ATEME MC3x00 Series User manual

www.ateme.com 26 Burospace –Route de Gisy –91570 Bièvres –France
MC3x00 Multiplexer & Gateway
User Manual –v3.8
Document identification
MC3x00-UM-v3.8

MC3x00 –User Manual
Page 2 / 213
Summary of changes
Document
Version
Date
Evolution description
2.14
2010
V2.14 Release
2.16
Nov 9th, 2011
V2.16 Release
Document template update
3.2
March 2012
V302 Release
3.4
August 2012
V3.4 Release
3.6
December 2012
V3.6 Release
3.8
March 2013
V3.8 Release

MC3x00 –User Manual
Page 3 / 213
Contents
1INTRODUCTION 12
2INSTALLATION AND SAFETY 13
2.1 THE 4RU CHASSIS....................................................................................................13
2.1.1 Ventilation 13
2.1.2 Replacing the power supply module 13
2.2 THE 1RU CHASSIS....................................................................................................14
2.2.1 Ventilation 14
2.2.2 Replacing the power supply module 14
2.3 SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS .........................................................................................14
2.4 INSTALLATION ...........................................................................................................15
2.4.1 Power supply rating 15
2.4.2 4RU chassis with 300 and 400W AC Power 15
2.4.3

MC3x00 –User Manual
Page 4 / 213
4ADMINISTRATIVE SETTINGS CONFIGURATION 25
4.1 ACCESSING THE WEB INTERFACE...............................................................................25
4.1.1 Assigning an IP Address 26
4.1.2 IPv6 Address Support 28
4.1.3 Management GUI 28
4.1.4 Management over IP-Data Port and VLANs 30
4.1.5 Internal Time Clock Setting / Network Time Protocol (NTP) Server 31
4.1.6 Password Protection in the GUI 32
4.1.7 Changing the Password for the GUI 32
4.1.8 Optional Languages 33
4.2 CONFIGURATION OF CLOCK REFERENCE MODULE........................................................34
4.2.1 Configuration 34
4.3 LICENSING................................................................................................................36
4.3.1 Ordering a License File 38
4.3.2 Installing a License File 38
5INPUT CONFIGURATION 39
5.1 THE INPUTS NODE.....................................................................................................39
5.2 INPUT ANALYSIS........................................................................................................40
5.2.1 Input Port Analysis 41
5.2.2 Input Service Filtering and Analysis 41
5.2.3 Input PID Analysis 43
5.3 MANUAL PSI.............................................................................................................45
5.3.1 MPTS Support 46
5.3.2 PSI Modifications of input services 47
5.3.3 Defining a component type for an incoming PID. 47
5.3.4 Changing the language descriptor of an incoming audio 48
5.3.5 Edit options on existing manual PSI 49
5.4 DVB-S/S2 INPUT ......................................................................................................49
5.5 ASI INPUT.................................................................................................................53
5.6 QAM/DVB-C INPUT ..................................................................................................55
5.7 COFDM/ DVB-T INPUT.............................................................................................58
5.8 IP INPUT...................................................................................................................61
5.8.1 Setup of IPv6 input 63
5.8.2 IGMP Source filtering on Switch IP input. 64
5.8.3 IP Input with FEC 65
5.8.4 Adding a New Input Stream 66
5.8.5 Removing a Multicast Input 66
5.8.6 IP Input seamless switching module 67
5.9 8VSB INPUT .............................................................................................................69
5.10 QAM-B INPUT...........................................................................................................71
5.11 DVB-T2INPUT..........................................................................................................73
6CONDITIONAL ACCESS CONFIGURATION 77
6.1 DESCRAMBLING –COMMON INTERFACE MODULE........................................................77
6.1.1 Descrambling a Service 78
6.1.2 Transporting a Descrambled Service to Multiple Output Modules/Ports 78
6.1.3 CAM Configuration 78
6.1.4 Alt CAM Mode 81
6.1.5 CAM Interface 81

