ASCOM I62 - Instruction sheet

Configuration Manual
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset
TD 92675EN
20 June 2012 / Ver. E

TD 92675EN
20 June 2012 / Ver. E
Configuration Manual
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset
About this document
Cross-references in the document
Throughout this document you will find cross-references in the text which indicate further
details that can be found in other sections of this document. The cross-references are
colored blue and linked to the relevant place in the document (example: see chapter 12.
Document History on page 71). Positioning your cursor over the cross-reference text and
clicking the left mouse button will take you to the relevant section.
To return to the original page after viewing a cross-referred page in Adobe Acrobat or Adobe
Reader, click on the “Previous View” arrow ( or ).

TD 92675EN
20 June 2012 / Ver. E
Configuration Manual
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset
Contents
1. Introduction ................................................................................................................... 1
1.1 Abbreviations and Glossary ................................................................................... 2
1.2 Functionality matrix ................................................................................................ 4
2. Pre-Installation.............................................................................................................. 5
2.1 VoWiFi System IP addresses ................................................................................... 5
3. Programming the VoWiFi Handset.............................................................................. 7
3.1 PDM ......................................................................................................................... 7
3.2 IMS3......................................................................................................................... 7
3.2.1 Over-the-Air.................................................................................................... 8
4. Installation of VoWiFi Handsets .................................................................................. 9
4.1 Installation with Central Device Management (IMS3) ............................................ 9
4.1.1 Create a Network Template in the IMS3......................................................... 9
4.1.2 Create a Common Template in the IMS3 ...................................................... 10
4.1.3 Create Numbers in the IMS3......................................................................... 10
4.1.4 Create a Network Template with Initial Configuration in the PDM .............. 11
4.2 Installation without Central Device Management (IMS3) .................................... 12
4.3 Installation using the Handset’s Admin Menu...................................................... 13
4.4 Configure a Handset with a Template................................................................... 13
4.4.1 Create a template ......................................................................................... 14
4.4.2 Apply a Template to a Handset with a Number ........................................... 14
4.4.3 Apply a Template to a Handset without a Number ..................................... 14
4.4.4 Save Handset Configuration as a Template ................................................. 15
4.4.5 Synchronizing a Handset with PDM ............................................................. 15
4.4.6 Configure Handset without Saving It in PDM ............................................... 15
5. Maintenance ................................................................................................................ 16
5.1 Handset ................................................................................................................. 16
5.1.1 Configure Spare Handsets without a Number in Large Systems................. 16
5.1.2 Upgrade Handset Software .......................................................................... 17
5.1.3 Upgrade Software OTA via TFTP................................................................... 17
5.1.4 Upgrade Software via PDM........................................................................... 18
5.1.5 Upgrade Software Over the Air (OTA) via Centralized Device Management
(IMS3) ............................................................................................................. 18
5.1.6 Recapture the Earlier Software..................................................................... 18
5.1.7 Upgrade Handset Functionality using License ............................................. 18
5.1.8 Perform a Factory reset ................................................................................ 21
5.2 Replacement of Handsets ..................................................................................... 22
5.2.1 Replacement Procedure Choice..................................................................... 22
5.2.2 Replacement of Handset with IMS3 ............................................................. 22

TD 92675EN
20 June 2012 / Ver. E
Configuration Manual
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset
5.2.3 Replacement of the Handset with PDM and IMS3........................................ 23
5.2.4 Replacement of Handset with PDM Only...................................................... 25
5.3 Change Number of a Handset ............................................................................... 26
5.4 Update Parameters via IMS3................................................................................. 27
5.5 Perform a Security Upgrade via IMS3 ................................................................... 27
5.6 Upgrade the Template .......................................................................................... 28
5.7 Create a Configuration Backup.............................................................................. 28
6. Handset Configuration................................................................................................ 29
6.1 Select Network ...................................................................................................... 29
6.1.1 Change Active Network ................................................................................ 29
6.1.2 Change Name of Network............................................................................. 29
6.1.3 Enable Switch between Networks ................................................................ 29
6.2 IP Address Settings ............................................................................................... 30
6.2.1 Automatic IP Address Settings..................................................................... 30
6.2.2 Static IP Address (Manual) Settings............................................................. 30
6.3 Network Settings .................................................................................................. 30
6.3.1 SSID............................................................................................................... 30
6.3.2 Voice Power Save Mode................................................................................ 31
6.3.3 World Mode Regulatory Domain .................................................................. 31
6.3.4 Radio and Channel Selection ........................................................................ 31
6.3.5 Transmission Power...................................................................................... 33
6.3.6 IP DSCP for Voice/Signaling .......................................................................... 33
6.4 Security Settings ................................................................................................... 33
6.4.1 Open.............................................................................................................. 33
6.4.2 WEP 64/128-bit Key .................................................................................... 34
6.4.3 WPA-PSK & WPA2-PSK ................................................................................. 34
6.4.4 802.1X with EAP-FAST ................................................................................. 34
6.4.5 802.1X with PEAP-MSCHAPv2 ..................................................................... 34
6.4.6 EAP-TLS......................................................................................................... 34
6.5 Handset Settings................................................................................................... 35
6.5.1 Automatic key lock ....................................................................................... 36
6.5.2 Phone lock..................................................................................................... 36
6.5.3 Audio adjustment ......................................................................................... 36
6.5.4 Headset Configuration.................................................................................. 37
6.5.5 In Charger Behavior ...................................................................................... 38
6.5.6 Configure Profiles ......................................................................................... 38
6.5.7 Hide Missed Call Window.............................................................................. 39
6.5.8 Battery Warning ........................................................................................... 39
6.5.9 Shared Phone................................................................................................ 39
6.5.10 Prevent Handset Switch off ....................................................................... 40

