ZiLOG Z8 GP ZGP323 User manual

ZiLOG Worldwide Headquarters • 532 Race Street • San Jose, CA 95126
Telephone: 408.558.8500 • Fax: 408.558.8300 • www.ZiLOG.com
Introduction
Thank you for purchasing the ZiLOG Z8 GP In-Circuit Emulator (ICE) and Development
Platform, ZGP323ICE15ZEM. The Z8 GP ICE provides Z8 GP family chip emulation
with a trace and event system for program debugging using ZDS II development tools.
Once your code is complete, use the included OTP programming module to burn your
design to OTP devices.
This startup guide tells you how to:
1. Install ZDS II software.
2. Configure the Z8 GP ICE for connection to your PC.
The kit includes a 28-PDIP target POD and programming adapter. Target
PODs and adapter support for other packages must be ordered separately. See
section “Adapter Kit Ordering Information” on page 23 for details.
3. Use a target POD to connect the Z8 GP ICE to a target board such as the Z8 GP
ZGP323 evaluation board (included) with a 20-, 28-, or 40-PDIP socket. (Converters
for 20- and 28-SOIC and 20-, 28-, and 48-SSOP sockets are available in the adapter
kits described on page 23.)
4. Connect the Z8 GP ICE to a supplied OTP programming module.
5. Use the supplied OTP programming module with ZDS II software to program a 20-,
28-, or 40-PDIP Z8 GP family device. (Adapters for 20- and 28-SOIC and for 20-, 28-
and 48-SSOP packages are available in the adapter kits described on page 23.)
6. Run a demonstration program to verify proper operation, illustrate basic operation of
the trace and event system, and burn a Z8 GP OTP device using the OTP program-
ming module.
Software Requirements
Table 1 lists the PC requirements for running ZDS II.
Note:
ZGP323ICE15ZEM
Z8 GP™ ZGP323 In-Circuit Emulator
and Development Platform
User Manual UM019301-0505

