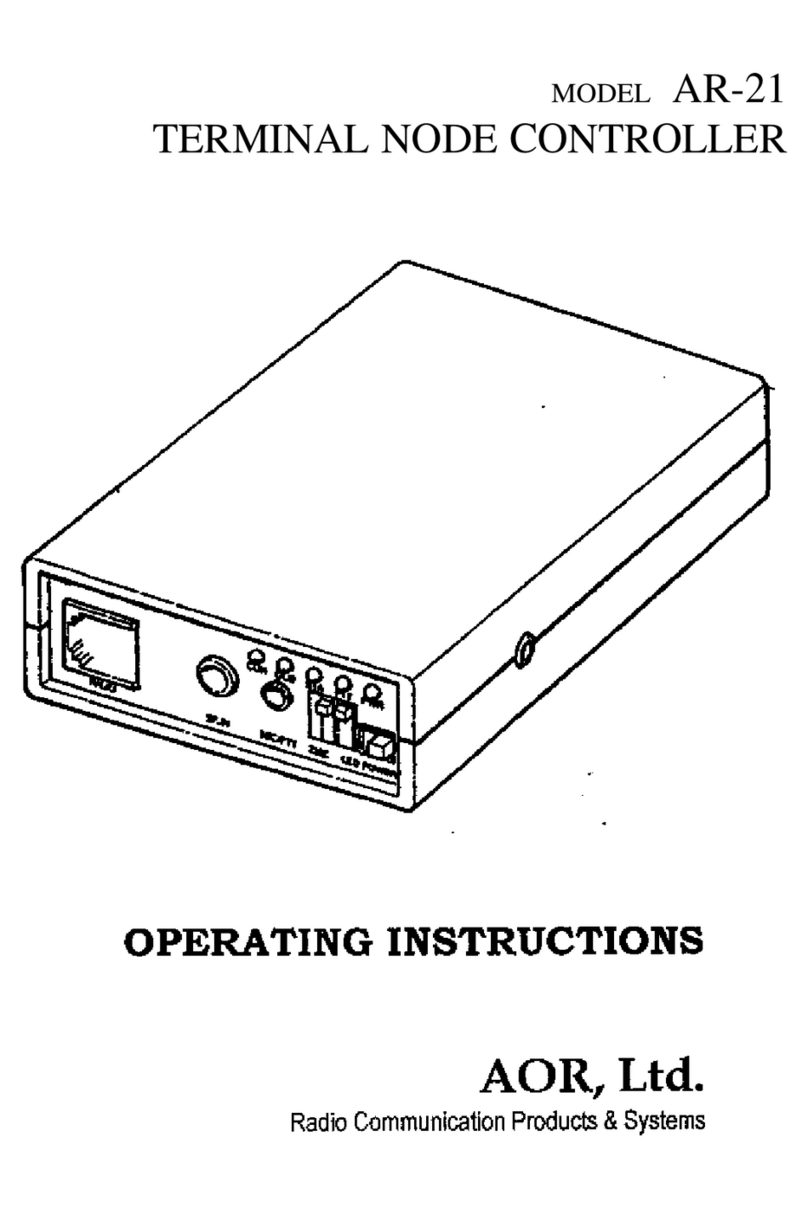
AR-210 Manual I
Page 2
FCC NOTICE
This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and if not installed and
used in accordance with the instruction manual, had cause interference to radio communications.
This equipment has been tested and found to well exceed the limit for a Class A computing device
pursuant to Subpart J of Part 15 of FCC Rules, which are designed to provide reasonable protec-
tion against such interference when operated in a commercial environment. If this equipment does
cause interference to radio or television reception, which you can determine by turning the equip-
ment off and on, try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
Move the computing device away from the receiver being interfered with.
Relocate the computing device with respect to the receiver
Re-orient the receiving antenna.
Plug the computing device into a different AC outlet so that the computing device and receiver
are on different branch circuits.
Disconnect and remove any I/O cables that are not being used.
(Unterminated I/O cables are a potential source of high RF emission levels.)
If you need additional help, consult your dealer or ask for assistance from the manufacturer. You
may also find the following booklet helpful: "How to Identify and Resolve Radio-TV Interference
Problems". This booklet is available from the U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C.
20402, Stock No. 004-000-00345-4.
AR-210 Operating Instructions
Copyright © 1992, AOR, Ltd. Tokyo Japan
by Toshi T. Totsuka
All Rights Reserved.
Credits
Portions of this manual was copied from the model HK-21 TNC operating manual under the accep-
tance and courtesy of the Heath Company, Benton Harbour, MI., U.S.A.
Portions of this manual was copied from the TAPR TNC-2 operating manual under the acceptance
and courtesy of the Tucson Amateur Packet Radio Corporation.
Trademarks
IBM, PC, XT, AT and PS/2 are registered trade marks of International Business Machines Corporation.
PC DOS is a registered trademark of the International Business Machines Corporation.
Apple and Apple Macintosh are registered trade marks of Apple Computer, Inc.
CompuServe is a registered trademark of CompuServe, Inc.
GEnine is a trademark of General Electric Corporation.
Hayes is a registered trademark of Hayes Microcomputer Products, Inc.
Procomm and Procomm Plus are registered trademarks of Datastorm Technologies, Inc.
Microsoft, MS and MS-DOS are reistered trademarks, and Windows is a trade mark of Microsoft Corporation.
VT-100 is a trade mark of Digital Equipment Corporation.