TD 92675EN
20 June 2012 / Ver. E
Configuration Manual
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset
6.5.11 Uploadable Language................................................................................. 40
6.5.12 Select Default Language ............................................................................ 41
6.5.13 Short cuts ................................................................................................... 41
6.5.14 Soft Key Functions During Call ................................................................... 42
6.5.15 Import Contacts .......................................................................................... 43
6.5.16 Company Phonebook.................................................................................. 43
6.5.17 Central Phonebook ..................................................................................... 43
6.6 Messaging and Alarm............................................................................................ 44
6.6.1 IP Address to the IMS3 ................................................................................. 44
6.7 Messaging Settings ............................................................................................... 44
6.7.1 Examples of TTR/TTP settings...................................................................... 45
6.8 Alarm Settings....................................................................................................... 47
6.8.1 Common Alarm Settings............................................................................... 48
6.8.2 Push Button Alarm ....................................................................................... 48
6.8.3 Test Alarm .................................................................................................... 48
6.8.4 Emergency Call Alarm ................................................................................... 49
6.8.5 Man-down and No-movement Alarm........................................................... 49
6.9 Telephony.............................................................................................................. 50
6.9.1 Endpoint ID and Endpoint number ............................................................... 50
6.9.2 VoIP Protocol................................................................................................. 50
6.9.3 Codec............................................................................................................. 51
6.9.4 Offer Secure RTP ........................................................................................... 52
6.9.5 Internal Call Number Length......................................................................... 52
6.9.6 Emergency Number ...................................................................................... 52
6.9.7 Voice Mail Number ........................................................................................ 52
6.9.8 Message Centre Number............................................................................... 53
6.9.9 Max number of Call Completions .................................................................. 53
6.9.10 Dial Pause Time .......................................................................................... 53
6.9.11 Direct off Hook from Charger ..................................................................... 53
6.9.12 Replace Call Rejected with User Busy ......................................................... 53
6.9.13 Busy on 1 / Disable call waiting ................................................................. 53
6.9.14 Calling Line Restriction ............................................................................... 53
6.10 Regional Settings ................................................................................................ 54
6.10.1 Set Time & Date .......................................................................................... 54
6.10.2 Select Default Language ............................................................................ 54
6.10.3 Dialing Tone Pattern................................................................................... 54
6.11 Display................................................................................................................. 54
6.11.1 User Display Text........................................................................................ 54
6.11.2 Rotate Display Text .................................................................................... 55
6.11.3 Font style.................................................................................................... 55
6.11.4 Backlight Timeout....................................................................................... 55