Z8 GP™ ZGP323 In-Circuit Emulator and Development Platform
User Manual
Page 2
Install the Software UM019301-0505
Install the Software
Follow these steps to install ZDS II with the ANSI C-Compiler.
1. Insert the ZDS II CD into your computer’s CD-ROM drive. DemoShield launches
automatically. If it does not automatically launch, go to the root of the CD-ROM and
double-click the file launch.exe.
2. DemoShield provides several installation choices. Select “Install ZDS II” to install
now. You can install other software and accompanying documentation later.
3. Follow the instructions on the screen to complete the installation.
4. To receive free technical support, please register your software at http://
www.zilog.com. Access the registration page by opening the Support menu at the top
of the web page and clicking “Product Registration.”
Install the Hardware
The Z8 GP ZGP323 ICE and Development Platform features an Ethernet interface and an
RS-232 serial port. Hardware installation consists of:
•Installing a target POD into a 20- or 28-PDIP socket on a target development board,
such as the Z8 GP ZGP323 evaluation board (included);
•Connecting the Z8 GP ICE to the target POD;
Table 1. ZDS II System Requirements
Recommended Configuration Minimum Configuration
• PC running MS Windows XP, SP1
• Pentium III/500 MHz processor
• 128 MB RAM
• 40 MB hard disk space
• Super VGA video adapter
• CD-ROM drive
• Ethernet port
• One or more RS-232 communications ports
• Internet browser (Internet Explorer or
Netscape)
• PC running MS Windows 98SE/WinNT 4.0–
SP6/Win2000–SP3/WinXP–SP1
• Pentium II/233 MHz processor
• 96 MB RAM
• 15 MB hard disk space (documentation not
included)
• Super VGA video adapter
• CD-ROM drive
• Ethernet port
• One or more RS-232 communications ports
• Internet browser (Internet Explorer or
Netscape)
Z8 GP™ ZGP323 In-Circuit Emulator and Development Platform
User Manual
Page 3
UM019301-0505 Install the Hardware
•Connecting the Z8 GP ICE to the OTP programming module; and
•Connecting the Z8 GP ICE to a PC.
You may have to reconfigure network settings on the PC or on the Z8 GP ICE before using
the emulator.
Installing a Target POD onto a Target Development Board
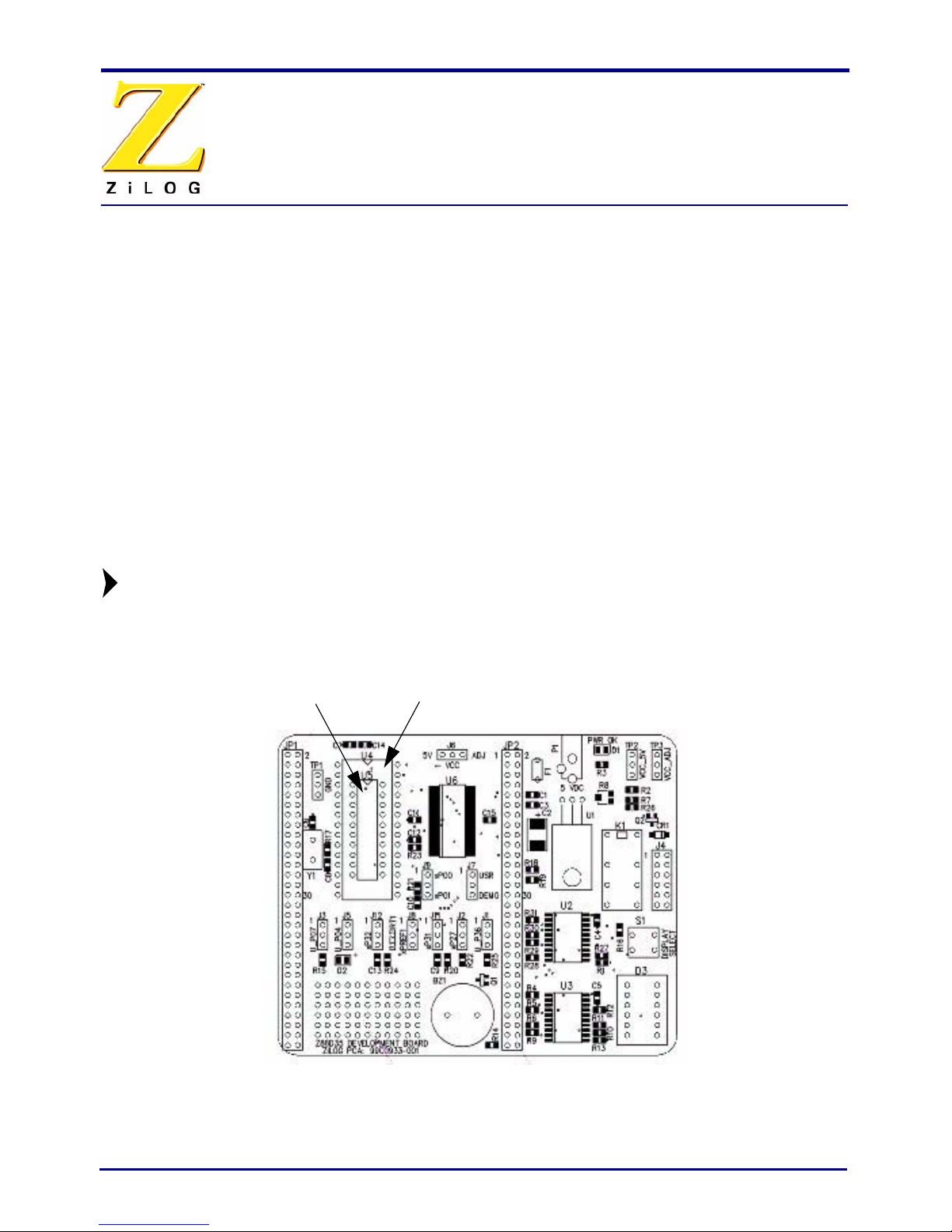
The Z8 GP ICE kit is ideal for use with a Z8 GP ZGP323 evaluation board (included, see
Figure 1) as a target development board. The 20-, 28, and 40-PDIP target PODs plug into
the associated PDIP sockets on the development platform.
If you are using a different target development board, use an appropriate target POD and
pin converter to connect the Z8 GP ICE to the board. For example, if your target board has
a 20-SOIC socket, mate the 20-PDIP target POD onto the 20-PDIP to 20-SOIC converter.
Then install the target POD and converter assembly into the board’s 20-SOIC socket.
If you are not using a target development board, insert the 34-pin null target
connector, p/n 93c0086-001, into Z8 GP ICE target interface connector P16.
Figure 1. Z8 GP ZGP323 Evaluation Board
Note:
20-PDIP 28-PDIP

