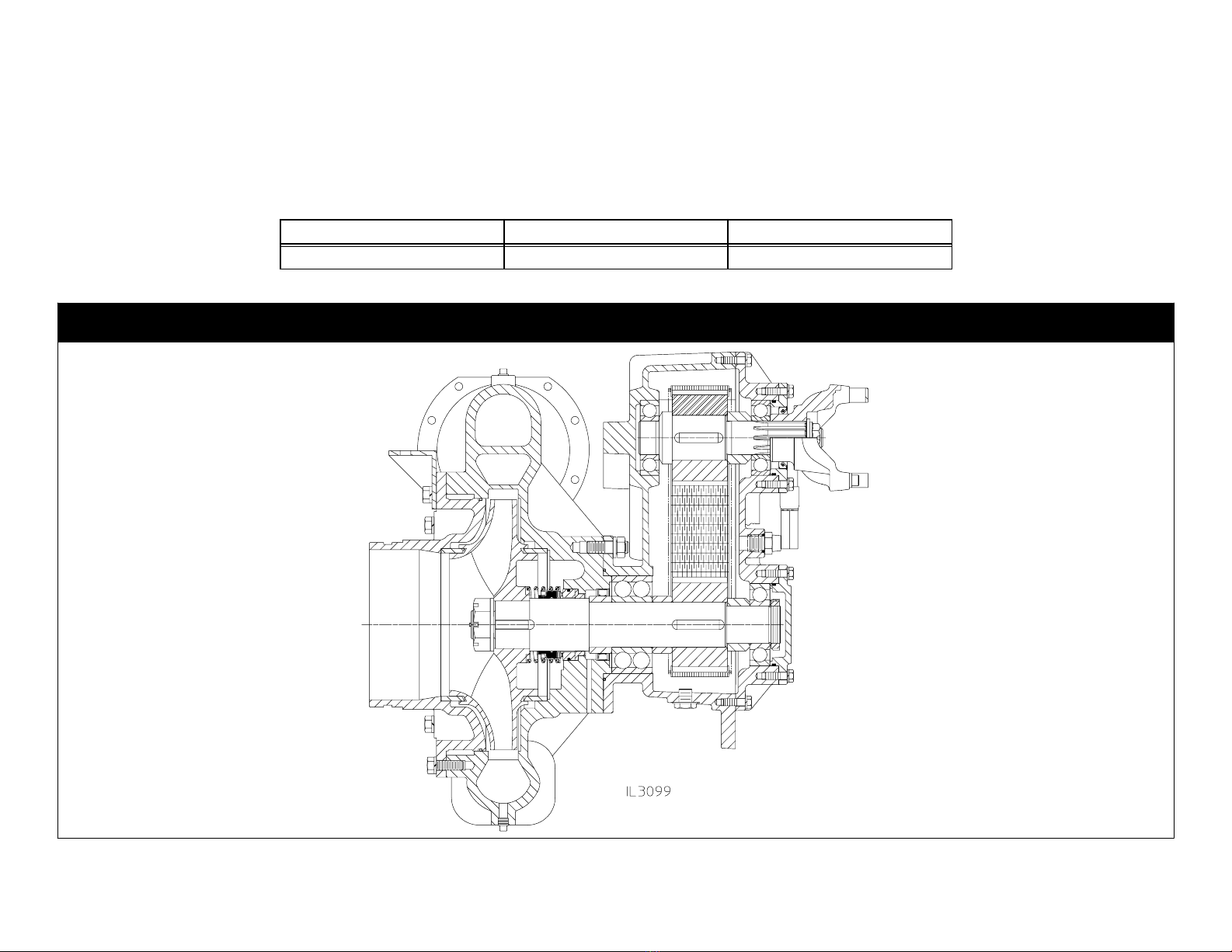
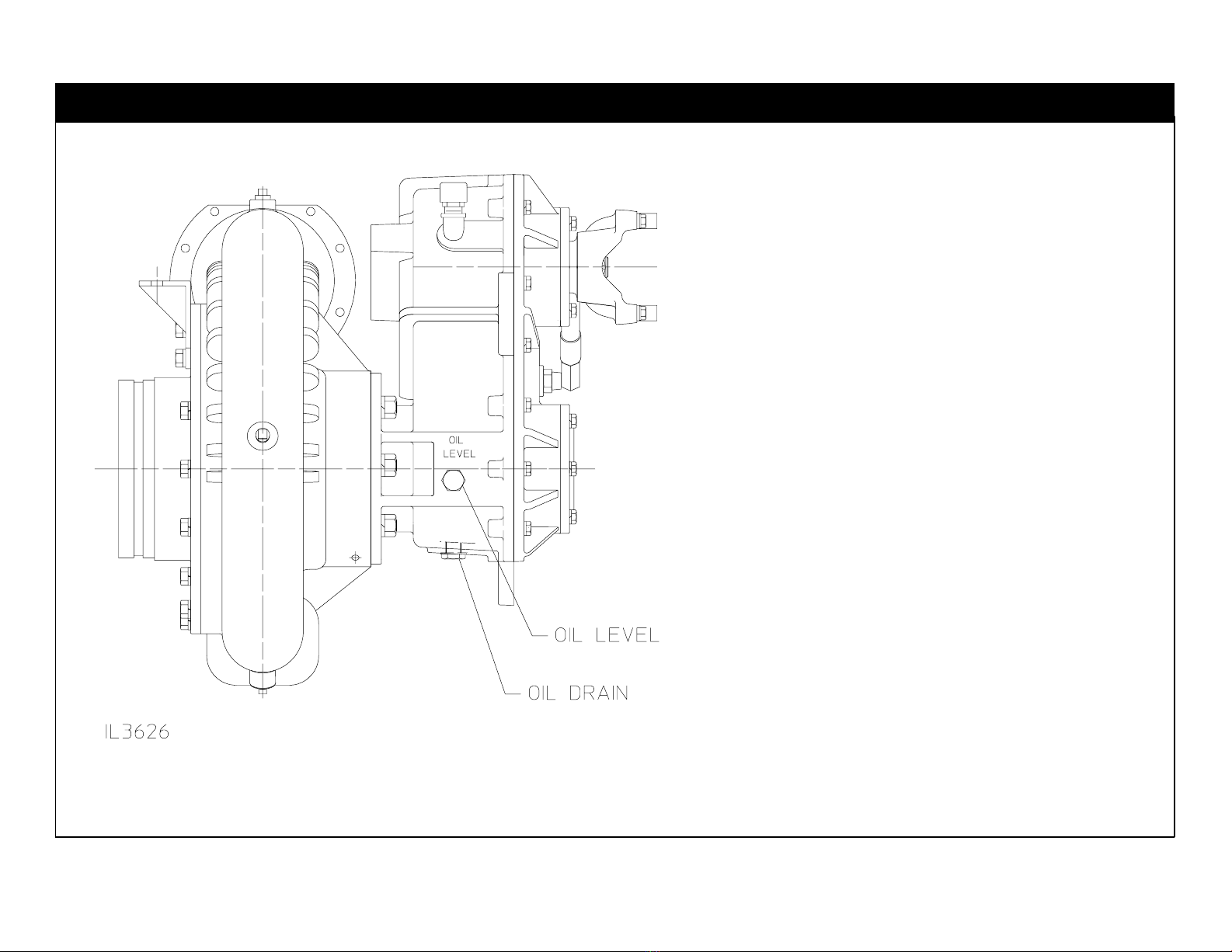
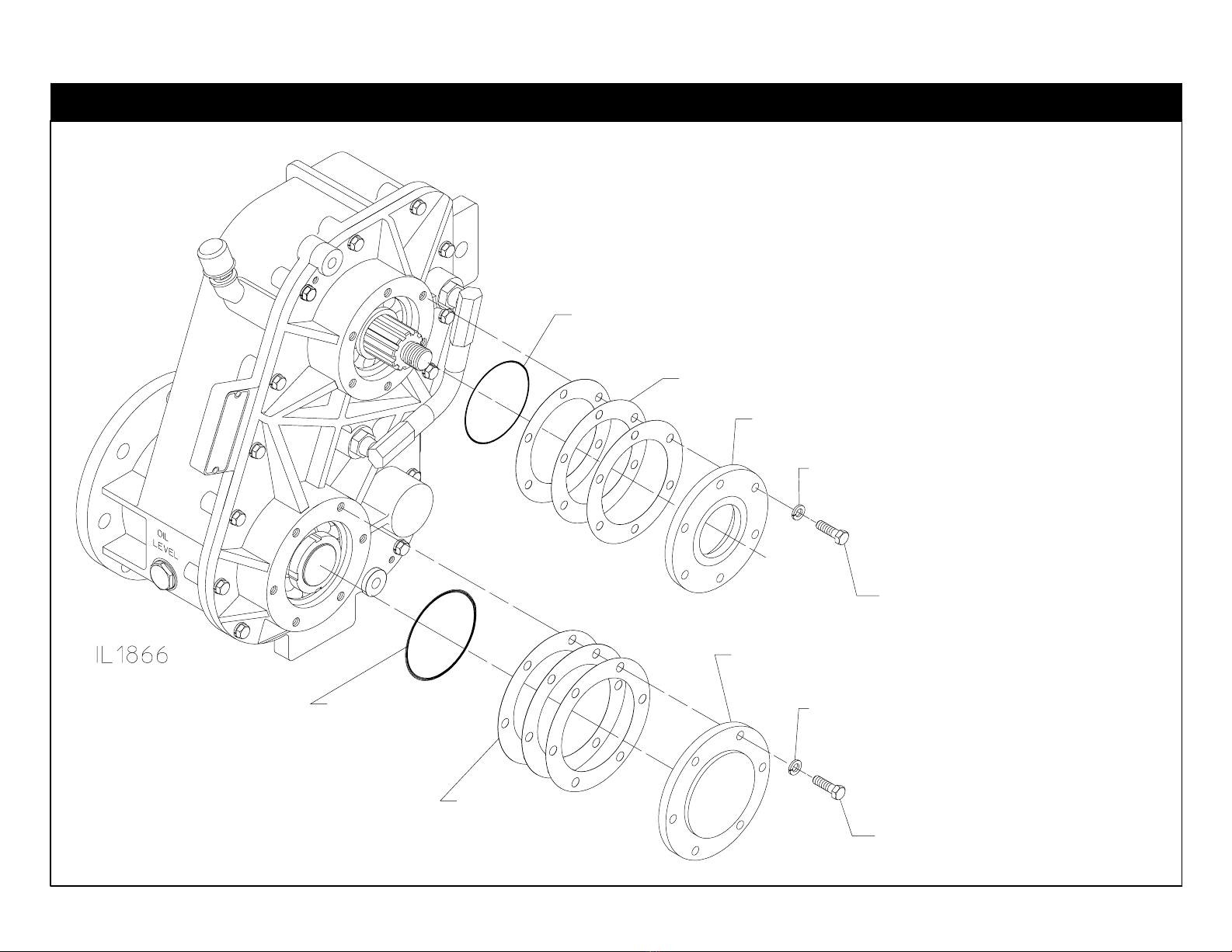
F-1031, Section 4312 Page 3 of 23
General Overhaul Information
Tools and Equipment
The following tools and equipment are needed to overhaul a pump:
1. Usual automotive mechanic's hand tools.
2. An arbor press for assembling or disassembling components.
3. An engine lathe for turning impeller hubs.
4. A suitable hoist and slings.
5. Torque capability up to 325 lb-ft.
While no special tools and equipment are required, a few special items are
illustrated or described so the mechanic can make them or they are available
from the apparatus manufacturer or the Waterous Company. These special
items are not absolutely necessary, but they will make the mechanic's work
much easier.
Preliminary Testing
Before disassembling a pump, test it thoroughly, if possible, and record the
results. A comparison of this test with periodic tests recommended in form
F-1031, Section 1000 can often reveal specific pump troubles. Excessive
speed, for instance, indicates that impellers and/or wear rings are probably
worn.
Cleaning