TD 92675EN
20 June 2012 / Ver. E
Configuration Manual
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset
6.11.5 Brightness................................................................................................... 55
6.11.6 Screen Saver ............................................................................................... 55
6.12 Menu Operation .................................................................................................. 55
6.12.1 Hide Menu Items......................................................................................... 55
6.12.2 Services....................................................................................................... 56
6.13 Push-To-Talk (PTT) Group Call ............................................................................ 56
6.14 Presence Management........................................................................................ 57
6.15 Location............................................................................................................... 57
6.15.1 Configure Handset for Cisco/Ekahau RTLS Solution................................... 58
7. Use Handset to Verify the VoWiFi System Deployment .......................................... 59
7.1 Site Survey Tool..................................................................................................... 59
7.2 Scan the Channels ................................................................................................. 59
7.2.1 Scan all Channels .......................................................................................... 59
7.2.2 Scan a Specific Channel................................................................................. 59
7.3 Range Beep............................................................................................................ 60
7.3.1 Configurable RSSI Threshold......................................................................... 60
7.3.2 Range Beep on a Configurable RSSI Threshold............................................. 60
8. Handset Internal Web Administration Page ............................................................ 61
8.1 Access the Handset´s Internal Web Administration page.................................... 61
8.1.1 General View ................................................................................................. 61
8.1.2 Troubleshoot View........................................................................................ 62
8.2 Change Administration Password......................................................................... 62
9. Administration ............................................................................................................ 63
9.1 Admin Menu Tree .................................................................................................. 63
9.2 Quick Access to the Handset’s Device Information............................................... 64
9.3 LED indications ...................................................................................................... 64
10. Troubleshooting........................................................................................................ 65
10.1 Fault Symptoms .................................................................................................. 65
10.2 Display Information............................................................................................. 66
10.3 Troubleshooting from the handset Internal Web Administration Page............. 69
11. Related Documents .................................................................................................. 70
12. Document History ..................................................................................................... 71
Appendix A: Working with Templates........................................................................... 72
A.1 Create a Template ................................................................................................. 72
A.2 Export a Template................................................................................................. 72
A.3 Import a Parameter File ........................................................................................ 72
A.4 Import a Template................................................................................................. 73
Index ................................................................................................................................74
TD 92675EN
20 June 2012 / Ver. E
Configuration Manual
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset
1
1. Introduction
1. Introduction
This document is a guide for installing, configuring and maintaining functionality of the
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handsets.
The Ascom Voice over Wireless Fidelity (VoWiFi) system provides wireless IP-telephony,
messaging and alarm functions to enterprise LANs. Using third-party WLAN products as well
as in-house developed hardware and software, the system enables data and voice
transmission together with seamless roaming.
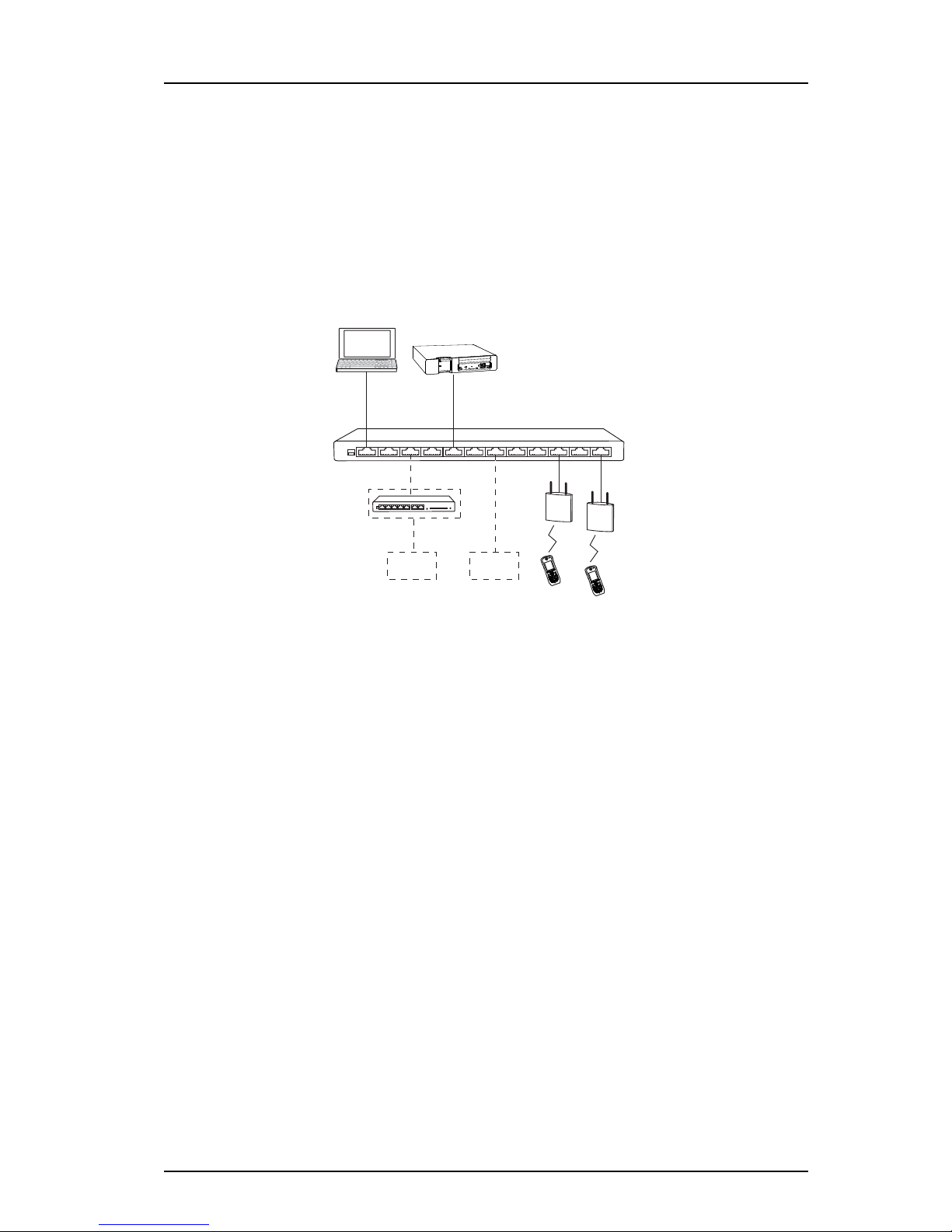
Figure 1.
AP AP
Device Manager
in IMS3
Switch to IP Backbone/LAN/Internet
VoIP Gateway
PBX
PDM
VoWiFi Handset
IP-PBX
Ascom VoWiFi System
This document is intended as a guide when installing the Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset in a
VoWiFi system. The document describes the settings needed to make the handset function
in a VoWiFi system and is relevant to the following personnel:
• System Administrator
• Service Technician
First configuration is done using the Portable Device Manager (PDM). In small systems
where it is possible to collect all handsets to update settings, daily maintenance is also done
by using the PDM. In larger installations, the Device Manager in the Messaging and Services
application (IMS3) makes it possible to administrate the handsets centrally via a web
interface without the need to collect the handsets.
The handset behavior can be customized to suite each user profile.
It is recommended that the reader has basic knowledge of the Ascom VoWiFi system and
basic knowledge of handset registration in the PBX.

TD 92675EN
20 June 2012 / Ver. E
Configuration Manual
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset
2
1. Introduction
1.1 Abbreviations and Glossary
802.11a IEEE 802.11 standard for transmission rate of up to 54Mbps, operates
in the 5GHz spectrum.
802.11b IEEE 802.11 standard for transmission rate of up to 11Mbps, operates
in the 2.4GHz spectrum.
802.11g IEEE 802.11 standard for transmission rate of up to 54Mbps, operates
in the 2.4GHz spectrum.
802.11d IEEE 802.11 standard for regulatory domains.
802.11e IEEE 802.11 standard that defines Quality of Service (QoS) for WLAN.
802.11i Standard for security improvements for 802.11.
802.11n IEEE 802.11 standard for transmission rate of up to 100 Mbps,
operates in the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands.
802.11D IEEE MAC Bridges standard (interworking for 802.11 among others).
802.11X IEEE standard for port-based Network Access Control (authentication).
Ad-hoc WLAN A WLAN between two wireless capable devices (normally PCs), where
no AP is involved.
AES Advanced Encryption Standard.
ALS Acoustic Location Signal
AP Access Point
BSS Basic Service Set. A WLAN with at least one AP thatis configured for it.
BSSID Basic Service Set Identifier. Hard coded name of an ad-hoc WLAN,
usually the MAC address of the radio. One type of SSID (the other
being ESSID).
CCX Cisco Compatible eXtension
Centralized
Management
Centralized Management makes it possible to configure handsets
without the administrator needs to collect them.
Device Manager Application for management of portables, editing of parameters and
updating the portables with new software, running on IMS3 and
Unite CM.
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. Used to send config parameters
to TCP/IP clients.
DNS Domain Name System
DSCP Differentiated Services Code Point. QoS on the Network Layer. Used
both for WLANS and LANs.
DTIM Delivery Traffic Indication Message
EAP Extensible Authentication Protocol.
EAP-FAST Flexible Authentication via secure tunneling.
EAP-TLS EAP-Transport Layer Security.
ELISE Embedded LInux SErver:
A hardware platform used for Unite modules
ESS Enhanced System Service:
Unite module that handles centralized number planning, remote
connection, system supervision, fault handling, group handling,
message routing, centralized logging, activity logging, and user access
administration.
ESS Extended Service Set. WLAN with multiple APs sharing the same SSID.

