~
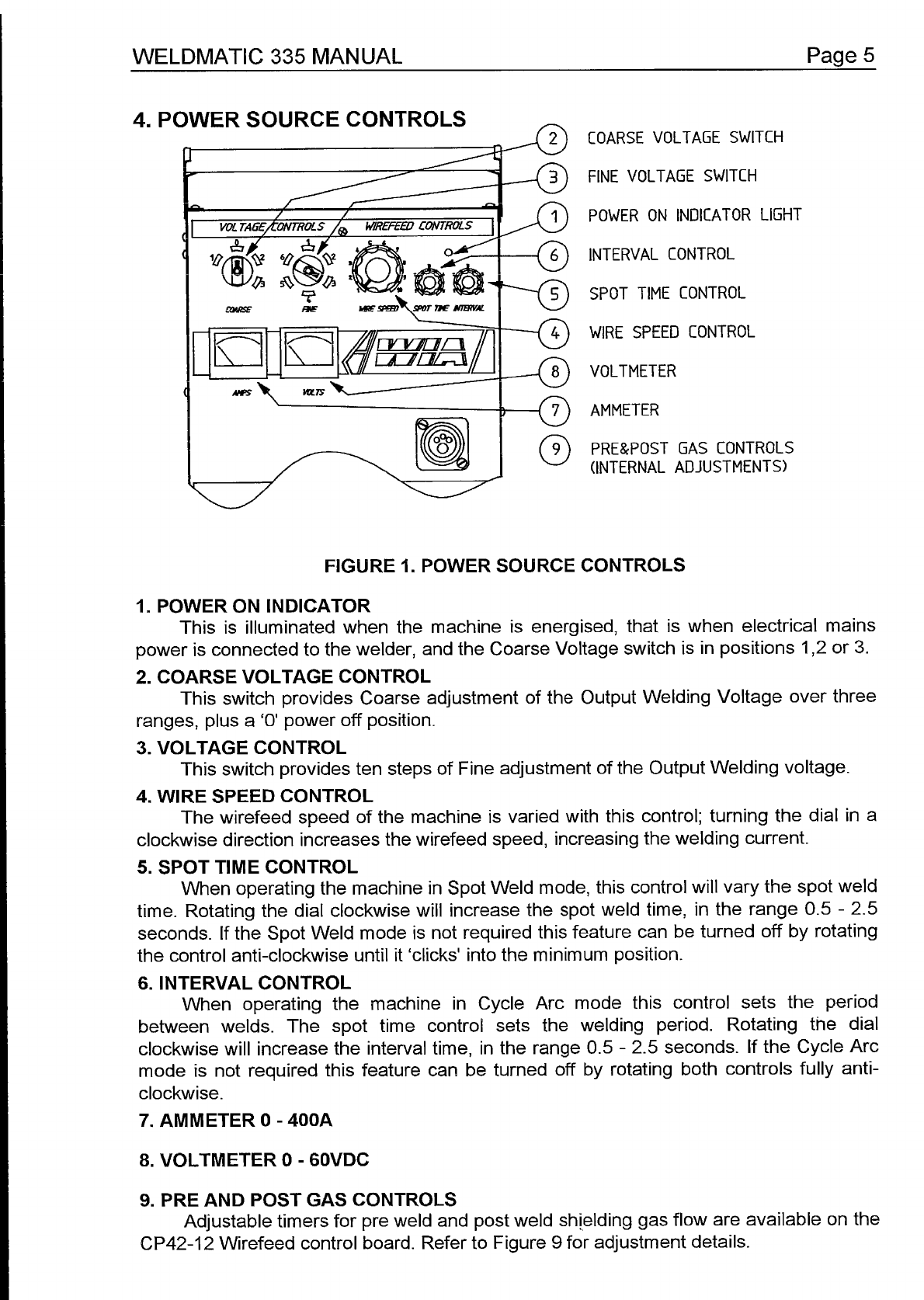
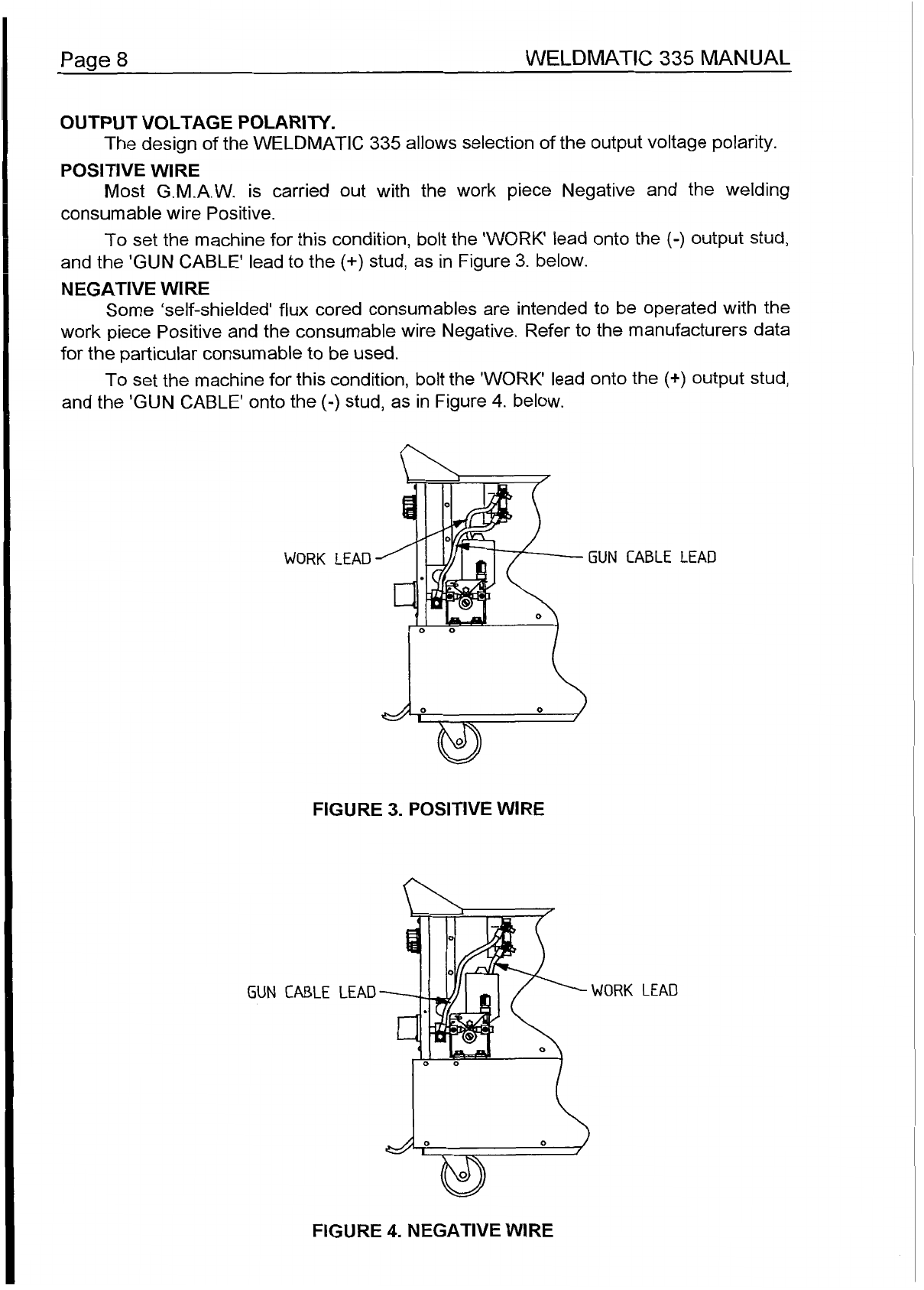
WELDMATIC
335
MANUAL
Paae
7
-
-cl
FITTINGTHE GUN CABLE
The BERNARDBEQA31OAEguncable is equippedwitha 'Euro8wirefeeder
connector which incorporates all required connection pointsto the gun cable for welding
current, shieldinggas and gun switch control.
To attach the guncable
to
the wirefeeding mechanism, engagethe mating
parts
of
the male and female Euroconnectors,thenrotate the lockingring clockwise to firmly
secure the connection.
FITTINGTHE GAS BOTTLE
Dependingon configuration of the cylinderto be used,the gas flowmeter
/
regulator
may be fitted directly to the cylinder, or in conjunctionwithan elbow fitting.
DO
NOT
apply any greaseto thesejoints, and tightenthe nuts securely.
Fit the end of the gasinlet hose from the backpanel of the machineto the
connector supplied with the flow regulator, and secure withthe clampalso supplied.
FITTINGTHE CONSUMABLE WIRE
The quality of the consumable wiregreatlyaffectshowreliablya gas metal arc
welder will operate. Forbest results when welding mild steel, werecommendquality WIA
AUSTMIG ES6. Dirty, rusty
or
kinked wire will not feed smoothly through the gun cable
and will cause erratic welding.Deposits from thewire will clog the gun cable liner
requiring
it
to be replacedprematurely.
Placethe
spool
of welding wire ontothe spool holder. The location pin should mate
withaholeprovidedon the wirespoolbody.Fitthe spool retaining'R' clip supplied.
Check the adjustment
of
the spool brake, which should be set to prevent over-run of the
wire spool at the end of a weld, without unduly loading the wirefeed motor. The braking