Z8 GP™ ZGP323 In-Circuit Emulator and Development Platform
User Manual
Page 4
Install the Hardware UM019301-0505
Connecting the Z8 GP ICE to the Target POD
Once you have installed the appropriate target POD (and converter, if required) onto the
target development board, connect the Z8 GP ICE to the target POD as follows:
•40-PDIP target POD:
– Connect the 16-circuit cable from P17 on the emulator to P17 on the 40-PDIP tar-
get POD.
– Connect the 34-circuit cable from P16 on the emulator to P16 on the 40-PDIP target
POD.
•20-PDIP and 28-PDIP target PODs: Connect the 34-circuit cable from P16 on the
emulator to P16 on the target POD. (Emulator connector P17 is not used.)
Connecting the Z8 GP ICE to the OTP Programming Module (Optional)
After developing and debugging your software, use the following instructions to connect
the Z8 GP ICE to the OTP programming module so you can burn your code onto chips.
1. Connect the 40-circuit ribbon cable from the Z8 GP ICE OTP Programming connector
to connector P1 on the OTP programming module.
2. The 40-PDIP ZIF socket on the OTP programming module is designed to accept 40-
PDIP OTP chips. The OTP programming adapters (see Table 4 on page 24) allow you
to adapt the ZIF socket to accept 20-SOIC, 20-SSOP, 20-PDIP, 28-SOIC, 28-SSOP,
28-PDIP, and 48-SSOP chip packages.
Once you have installed the OTP chip into the ZIF socket (or programming adapter), you
are ready to program the chip using the instructions in “OTP Programming” on page 18.
Connecting the Z8 GP ICE to a PC
1. Connect a CAT-5 crossover cable from the PC to the Ethernet port on the Z8 GP ICE.
See Figure 2.
If you prefer, you can connect the emulator to an Ethernet hub using a stan-
dard CAT-5 patch cable.
Note:

Z8 GP™ ZGP323 In-Circuit Emulator and Development Platform
User Manual
Page 5
UM019301-0505 Install the Hardware
2. Connect the serial COM port on the PC to the SETUP serial port on the Z8 GP ICE
using the DB9-to-DB9 serial cable. See Figure 3.
Figure 2. Connecting a PC to the Z8 GP ICE
Figure 3. Z8 GP ICE Rear Panel
3. Connect a 5VDC power supply to the Z8 GP ICE. The 3.3VDC should illuminate (see
Figure 3). If the 3.3VDC LED fails to illuminate or the ICE Fail LED illuminates (see
Figure 5), there is a problem with the unit. Contact ZiLOG support at http://
www.zilog.com for a replacement unit.
Figure 4. Z8 GP ICE Top View
PC Z8 GP
ICE
CAT-5 Crossover Cable
DB9-to-DB9 Cable
J9
Out In
Target Trigger
1
J8
GND
1
J7
Int Target
CLK Source
1
OTP Programming
P17
P16
Target Interface
Target Interface
D1

Z8 GP™ ZGP323 In-Circuit Emulator and Development Platform
User Manual
Page 6
Configure the Hardware UM019301-0505
Figure 5. Z8 GP ICE Front-Panel
Configure the Hardware
Configuring the Z8 GP ICE consists of selecting emulator jumper options and setting up
Ethernet communications between the emulator and your PC.
Setting Jumpers on the Z8 GP ICE
There is one jumper on the Z8 GP ICE. Jumper J7 allows you to select whether the emula-
tor uses the target board clock or is programmable using the programmable clock settings
in ZDS II.
Table 2. Jumper J7 Settings on the Z8 GP ICE
Emulator... Jumper Position
uses the target clock. 1 - 2 (default)
uses the internal ZDS II
programmable clock.
2 - 3
ICE Fail LEDICE Run LED

