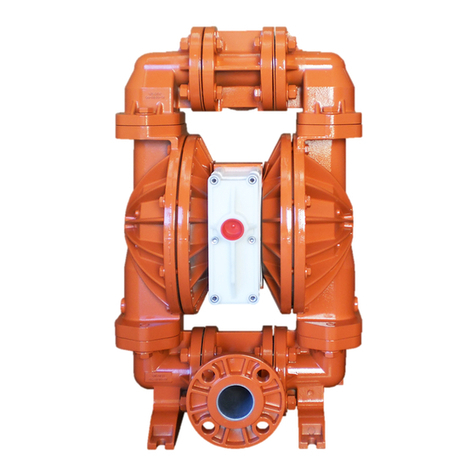
The P4 pump has a 38 mm (1-1/2") inlet and 38 mm (1-1/2")
outlet and is designed for flows to 354 lpm (94 gpm). The
P4 Plastic pump is manufactured with wetted parts of pure,
unpigmented, PTFE or polypropylene. The P4 Plastic is
constructed with a polypropylene center block. A variety of
diaphragms and O-rings are available to satisfy temperature,
chemical compatibility, abrasion and flex concerns.
The suction pipe size should be at least 38 mm (1-1/2")
diameter or larger if highly viscous material is being pumped.
The suction hose must be non-collapsible, reinforced type
as the P4 is capable of pulling a high vacuum. Discharge
piping should be at least 38 mm (1-1/2"); larger diameter can
be used to reduce friction losses. It is critical that all fittings
and connections are airtight or a reduction or loss of pump
suction capability will result.
For P4 Plastic models, Wilden offers 150 lb standard and
metric flanges. The following details should be noted when
mating these to pipe works:
• A 60–80 shore gasket that covers the entire ßflange face
should be used.
• The gasket should be between 1.91 mm (0.075") and 4.45
mm (0.175") thickness.
• Mating flanges with flat as opposed to raised surfaces
should be used for proper mechanical sealing.
• The flanges should be tightened to a minimum of 6.8
N•m (5 ft-lb) but no more than 13.5 N•m (10 ft-lb).
INSTALLATION: Months of careful planning, study,
and selection efforts can result in unsatisfactory pump
performance if installation details are left to chance.
Premature failure and long term dissatisfaction can be
avoided if reasonable care is exercised throughout the
installation process.
LOCATION: Noise, safety, and other logistical factors usually
dictate where equipment be situated on the production
floor. Multiple installations with conflicting requirements
can result in congestion of utility areas, leaving few choices
for additional pumps.
Within the framework of these and other existing conditions,
every pump should be located in such a way that five
key factors are balanced against each other to maximum
advantage.
ACCESS: First of all, the location should be accessible. If
it’s easy to reach the pump, maintenance personnel will
have an easier time carrying out routine inspections and
adjustments. Should major repairs become necessary, ease
of access can play a key role in speeding the repair process
and reducing total downtime.
AIR SUPPLY: Every pump location should have an air line
large enough to supply the volume of air necessary to
achieve the desired pumping rate (see Section 5). Use air
pressure up to a maximum of 8.6 bar (125 psig) depending
on pumping requirements.
For best results, the pumps should use a 5µ micron air
filter, needle valve and regulator. The use of an air filter
before the pump will insure that the majority of any pipeline
contaminants will be eliminated.
SOLENOID OPERATION: When operation is controlled by a
solenoid valve in the air line, three-way valves should be
used, thus allowing trapped air to bleed off and improving
pump performance. Pumping volume can be set by
counting the number of strokes per minute and multiplying
by displacement per stroke.
Sound levels are reduced below OSHA specifications using
the standard Wilden muffler element. Other mufflers can be
used but usually reduce pump performance.
ELEVATION: Selecting a site that is well within the pump’s
dynamic lift capability will assure that loss-of-prime troubles
will be eliminated. In addition, pump efficiency can be
adversely affected if proper attention is not given to site
location.
PIPING: Final determination of the pump site should not be
made until the piping problems of each possible location
have been evaluated. The impact of current and future
installations should be considered ahead of time to make
sure that inadvertent restrictions are not created for any
remaining sites.
The best choice possible will be a site involving the shortest
and straightest hook-up of suction and discharge piping.
Unnecessary elbows, bends, and fittings should be avoided.
Pipe sizes should be selected so as to keep friction losses
within practical limits. All piping should be supported
independently of the pump. In addition, the piping should
be aligned so as to avoid placing stresses on the pump
fittings.
Flexible hose can be installed to aid in absorbing the forces
created by the natural reciprocating action of the pump. If the
pump is to be bolted down to a solid location, a mounting
pad placed between the pump and the foundation will assist
in minimizing pump vibration. Flexible connections between
the pump and rigid piping will also assist in minimizing
pump vibration. If quick-closing valves are installed at any
point in the discharge system, or if pulsation within a system
becomes a problem, a surge suppressor should be installed
to protect the pump, piping and gauges from surges and
water hammer.
When pumps are installed in applications involving flooded
suction or suction head pressures, a gate valve should be
installed in the suction line to permit closing of the line for
pump service.
For P4 Plastic models, a non-raised surfaced-flange adapter
should be utilized when mating to the pump’s inlet and
discharge manifolds for proper sealing.
If the pump is to be used in a self-priming application, be
sure that all connections are airtight and that the suction lift
is within the model’s ability. Note: Materials of construction
and elastomer material have an effect on suction lift
parameters. Please consult Wilden distributors for specifics.
Pumps in service with a positive suction head are most
efficient when inlet pressure is limited to 0.5–0.7 bar (7–10
psig). Premature diaphragm failure may occur if positive
suction is 10 psig and higher.
THE MODEL P4 CHAMP WILL PASS 0.5 MM (3/16") SOLIDS.
WHENEVERTHE POSSIBILITY EXISTSTHAT LARGER SOLID
OBJECTS MAY BE SUCKED INTO THE PUMP, A STRAINER
SHOULD BE USED ONTHE SUCTION LINE.
CAUTION: DO NOT EXCEED 8.6 BAR (125 PSIG) AIR SUPPLY
PRESSURE.
P4 PUMPS CANNOT BE SUBMERGED. FOR SUBMERGED
APPLICATIONS, USE A WILDEN T4 PUMP.
WILDEN PUMP & ENGINEERING, LLC 8 WIL-10160-E-10
Section 6
SUGGESTED INSTALLATION