can be adjusted bythe Nyloc nut using a 15/16"
AF
or 24mm socket wrench.
SELECTION
OF
START MODE
The
WELDMATIC
335
offers selection between 'Creep' and 'Standard' arc starting
modes. In creep mode,the electrode wireisfed at a reduced speedwhen thegun-switch
is
first closed. Once the arc is initiated, the wire accelerates to full welding speed. This
mode producesasofterarcstartwhich is recommended for aluminium welding
applications. If a faster arc startis required, standard modeshould be selected.
The selector switch is located on the wirefeed control board CP42-12 as shown in
Figure 11.Slide the switch upwards to select'Creep' mode, and downwards to select
'Standard' mode.
FEEDINGTHE CONSUMABLE WIRE
I
WIRE INCH
Withreference to Figure14,release the pressurescrew (IO), and rotate the
pressure arm
(8)
to the open position. The end of the welding wire can now be passed
through the inlet guide, over the bottom driven roller, andintothe output wire guide tube.
Check that the drive roller groove
is
correct for the wire in use. The appropriate size is
stamped onthe visible side of the installed roller. Check also thatthe correct size contact
tip is fitted at the gun end. Drive roller and tip details are available in Section
11
of this
manual.
Return the pressure arm to the closed position and, adjust the compressionscrew
to provide sufficient clamping of the drive rolls driveto achieve constantwirefeed. Do not
over tighten.
Withthe machine energised,close the gun switch to feedwire through the gun
cable.
If
creep speed
is
selected the wire will be initially fed at reduced speed, however
after a
short
timed periodthe ratewill increaseto
full
welding speed.