TD 92675EN
20 June 2012 / Ver. E
Configuration Manual
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset
3
1. Introduction
ESSID Extended Service Set Identifier. Identifying name of a WLAN - strictly it
is the identifying name of an AP and distinguishes WLANS from
another. ESSID is one type of SSID (the other being BSSID).
IGWP IP Gateway PRI for connection to traditional ISDN-based PBXes. Ascom
VoIP Gateway.
IM Interactive Messaging makes it possible to access information from an
application and control it by selecting a choice received in a message.
IMS3 Integrated Wireless Messaging and Services:
Unite module that enables wireless services to and from the handsets
in a WLAN system. It also includes the Device Manager.
License An authorization to use a licensed function.
MAC Medium Access Control.
Messenger VoWiFi Handset license for Messaging solutions
MWI Message Waiting Indication
NTP Network Time Protocol
OTA Over The Air
PBX Private Branch Exchange:
Telephone system within an enterprise that switches calls between
local lines and allows all users to share a certain number of external
lines.
PEAP Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol.
PDM Portable Device Manager
Used for management of portables, editing of parameters and
updating the portables with new software.
PEAP Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol.
PRI Primary Rate Interfaces
Protector VoWiFi Handset license for Personal security.
RSSI Received Signal Strength Indication.
RTLS Real-Time Location System
RTS Request-To-Send.
PTT Push-To-Talk
Services Services are predefined functions such as Phone Call, Send Data, Send
Message etc. that can be accessible from the Service menu.
SIP Session Initiation Protocol
SSID Service Set Identifier. User friendly name of a WLAN. Identifier
attached to packets sent over a WLAN that acts as a password. Daily
used term for ESSID in a wireless ESS topology.
STA Station. Client in a WiFi network.
QoS Quality of Service: Defines to what extent transmission rates, error
rates etc. are guaranteed in advance.
Talker VoWiFi Handset with basic functionality
Unite Name of Ascom IP based system for handling, events, messages and
alarms.
Unite CM Unite Connectivity Manager:
Unite module that enables messaging and alarm handling in a WLAN
system. It also includes the Device Manager.
UP 6 User Presence (value between 0-7). Wireless QoS at the MAC Layer.

TD 92675EN
20 June 2012 / Ver. E
Configuration Manual
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset
4
1. Introduction
1.2 Functionality matrix
The following matrix shows which functionality that currently can be used by the different
versions and requires settings in the PDM.
The three versions Talker, Messenger and Protector use the same hardware and software
(except , and features are enabled by licensing. The Talker version is an unlicensed VoWiFi
Handset with basic functionality, and the Messenger and Protector versions are licensed
VoWiFi Handsets with additional functionalities such as messaging and alarm, respectively.
VoIP Voice over IP.
VoWiFi Wireless version of VoIP and refers to an IEEE 802.11a, b, g and n
network.
VoWLAN Voice over WLAN.
WEP Wired Equivalent Privacy.
Wi-Fi Wireless Fidelity. Has become a name for wireless LAN networks.
Originator is Wi-Fi Alliance.
WLAN Wireless Local Area Network. Refers to an IEEE 802.11a, b, g and n
network.
WMM Wi-Fi Multimedia. A Wi-Fi Alliance interoperability certification, based
on the IEEE 802.11e standard. Provides basic QoS features to IEEE
802.11 networks.
WPA/WPA2 Wi-Fi Protected Access 2. Security method based on 802.11i standard
for wireless networks (data protection and network access control).
Talker Messenger Protector
Company Phonebook Yes Yes Yes
Central Phonebook Yes Yes Yes
Centralized Management Yes Yes Yes
Customized GUI Yes Yes Yes
Interactive Messaging (IM) No Yes Yes
Location Yes Yes Yes
Push to Talk (PTT) No Yes Yes
Multifunction button Yes Yes No
PushButtonAlarm NoNoYes
Man-down and No-movement alarma
a. Applicable to Protector only. The handset version must be WH1-AAAA/2A or above (see label under
battery cover). These functions require a license.
No No Yes
Acoustic Location Signal (ALS) No No Yes
Services No No Yes
Voice Mail Yes Yes Yes
Upload Language Yes Yes Yes
Clear lists in charger Yes Yes Yes
TD 92675EN
20 June 2012 / Ver. E
Configuration Manual
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset
5
2. Pre-Installation
2. Pre-Installation
Before installing handsets in a VoWiFi system, make sure that all equipment is available. It is
recommended to set up chargers and charge the handset batteries before installation, and
to have a number plan available for the handsets. Also be sure that the IP addressing plan is
set up to support the amount of handsets to be deployed.
We assume that the VoWiFi system is installed including some or all of the following
components (depending on system configuration):
• VoIP Gateway. This is the gateway for ISDN primary rate interfaces (PRI) in the Ascom
VoWiFi. It serves as a link between traditional telephony and VoWiFi telephony.
• DHCP Server. A DHCP server allows devices to request and obtain an IP address from a
server which has a list of addresses available for assignment. If the WLAN does not have
access to a DHCP server, a list of static IP addresses is necessary.
• Portable Device Manager. ThePDM is used for administration and programming of the
handsets. All settings and updates are in this case done via the DP1 Desktop
Programmer cradle connected over USB.
• IMS3. The IMS3 handles all communication between the WLAN and its built-in Device
Manager. Before installing the handset, make sure the IMS3 IP address is available.
For effective administration of a VoWiFi system with several handsets, it is required to have
both a PDM and a Device Manager included in the IMS3. In this case, the PDM is only used to
allow the handset to access the WLAN system. All other settings and updates are done with
the Device Manager in the IMS3.
2.1 VoWiFi System IP addresses
Complete the table below with the IP addresses, as a help when configuring the handsets.
Table 1.
Device IP address/Number/Port Required
VoIP GatewayaIf used
IP-PBX If used
IMS3 If used
Subnet MaskbIf used
Number plan N/A Yes
NTP Server addressc
DNS Server addressb
VoIP settingsdYes
Central Phonebook If used
ESS If used
Syslog server If used
TFTP server If used
Ekahau RTLSeIf used
DHCP range
a. The VoIP Gateway is not needed if an IP-PBX is used.
b. Only required if no DHCP is used, that is, static IP is used.
c. Depending on system configuration
d. Gatekeeper IP address or SIP proxy IP address used to access the PBX.
e. The IP address and port to the location server.

