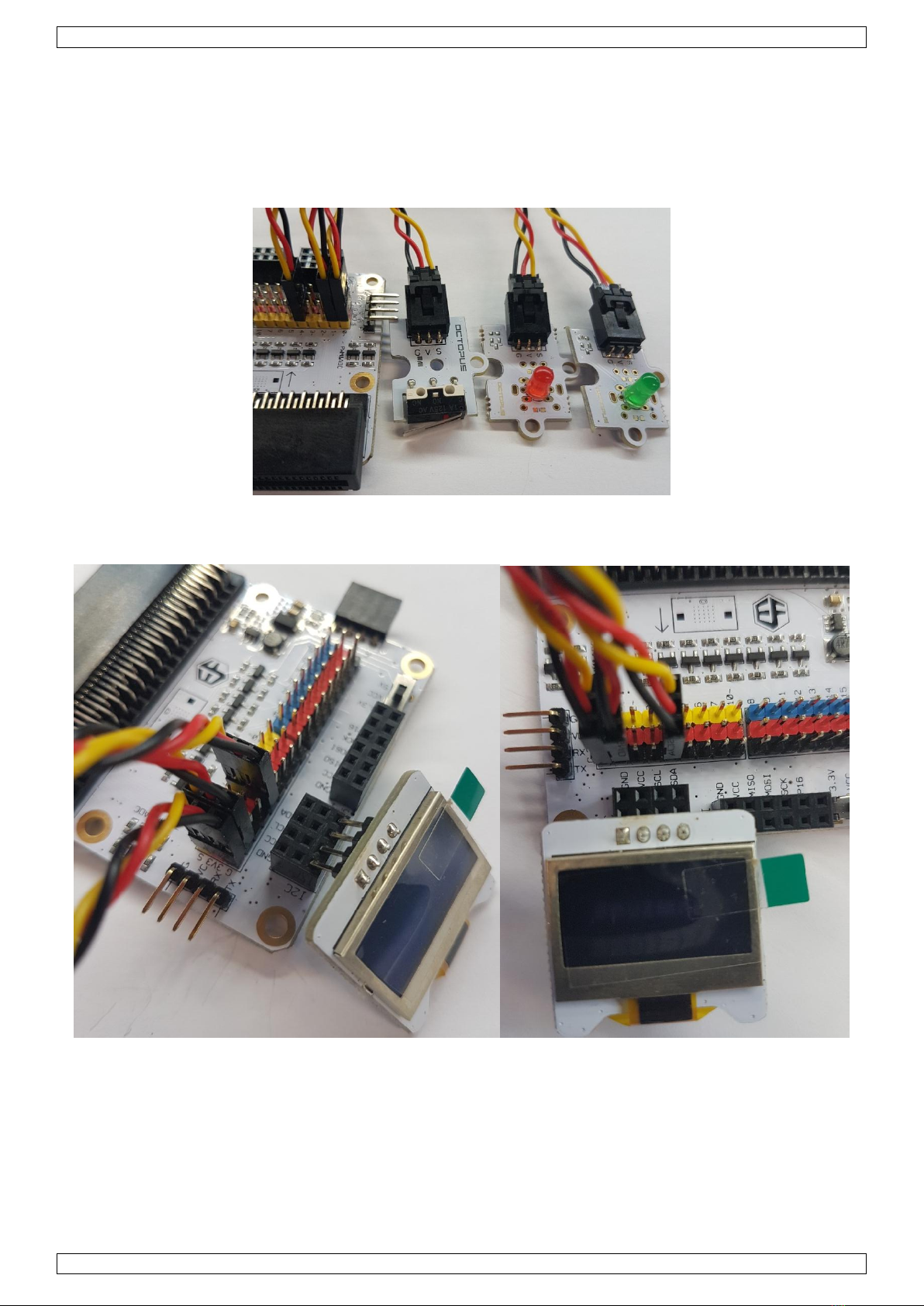
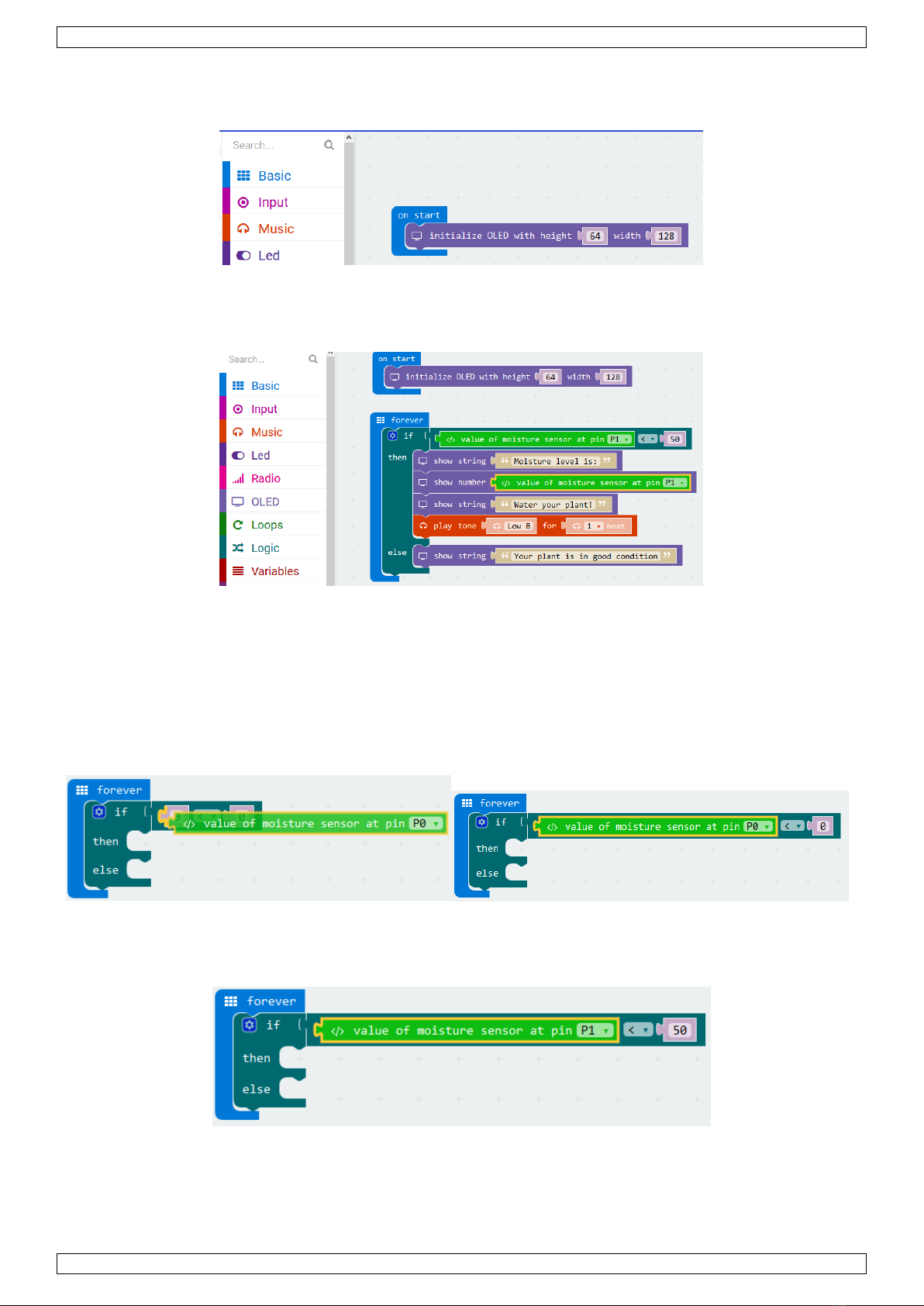
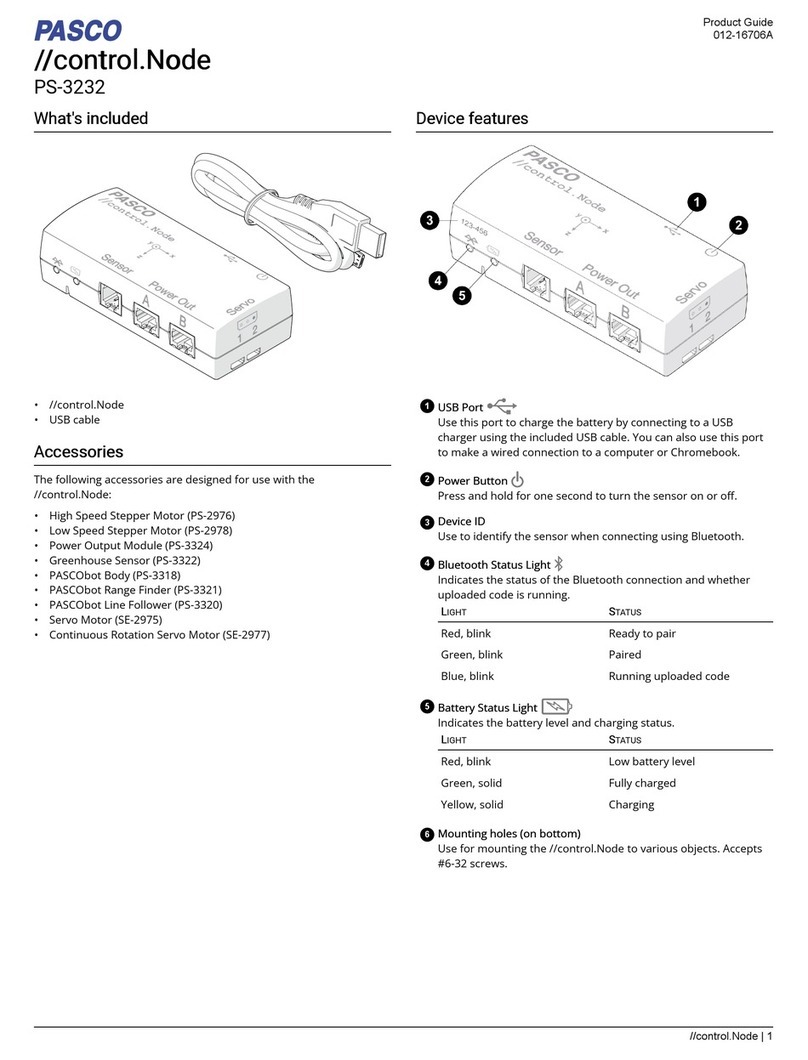
VMM502
V. 01 –17/01/2019 2 ©Velleman nv
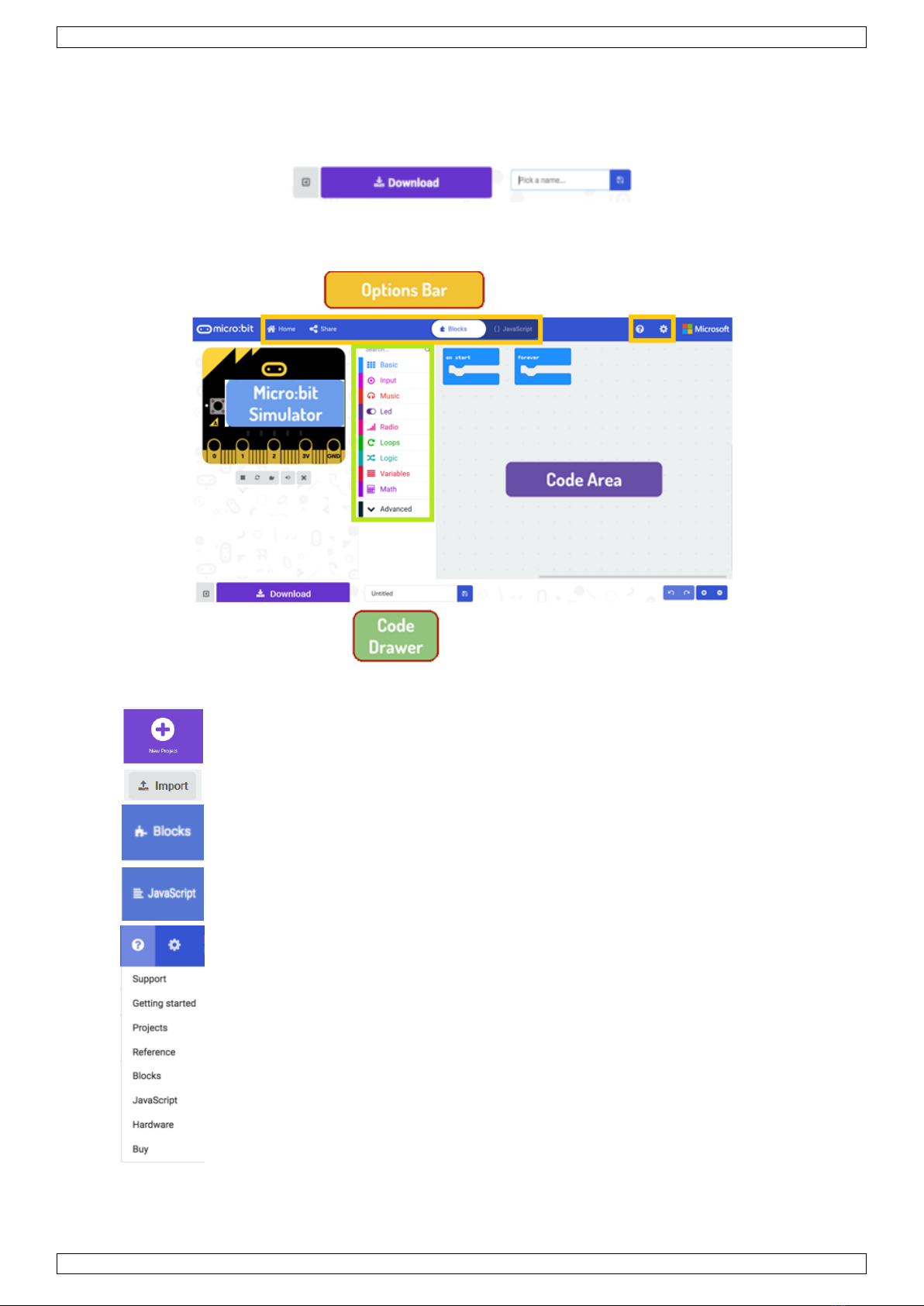
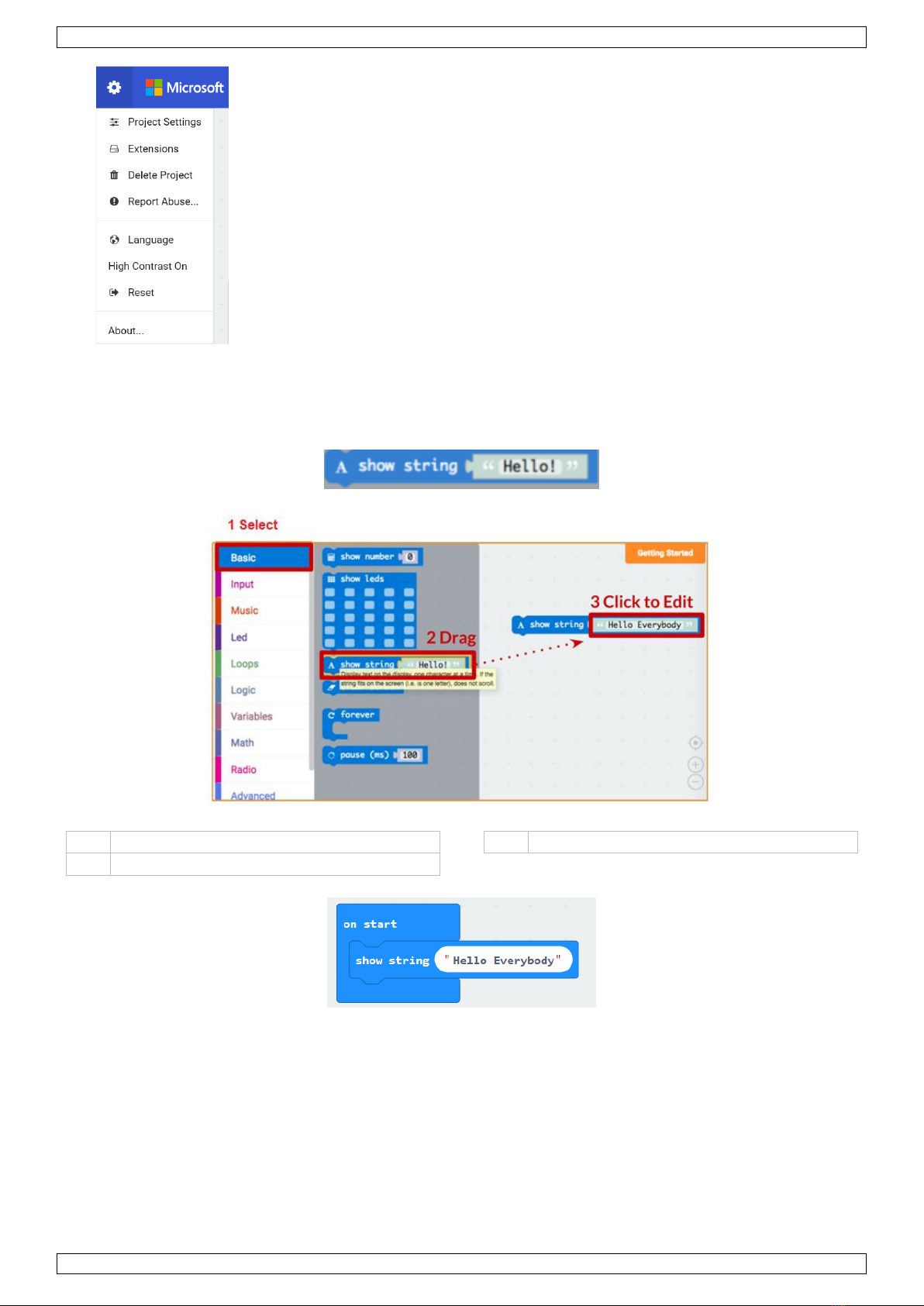
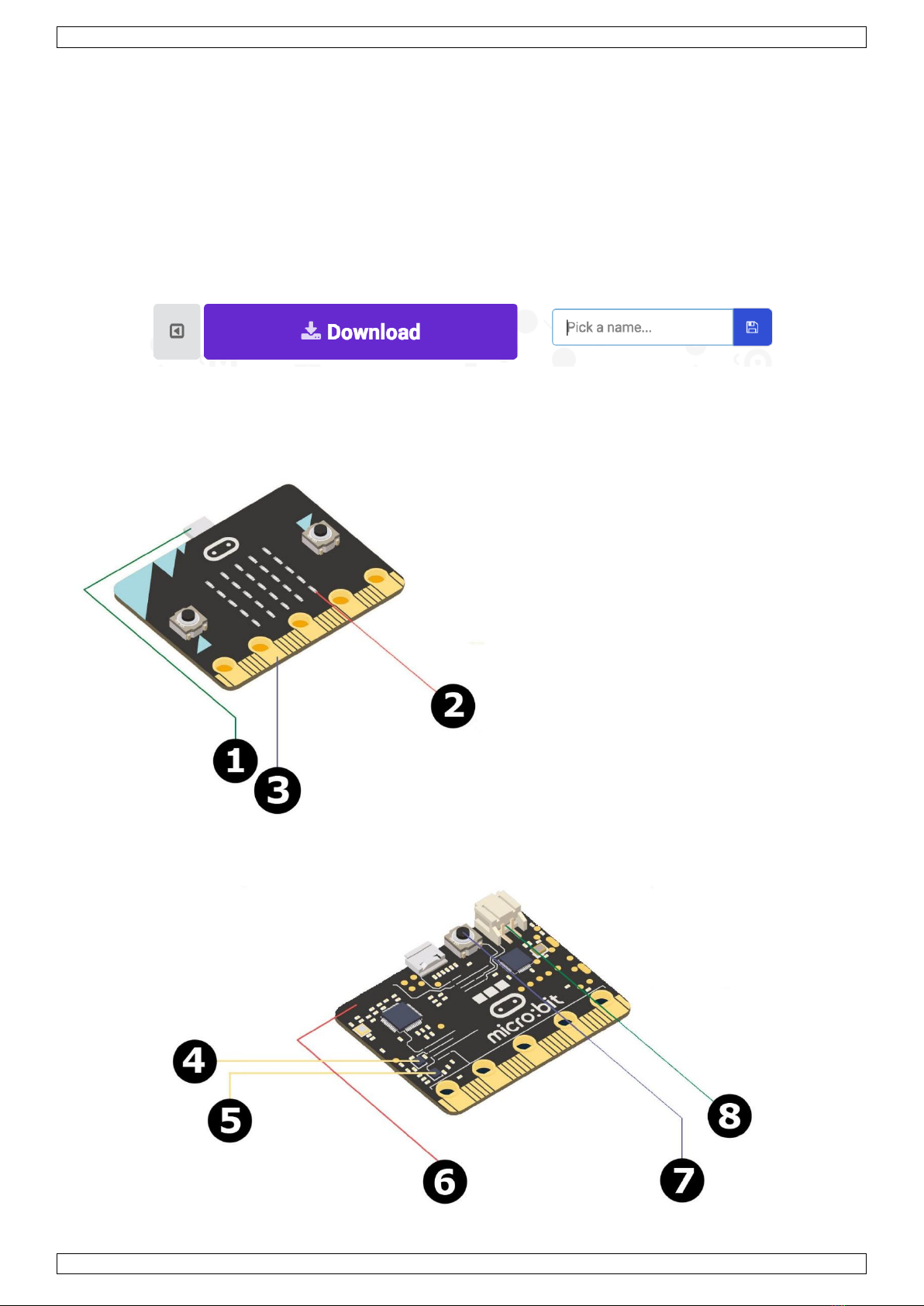
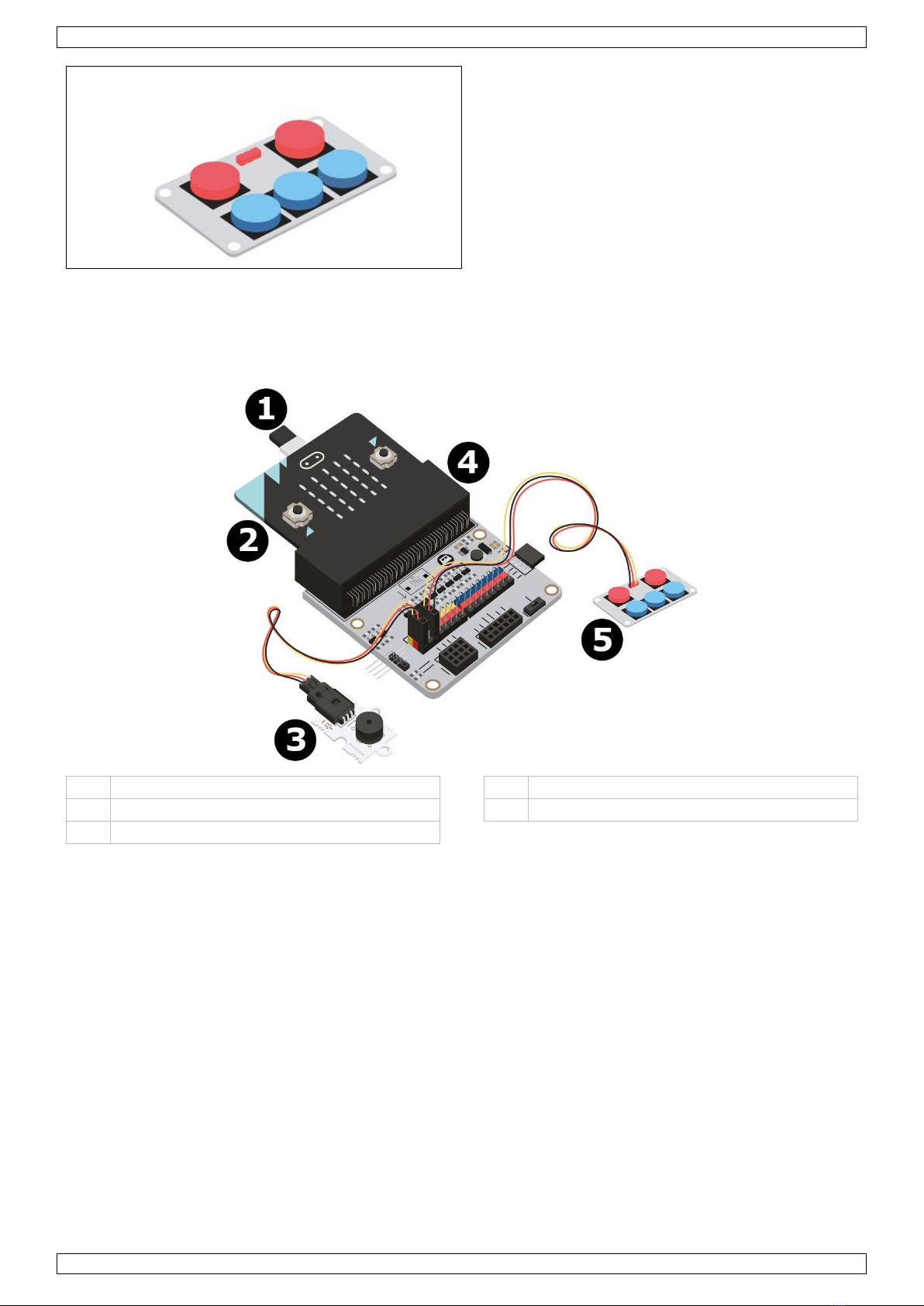
USER MANUAL
1. Introduction
To all residents of the European Union
