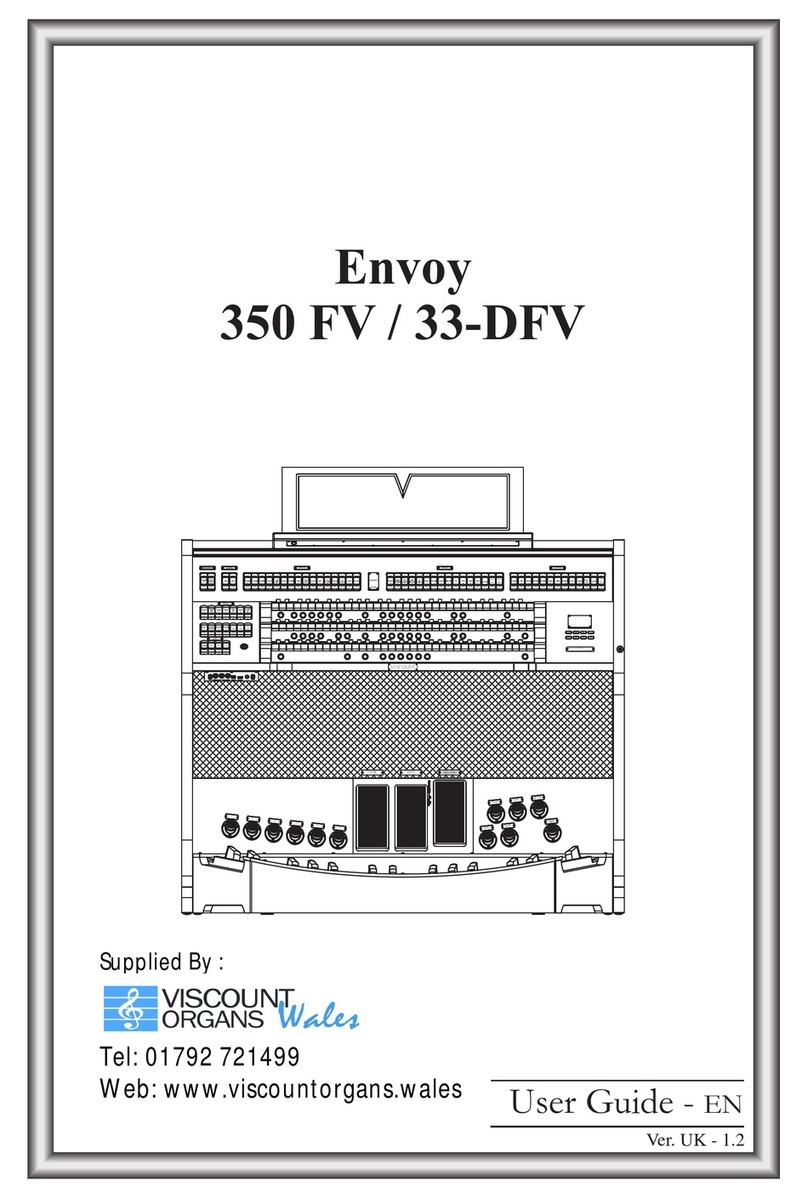
Owner's Manual – Viscount Cadet 21
5
A BRIEF NOTE ON TEMPERAMENTS
In the “natural” tunin system, based on the acoustic phenomenon of harmonic voices, two important musical
intervals, the major third and the perfect fifth, cannot be made to coexist in the “pure” state (i.e. beat-free).
Therefore, over the centuries a variety of compromise solutions known as TEMPERAMENTS have been invented
and realised.
These ive the priority to one interval or the other, and modify them in various ways..
In ancient times and in the Middle A es, until the end of the 15th Century, the “Pytha orean” tunin system, in
which the fifths were kept perfectly pure, was used. The resultin major third interval was particularly unpleasant
and was therefore considered a dissonance. However, the music of the time was mainly monodic and the first
vocal and instrumental polyphonic forms made wide use of the interval of a fifth. With the early Renaissance and
the start of the reat a e of vocal polyphony, the interval of a major third radually came to be heard as a
consonance. The instruments with fixed tunin , such as the or an and harpsichord, were adapted to this situation
by usin a system of temperament known as Meantone, which ave priority to the major third over the fifth. This
temperament is particularly important since it was in normal use in Europe in the 16th and 17th Centuries, until
the be innin of the 18th. Here are the temperaments offered by the Cadet 21, first of all the MEANTONE.
MEANTONE
- 8 pure major thirds: E flat – G / B flat – D / F – A / C – E / G – B / D – F # / A – C# / E – G.
- 4 unusable major thirds (diminished fourths): B – D# / F# - A# / C# - E# / A flat - C.
- 1 fifth known as the “wolf” (very dissonant extended fifth): G# - E flat.
- Hi hly irre ular chromatic scale (meanin that chromatic compositions are iven a very distinctive voice)
- Keys usable with this temperament: C maj. / D maj. / G maj. / A maj. / B flat maj. and the relative minors.
The temperaments which follow allow all the major and minor keys to be used, althou h those with the most
alterations have a hi hly distinctive voice, in contrast with the modern equal temperament.
WERCKMEISTER
This temperament, invented by the or anist and musical theorist Andreas Werckmeister, is recommended for
performin the German musical repertoire of the late 1600s.
KIRNBERGER
This temperament, developed by Johann Philipp Kirnber er, pupil of J.S. Bach, is also suitable for playin the
German baroque composers and the works of Bach.
PYTHAGOREAN
This temperament, in which the fifths were preserved perfectly pure, dates from the Middle A es up to the 15th
century, and can therefore be used for compositions of that period.