TD 92675EN
20 June 2012 / Ver. E
Configuration Manual
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset
6
2. Pre-Installation
The ESS might be used for setting up personal login accounts to the Device Manager in the
IMS3. The ESS is also used for advanced messaging management.

TD 92675EN
20 June 2012 / Ver. E
Configuration Manual
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset
7
3. Programming the
3. Programming the VoWiFi Handset
This chapter describes how to configure handsets in three different ways:
• It is possible to configure the handset by inserting it into a DP1 Desktop Programmer
cradle connected via USB to the PDM.
• It is possible to configure the handset via over-the-air (OTA) using the Device Manager in
the IMS3.
NOTE: This requires that the IP address to the IMS3 has been configured in the handset. The
IP address is configured using PDM or via the handset’s Admin menu.
• It is possible to configure the basic network settings of the handset via its Admin menu.
See 9. Administration on page 63 for more information about the settings that can be
made.
It is recommended to use the Device Manager in IMS3 to configure handsets in a large
system. The reason is that it enables to install, upgrade and configure a large amount of
handsets simultaneously. Another benefit is that the collection of the handsets from the
user is not needed.
The PDM enables configuration of one handset at the time inserted in the DP1 Desktop
Programmer connected via USB to the administrator’s computer.
It is also possible to upgrade the handset’s software via an TFTP server1and is
recommended for software upgrade over-the-air (OTA) in small systems when no IMS3 is
available.
Tip: It is recommended to use templates when configuring handsets. By using a template,
the same configuration can easily be applied to many handsets simultaneously.
3.1 PDM
The PDM runs on a PC and is used for configuring the handset as follows:
• Connect a DP1 Desktop Programmer cradle via USB to the computer running PDM.
• Start PDM.
• Place the handset in this cradle connected to PDM.
For instructions on how to install and use the PDM, see Installation and Operation Manual,
Portable Device Manager (PDM), TD 92325EN.
Figure 2.
PDM
Configuration of handsets via PDM
3.2 IMS3
The IMS3 runs on an ELISE3 module.
1. If TFTP server is used, it is only possible to upload software to the handset. Additional configuration, such as parameter
settings, is performed via PDM or the Device Manager in IMS3.
TD 92675EN
20 June 2012 / Ver. E
Configuration Manual
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset
8
3. Programming the
For instructions on how to use the IMS3, see Installation and Operation Manual, IMS3,
TD 92762EN.
3.2.1 Over-the-Air
There is no external equipment needed besides the Device Manager in IMS3 and VoWiFi
system. Please proceed with 4. Installation of VoWiFi Handsets on page 9.
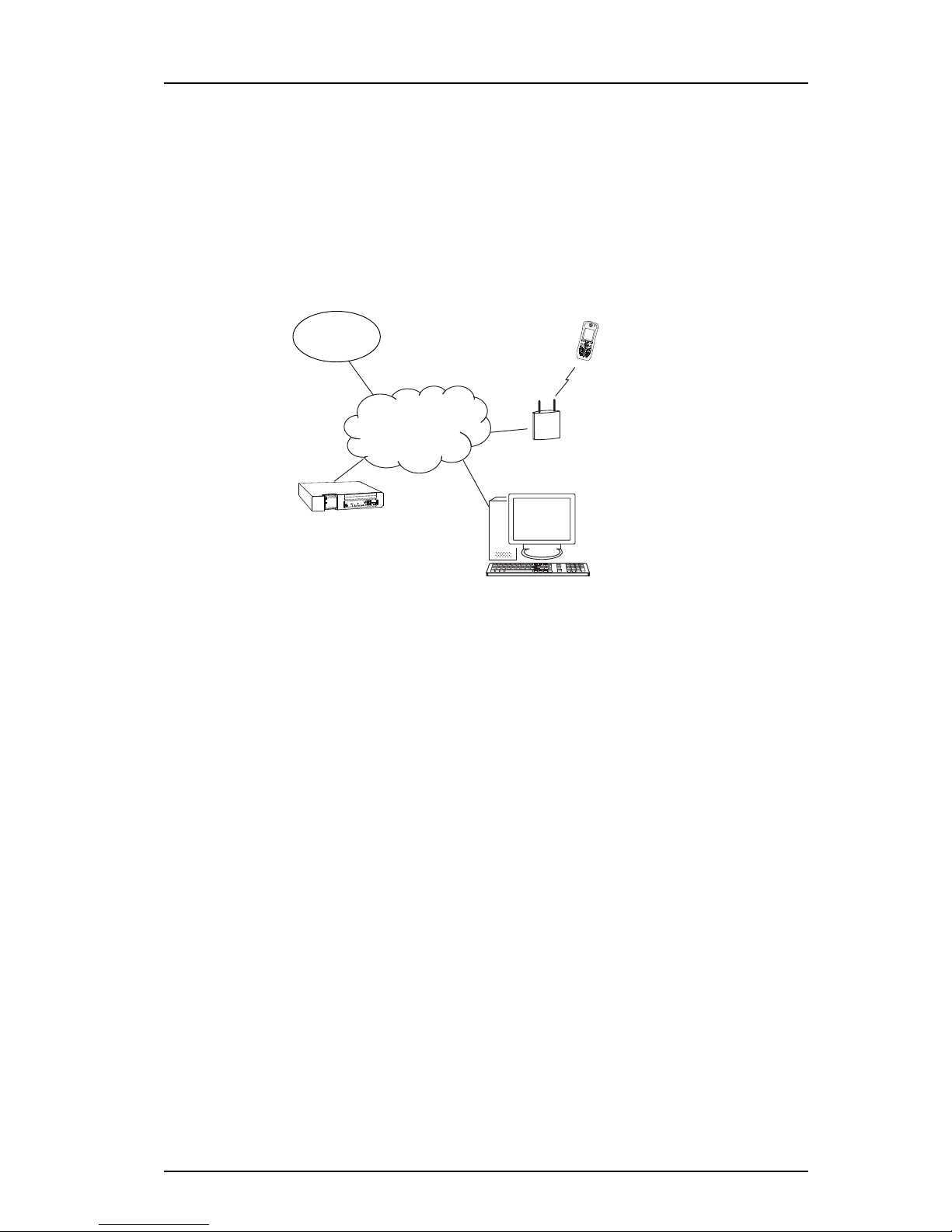
Figure 3.
Client
Device Manager
in IMS3
Access Point
Ascom
VoWiFi
System
IP AP
Configuration of handsets Over-the-Air (OTA)