Important environmental information about this product
This symbol on the device or the package indicates that disposal of the device after its lifecycle could
harm the environment. Do not dispose of the unit (or batteries) as unsorted municipal waste; it
should be taken to a specialized company for recycling. This device should be returned to your
distributor or to a local recycling service. Respect the local environmental rules.
If in doubt, contact your local waste disposal authorities.
Thank you for choosing Velleman®! Please read the manual thoroughly before bringing this device into service.
If the device was damaged in transit, do not install or use it and contact your dealer.
2. Safety Instructions
This device can be used by children aged from 8 years and above, and persons with
reduced physical, sensory or mental capabilities or lack of experience and knowledge if
they have been given supervision or instruction concerning the use of the device in a
safe way and understand the hazards involved. Children shall not play with the device.
Cleaning and user maintenance shall not be made by children without supervision.
Indoor use only.
Keep away from rain, moisture, splashing and dripping liquids.
3. General Guidelines
Refer to the Velleman®Service and Quality Warranty on the last pages of this manual.
Familiarise yourself with the functions of the device before actually using it.
All modifications of the device are forbidden for safety reasons. Damage caused by user
modifications to the device is not covered by the warranty.
Only use the device for its intended purpose. Using the device in an unauthorised way
will void the warranty.
Damage caused by disregard of certain guidelines in this manual is not covered by the
warranty and the dealer will not accept responsibility for any ensuing defects or
problems.
Nor Velleman nv nor its dealers can be held responsible for any damage (extraordinary,
incidental or indirect) –of any nature (financial, physical…) arising from the possession,
use or failure of this product.
Due to constant product improvements, the actual product appearance might differ from
the shown images.
Product images are for illustrative purposes only.
Do not switch the device on immediately after it has been exposed to changes in
temperature. Protect the device against damage by leaving it switched off until it has
reached room temperature.
Keep this manual for future reference.