The continued satisfactory operation of a pump depends to a great extent
upon the cleanliness of its internal parts. Sand, dirt or other abrasive material
will wear bearings, gears and related parts. Before disassembling a pump for
repairs, be sure to clean its exterior. Make sure the working space, benches
and tools are clean. Use only clean, lint-free cloths to wipe off components.
Before reassembling a pump or its components, be sure to clean them thor
oughly.
Pump Bodies and Impellers
Flush out these components and related parts with clean water. Use a stiff
brush to remove loose scale, caked sediment, etc. Be sure to remove all
traces of old gaskets. Examine pump bodies, covers, adapters and fittings for
cracks, severe corrosion or other damage. Almost all damage to these parts
results from improper use or maintenance, or from freezing. Replace defective
parts.
Bearings, Gaskets, Seals and O-rings
Parts of this nature are frequently damaged during removal or disassembly. In
addition, they sometimes deteriorate or lose their effectiveness because of
age or misuse. Replacing these parts whenever overhauling a pump is a good
policy.
Impeller Shafts
Examine shaft for severe scratches, grooves or corrosion - especially under
packing or mechanical seals. If scratches are not severe, and are not under
packing and seals, clean them with a fine-cut file. Grooves are usually per
missible if they are not sharp or too deep. Even slight longitudinal scratches
will cause leaks and should be removed.
Installing Ball Bearings
Most Waterous pumps are designed so that ball bearings fit tightly on their
shafts and have relatively loose fits in the bearing housings. When mounting
these bearings on shafts, always apply force to the inner races. When bear
ings have a tight fit in the housings, and a heavy force is necessary to install
them, be sure to apply force only to the outer bearing races. For either type of
fit, applying force to the wrong bearing race may damage the balls and race.
Transmission Case Gaskets
To provide added sealing for gaskets between transmission halves, coat both
sides of these gaskets with a suitable sealant. A compound such as Permatex
Super 300 is recommended for this application. Be sure all traces of previous
gaskets and sealant are removed before installing new gaskets.