TD 92675EN
20 June 2012 / Ver. E
Configuration Manual
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset
9
4. Installation of VoWiFi
4. Installation of VoWiFi Handsets
This section describes the recommended procedure for installing and configuring handsets.
There are several ways to install a handset, but the procedures described here guarantees
simple maintenance of the network.
It is recommended to use the Device Manager in IMS3 to install and maintain handsets in a
large network. The reason is that it enables to install, upgrade and configure a large amount
of handsets simultaneously. Another benefit is that the collection of the handsets from the
user is not needed due to configuration is performed over the air (OTA). The handset must
first be configured in the PDM to access the IMS3 later on. See Installation steps in large
VoWiFi Systems using IMS3 and PDM.
The PDM enables administration of one handset at the time inserted in a Desktop
Programmer (DP1) connected via USB to the administrator’s computer. See Installation
steps in small VoWiFi Systems using PDM.
Installation steps in large VoWiFi Systems using IMS3 and PDM
NOTE: If the handset to be installed must use certificate to access a WLAN, follow the
instructions in chapter 4.2 Installation without Central Device Management (IMS3) on
page 12.
These WLAN settings are common network settings for all handsets.
1 Create templates in the Device Manager in IMS3; one with network settings and
another with common settings.
2 Create Numbers and apply the templates.
3 Create a template with identical network settings in the PDM.
See 4.1 Installation with Central Device Management (IMS3) on page 9 for more
information.
Installation steps in small VoWiFi Systems using PDM
1 Create Numbers.
2 Create one template for all settings in the PDM.
See 4.2 Installation without CentralDevice Management (IMS3) on page 12 for more
information.
4.1 Installation with Central Device Management (IMS3)
When installing a large amount of handsets in a VoWiFi system, it is recommended to have
both the IMS3 and the PDM to make the maintenance and handling of the system as simple
as possible.
4.1.1 Create a Network Template in the IMS3
Create one template that contains the network parameters (also include the security
settings). Besides the network parameters, additional parameters might also be set, for
example VoIP settings and IP address to IMS3. The template must be created to prevent
the IMS3 from restoring the parameters to default during the first synchronization.
NOTE: Only select the parameters that are changed, if all parameters are selected the system
performance decreases.

