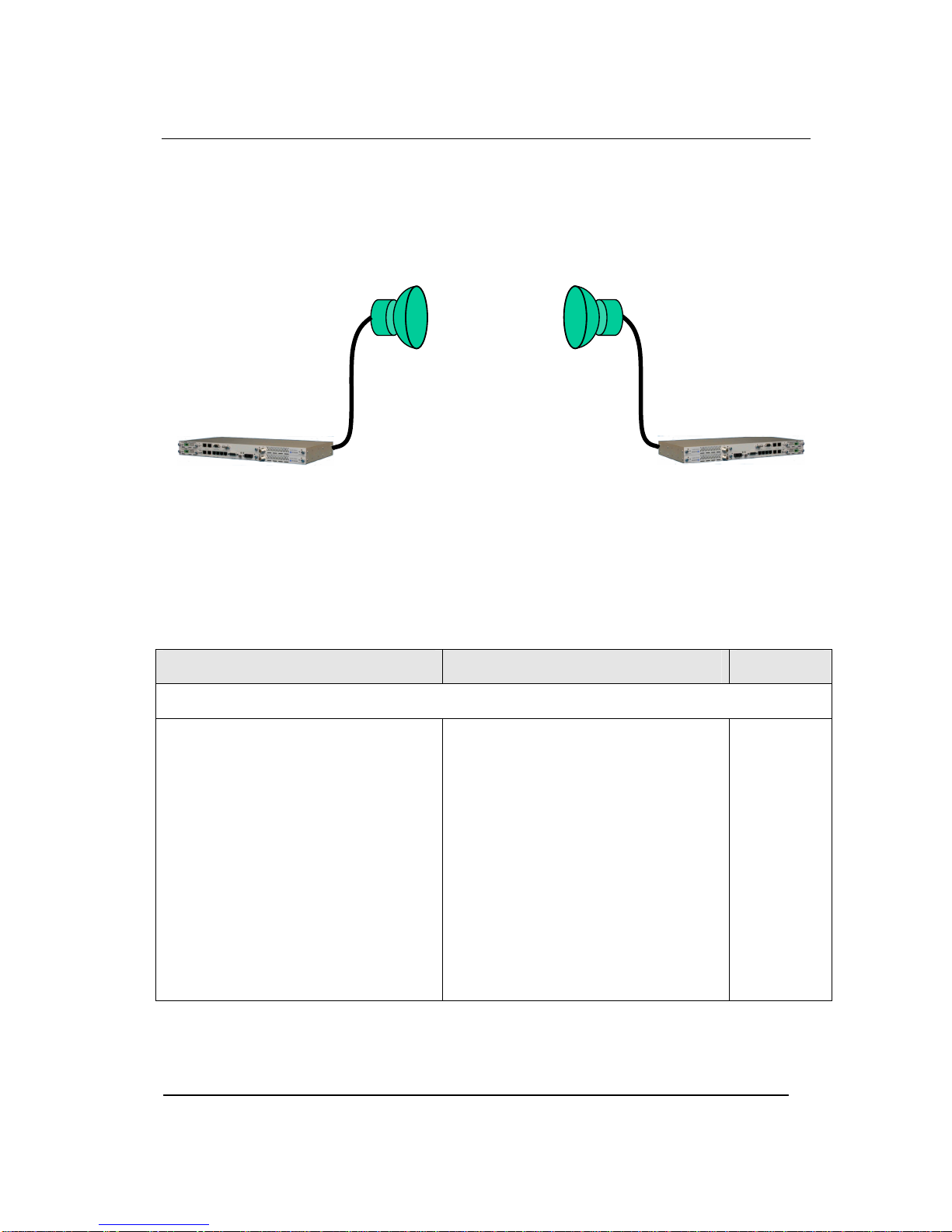
This manual is provided by WNI Global and its confidentiality is preserved. Without the pre-written consent from WNI Global, anyone
may not disclose, extract, cite or publish any part or all parts of this manual. Version No.: V2.0
Table of Contents
1
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION.......................................................................................................................1-1
1.1
About This Manual..........................................................................................................................................1-1
1.2
Introduction .....................................................................................................................................................1-1
1.3
System Features...............................................................................................................................................1-4
1.4
Physical Description........................................................................................................................................1-5
1.4.1
Front Panel Indicators................................................................................................................................1-6
1.4.2
Front Panel Connections............................................................................................................................1-6
1.5
System Description........................................................................................................................................1-10
1.6
Consecutive Point Architecture....................................................................................................................1-13
1.7
Power Management.......................................................................................................................................1-15
1.8
Network Management...................................................................................................................................1-16
1.9
ODU data........................................................................................................................................................1-16
1.9.1
Feature Summary.....................................................................................................................................1-16
1.9.2
ODU Specification summary...................................................................................................................1-17
1.9.3
IDU Software Selectable Capacities........................................................................................................1-18
2
INSTALLATION...................................................................................................................................2-19
2.1
Unpacking ......................................................................................................................................................2-19
Challenger L ODU ..................................................................................................................................................2-19
2.2
Notices.............................................................................................................................................................2-20
2.3
PRE-INSTALLATION NOTES...................................................................................................................2-21
2.3.1
Back-to-Back Bench Testing...................................................................................................................2-21
2.4
Overview of Installation and Testing Process.............................................................................................2-22
2.5
Site Evaluation...............................................................................................................................................2-23
2.5.1
Preparing for a Site Evaluation................................................................................................................2-24
2.5.2
Site Evaluation Process............................................................................................................................2-25
2.5.3
Critical System Calculations....................................................................................................................2-27
2.5.4
Documenting a Site Evaluation ...............................................................................................................2-29
2.6
Installation of the Challenger L Digital Radio............................................................................................2-32
2.6.1
Installing the Challenger L IDU ..............................................................................................................2-32
2.6.2
Preparing for ODU Installation................................................................................................................2-33
2.6.3
Routing the ODU/IDU Interconnect Cable..............................................................................................2-35
2.6.4
Connecting the Challenger L IDU to the PC and Power Source .............................................................2-36
3
SUMMARY SPECIFICATION................................................................................................................3-1
4
FRONT PANEL CONNECTORS...........................................................................................................4-1