Z8 GP™ ZGP323 In-Circuit Emulator and Development Platform
User Manual
Page 7
UM019301-0505 Configure the Hardware
Setting Up Ethernet Communications
The default IP address and subnet mask of the Z8 GP ICE are 192.168.1.50 and
255.255.255.0, respectively. To enable communication between the PC running ZDSII and
the Z8 GP ICE, you must either change the PC’s Ethernet settings to match those of the Z8
GP ICE or vice versa.
If using the PC in a stand-alone configuration, set the PC’s IP address to 192.168.1.21 and
its subnet mask to 255.255.255.0. See “Changing the PC’s Settings to Match the Z8 GP
ICE” on page 7.
In a networked environment, set the Z8 GP ICE IP address and subnet mask to match the
network setup. See “Changing Z8 GP ICE Settings to Match the PC” on page 11.
Changing the PC’s Settings to Match the Z8 GP ICE
After completing the following steps to change the PC’s Ethernet settings, proceed to Run-
ning a Sample Project on page 14.
The following instructions are for MS Windows XP. If your Windows operat-
ing system is different, refer to your MS Windows OS online help for details.
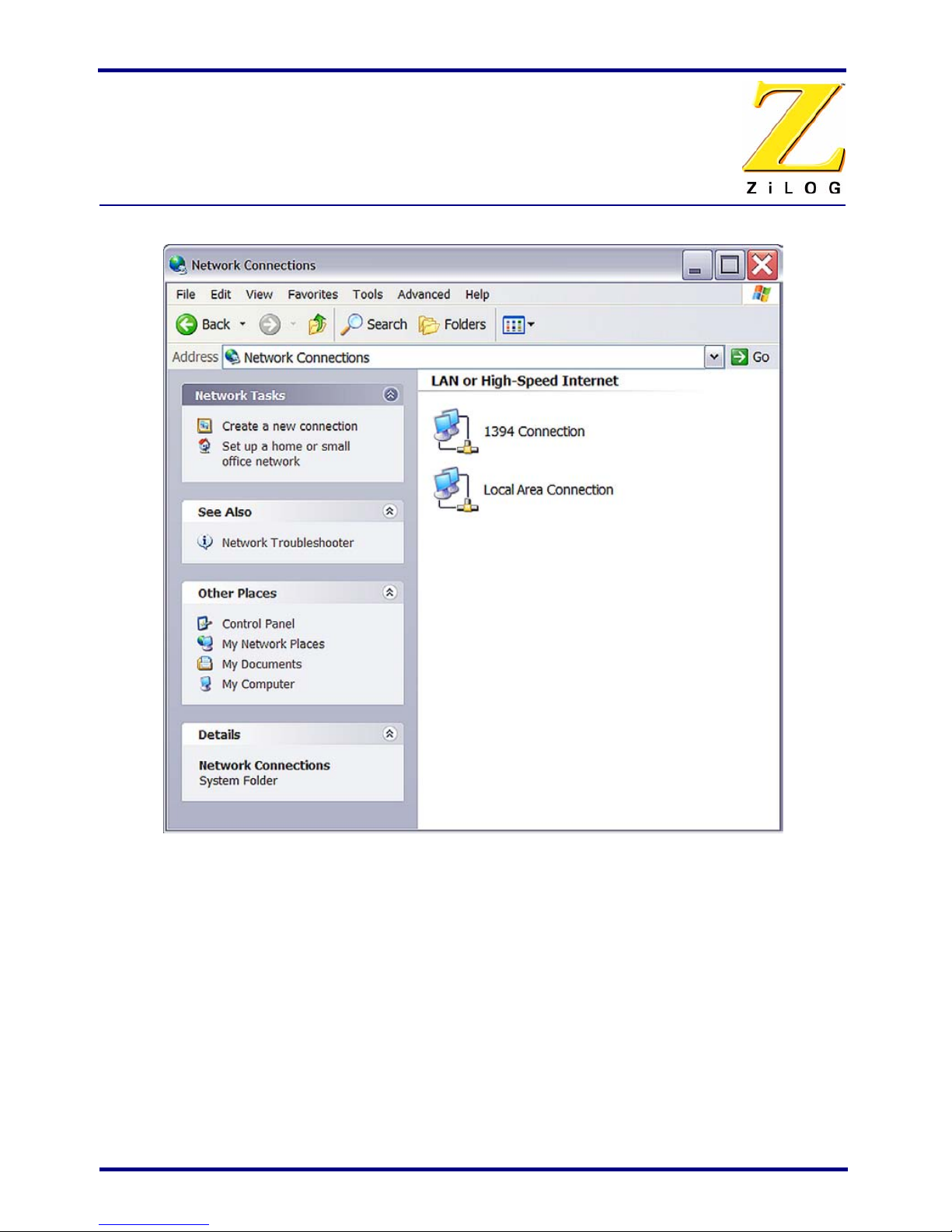
1. Open the Windows Control Panel and double-click the Network and Internet
Connections icon. The Network Connections dialog box appears (see Figure 6).
Note:
Z8 GP™ ZGP323 In-Circuit Emulator and Development Platform
User Manual
Page 8
Configure the Hardware UM019301-0505
Figure 6. The Network Dialog

Z8 GP™ ZGP323 In-Circuit Emulator and Development Platform
User Manual
Page 9
UM019301-0505 Configure the Hardware
2. In the panel labeled LAN or High-Speed Internet, double-click the Local Area Connec-
tion icon. The Local Area Connection Status dialog box appears (Figure 7).
Figure 7. The Local Area Connection Status Dialog

Z8 GP™ ZGP323 In-Circuit Emulator and Development Platform
User Manual
Page 10
Configure the Hardware UM019301-0505
3. In the Local Area Connection Status dialog box, click the Properties button. The Local
Area Connection Properties dialog box appears (Figure 8).
Figure 8. The Local Area Connection Properties Dialog
Other manuals for Z8 GP ZGP323
1
Table of contents
Other ZiLOG Motherboard manuals

ZiLOG
ZiLOG Z183 EMAC User manual

ZiLOG
ZiLOG Z51F0811 MCU User manual

ZiLOG
ZiLOG Z8 Encore! User manual

ZiLOG
ZiLOG Z8 Encore! User manual

ZiLOG
ZiLOG GP ZGP323 ICE User manual

ZiLOG
ZiLOG Z8 Encore! XP F0822 Series Flash MCU User manual

ZiLOG
ZiLOG Z8F08A28100KITG User manual

ZiLOG
ZiLOG Z8 Encore! 8K/4K MCU User manual

