TD 92675EN
20 June 2012 / Ver. E
Configuration Manual
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset
10
4. Installation of VoWiFi
1 Open a web browser and enter the address to the IMS3.
2 Click “Device Manager“. You might be prompted to log on the Device Manager.
3 Select the Templates tab and click “New“. The New template window is opened.
4IntheDevice type and Parameter version drop-down lists, select the corresponding
device type and parameter version to use, respectively.
5IntheName field, enter a descriptive name of the template.
6Click“OK“.
7 Set the following network parameters:
• Network settings1(located under Network > Network A, B, C, or D)
• VoIP settings2(located under VoIP)
• Syslog settings3(if any) (located under Device > General)
• Unite settings4(located under Device > Unite)
8 Click “OK“ to save the template.
Tip: See Appendix A for tip on how to work with templates when using both PDM and IMS3.
4.1.2 Create a Common Template in the IMS3
Create another template with the common handset settings applicable to all handsets
(exclude the parameters and security settings configured in the Network template). This
template contains for example, hidden menu items in the display, certain level of ring signal
and vibrators.
NOTE: Only select the parameters that are changed, if all parameters are selected the system
performance decreases.
1 Open a web browser and enter the address to the IMS3.
2 Click “Device Manager“.
3 Select the Templates tab and click “New“.
4 In the Device Type and Parameter version drop-down lists, select the corresponding
device type and parameter version to use, respectively.
5 In the Name field, enter a descriptive name of the template.
6 Set the specific parameters. See section 4.4 Configure a Handset with a Template on
page 13 for more information.
4.1.3 Create Numbers in the IMS3
Create a range of Numbers and apply the templates previously created in the IMS3.
IMPORTANT: Do not add numbers already used because these handsets already exist in the
system although not saved in the Device Manager in IMS3. The Device Manager
will overwrite the existing parameters in the handset.
NOTE: The parameter version of the template must be equal to or less than the selected
parameter version.
1 Open a web browser and enter the address to the IMS3.
1. All required system settings for the WLAN. For example SSID and Security mode.
2. For example VoIP protocol, Gatekeeper IP address or SIP proxy IP address used to access the PBX.
3. The parameter “Syslog“ must be enabled in order to set the “Syslog IP address“.
4. IP address and password (if any) to the IMS3.

TD 92675EN
20 June 2012 / Ver. E
Configuration Manual
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset
11
4. Installation of VoWiFi
2 Click “Device Manager“.
3 Select the Numbers tab and click “New“. The New numbers window is opened.
4IntheDevice Type and Parameter version drop-down lists, select the device type and
the parameter version to use, respectively.
NOTE: The device type and parameter version must match the handsets to be used to apply
the template.
5InthePrefix field, enter the numbers’ prefix (if needed).
6 Create a range of numbers by selecting the “Range“ option. Enter the start call
number and the end call number in the fields, respectively. Click “OK”.
NOTE: The maximum range that can be added at a time are 100 numbers.
7 Apply the network settings template to the selected handsets. See 4.4.2 Apply a
Template to a Handset with a Number on page 14.
8 Apply the common settings template to the selected handsets. See 4.4.2 Apply a
Template to a Handset with a Number on page 14.
9ClosetheIMS3.
4.1.4 Create a Network Template with Initial Configuration in the PDM
In a factory delivered handset, the WLAN settings are not configured that is required to
access the IMS3. Using the PDM allows the handset to be primed with the WLAN parameters
and allows it to log in to the Device Manager in IMS3 for future management over the air.
Create a template with the basic network settings and IP address to IMS3. This template is
only used once for each handset since it must access the WLAN and then log on the Device
Manager. After log in, the settings in the handset are changed according to the templates in
the Device Manager in IMS3.
1 Open the PDM.
2 Do one of the following:
• If a network template was created in the Device Manager in IMS3, export this
template and import it to PDM. See Appendix A for more information.
(Recommended)
• Create a template (see 4.4.1 Create a template on page 14) with the following
network parameters:
- Network settingsa(located under Network > Network A (B, C, or D)
- Unite settingsb(located under Device > Unite)
Note: The parameters in this template should be identical to the parameters
in the network template created in the IMS3.
3 Put the handset in the Desktop Programmer (DP1) cradle.
4 Run the template. See 4.4.3 Apply a Template to a Handset without a Number on
page 14.
5 Remove the handset when synchronization is finished.
6 Enter the Number and the password 1(if any). Press “Login“.
a. All required system settings for the WLAN. For example SSID and Security mode.
b. IP address and password (if any) to IMS3.
1. The password is only required if the “Password“ parameter is set.

TD 92675EN
20 June 2012 / Ver. E
Configuration Manual
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset
12
4. Installation of VoWiFi
Settings that were stored for the handset in the Device Manager in IMS3 will now be
downloaded to the handset. This can, for example, be unique soft- or hot keys that have
been prepared earlier. When the settings have been downloaded to the handset, it might be
restarted depending on the parameter changes.
7 Repeat step 3 – 6 for all handsets.
4.2 Installation without Central Device Management (IMS3)
In a small VoWiFi system, the administration can be handled using only the PDM.
The synchronization is in this case not handled automatically by the system when a
handset’s parameters are changed in the PDM. When the parameters have been changed in
PDM, each handset must be placed in the Desktop Programmer (DP1) cradle connected to
the administrator’s computer in order to synchronize the parameters with the handset.
1 Open the PDM.
2IntheNumbers tab, click “New“. The New numbers window is opened.
3IntheDevice Type and Parameter version drop-down lists, select the matching device
type and the parameter version for the handset to be use, respectively.
4InthePrefix field, enter the numbers’ prefix (if needed).
5 Create a range of numbers by selecting the “Range“ option. Enter the start call
number and the end call number in the fields, respectively.
6Click“OK”.
7 Create a network settings template (see 4.4.1 Create a template on page 14) with
the following network parameters:
• Network settings1(located under Network > Network A, B, C, or D)
8 Create another template (see 4.4.1 Create a template on page 14) with the common
handset settings applicable to all handsets (exclude the network parameters and
used security settings). Example of parameters settings:
• VoIP settings2(located under VoIP)
• Software TFTP IP address (if any) (located under Device > General)
• Syslog settings3(if any) (located under Device > General)
In addition, settings for hiding menu items in the display, certain level of ring signal
and vibrators etc. can also be configured.
9 Apply the network settings template to the handset, see 4.4.2 Apply a Template to a
Handset with a Number on page 14.
10 Apply the common settings template to the handset, see 4.4.2 Apply a Template to a
Handset with a Number on page 14.
11 Put the handset in the Desktop Programmer (DP1) cradle.
12 In the Device Wizard window, select “Associate with number“ and press “OK“.
13 Select the handset to associate with. Press “OK“.
The number and parameter settings saved in the PDM will now be synchronized with the
handset. In addition, the handset’s Device ID will also be synchronized with the number in
the PDM.
If certificates must be used to access a VoWiFi system, also perform the steps 14 - 19.
1. All required system settings for the WLAN. For example SSID and Security mode.
2. VoIP protocol, Gatekeeper IP address or SIP proxy IP address used to access the PBX.
3. The parameter “Syslog“ must be enabled in order to set the “Syslog IP address“.

TD 92675EN
20 June 2012 / Ver. E
Configuration Manual
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset
13
4. Installation of VoWiFi
14 In the Numbers tab, right-click the handset’s number and select “Edit certificates“. An
Edit certificate window opens.
15 In the Root tab and Client tab, click “Edit“ and select the certificates to import. Click
“Close“.
16 In the Numbers tab, right-click the handset’s number and select “Edit parameters“.
17 Select “Network X“ (Xrepresents A, B, C, or D).
18 In the Security mode drop-down list, select “EAP-TLS“.
19 In the EAP client certificate drop-down list, select the client certificate to be used.
Click “OK“.
20 Remove the handset when synchronization is finished.
Repeat the steps 11-13, 20 (if needed, perform the steps 14-19) for all handsets.
4.3 Installation using the Handset’s Admin Menu
It is possible to install a handset using its Admin menu. This is useful when no PDM/IMS3 is
available and the handset needs to be installed quickly.
NOTE: It is only possible to configure the basic settings via the Admin menu.
1 There are two options to access the Admin menu:
• If the handset has been factory reset or not been configured; in idle mode, enter
40022.
• If the handset has been configured; press “Menu“, select “Settings“ and enter
40022.
2 Set the following parameters:
• Network settings1(located under Network setup)
• VoIP settings2(located under VoIP)
• Unite settings3(if any) (located under Unite)
• Syslog settings4(if any) (located under Syslog)
4.4 Configure a Handset with a Template
It is possible to select a handset in the PDM and directly change one or more configuration
parameters. By using a template, the same configuration can easily be applied to many
handsets simultaneously. Templates are also an efficient way to give good control over
which changes that are applied to each handset.
Templates enables configuration of all aspects of a handset from sound volume to keypad
short cuts.
Your supplier can provide example templates for different PBX:s. The handset will have full
functionality towards the PBX even without such a template. By using such a template,
though, the handset will be customized for that PBX with menu options for PBX specific
functions.
1. All required system settings for the WLAN. For example SSID and Security mode
2. VoIP protocol, Gatekeeper IP address or SIP proxy IP address used to access the PBX.
3. IP address and password (if any) to the IMS3.
4. The parameter “Syslog“ must be enabled in order to set the “Syslog IP address“.

TD 92675EN
20 June 2012 / Ver. E
Configuration Manual
Ascom i62 VoWiFi Handset
14
4. Installation of VoWiFi
4.4.1 Create a template
1 Open the PDM or the Device Manager in the IMS3.
2 Select the Templates tab and open the menu “Template > New...“. The New Template
window is opened.
3 Select the device type and parameter version that matches the software version
installed on the handset. Give the template a descriptive name.
The parameters that are not part of the template will be left unchanged on the handset. The
parameter version of an installed handset is visible under the Numbers tab or the Devices
tab.
4Click“OK“.
5 Select the check box of each parameter that you want to be part of this template and
enter the proper value.
6 Click “OK“ to save the template.
4.4.2 Apply a Template to a Handset with a Number
1 Open the PDM or the Device Manager in the IMS3.
2IntheNumbers tab, select the handset(s) you want to apply the template to.
NOTE: If several handsets shall be selected, they must be of the same device type and have
the same parameter version.
3 Make a right-click and select “Run template...“.
Only templates with a parameters version matching the selected handsets will be shown.
Select the template you want to apply and click “OK“.
The template is applied. The number of parameters in the template will affect the time it
takes to apply the template to the selected handsets.
When looking at a handset under the Numbers tab, the column “Last run template“ will
show the name of the most recently applied template.
Tip: It is also possible to apply a template on several handsets of the same device type
simultaneously using the Baseline function, see Installation and Operation Manual, IMS3,
TD 92762EN. This function cannot be used to download certificates to the handsets.
4.4.3 Apply a Template to a Handset without a Number
NOTE: This feature is only applicable for the PDM.However, in the Device Manager in IMS3, it
is possible to apply a template to a handset without a number using the Baseline
function. The Baseline function or a template cannot be used to download certificates
to the handsets. See Installation and Operation Manual, IMS3, TD 92762EN.
It is possible to apply a template to ahandset without a number in the PDM.
1 Put the handset in the Desktop Programmer (DP1) cradle
2IntheFound Device Wizard window, select the “Run template“ option.
3 Click “Next >“.
Only templates with a parameter version matching the selected handset will be shown.
4 Select the template that shall be applied and click “OK“.
The template is applied. The number of parameters in the template will affect the time it
takes to apply the template to the selected handset.
Other manuals for I62 -
11
Table of contents
Other ASCOM Telephone Accessories manuals