MC3x00 –User Manual
Page 5 / 213
6.1.6 Navigation 81
6.1.7 Multiple Users and CAM access 82
6.1.8 Error Handling 83
6.2 BULK DESCRAMBLING................................................................................................84
6.2.1 Verimatrix Configuration 85
6.2.2 BISS Scrambling and Descrambling 87
6.3 SCRAMBLING ............................................................................................................89
6.3.1 Scrambler Module Configuration 90
7DECODER OUTPUT CONFIGURATION 99
7.1 CHANNEL CONFIGURATION ........................................................................................99
7.1.1 Decoder Status 101
7.1.2 Decoder Parameter Configuration 104
7.1.3 Dolby® Digital Plus Professional Decoder 109
7.1.4 VBI/Test lines (or VBI/VANC/Test lines) 113
7.1.5 Descrambling for the Decoder Module 114
7.1.6 Upconverter: RF Parameter Configuration 114
7.1.7 Semi-agile frequency setting 114
7.1.8 Video Sync Shutoff 116
7.1.9 RF/NICAM or RF/A2 Parameter Configuration 117
7.1.10 TVMOD- PAL/SECAM switching in Decoders 118
7.1.11 Carrier offset in TVMOD 118
7.2 GENLOCK FEATURE .................................................................................................119
7.3 ON SCREEN DISPLAY MESSAGING (OSDM)..............................................................120
7.3.1 Enabling OSD Messaging 121
7.3.2 Disabling OSD Messages 121
8DIGITAL OUTPUT CONFIGURATION 122
8.1 INPUT STREAM SELECTION ......................................................................................123
8.2 AUTO SERVICE MODES............................................................................................124
8.2.1 Configuring an output with Auto All Services 124
8.3 TRANSPORT STREAM GENERATION ..........................................................................125
8.3.1 Transport Settings 129
8.3.2 Port Settings 130
8.3.3 EMM 130
8.3.4 PSI 132
8.3.5 EPG 132
8.3.6 Service 133
8.3.7 Components 134
8.3.8 Manual Mapping 135
8.3.9 Scrambling 138
8.4 OUTPUT PORT SETTINGS.........................................................................................140
8.4.1 IP Output module 140
8.4.2 ASI Output Module 143
8.4.3 QAM Output Module 145
8.4.4 COFDM Output Module 146
8.4.5 DVB-S/S2 Output Module 147
8.4.6 DVB-T2 Output Module 150
8.5 OUTPUT OPTIONS ...................................................................................................151
8.5.1 Virtual MPTS Output 151
8.5.2 MPTS Transparent Mode 151

MC3x00 –User Manual
Page 6 / 213
8.5.3 MPTS Semi-Transparent Mode 152
8.6 PSI/PSIP CONFIGURATION......................................................................................153
8.6.1 Editing the PSI Network configuration 154
8.6.2 Editing the PSI Default Values 155
8.6.3 Editing the Logical Chanel Descriptor (NIT) 156
8.6.4 Editing the BAT table 158
8.6.5 Editing the TOT Local Time Offset Descriptor 158
8.6.6 PSI Synchronization 160
8.6.7 Inserting Generic Descriptors 161
8.6.8 Modifying PSI Generation Settings 163
8.6.9 DVB ATSC, ATSC DVB Conversion 165
8.6.10 SI Domain Support 165
9FM RADIO OUTPUT CONFIGURATION 167
9.1 CONFIGURING GLOBAL PARAMETERS FOR A MODULE................................................167
9.2 CONFIGURING RADIO SERVICES...............................................................................168
9.3 CONFIGURING RDS OUTPUT....................................................................................170
9.3.1 Manual RDS 171
9.3.2 Ancillary and Auxiliary RDS 171
9.3.3 Dynamic Looping 173
9.3.4 Stereo override 173
10 DIGITAL PROCESSING MODULES 174
10.1 AUDIO LEVELING MODULE .......................................................................................174
10.2 ELECTRONIC PROGRAM GUIDE (EPG)......................................................................175
10.2.1 EPG Status 175
10.2.2 Setting up EPG 176
10.3 ADDING EPG INFORMATION TO A TRANSPORT STREAM .............................................178
10.3.1 Playout Rate, Playout Limit, and Priority 179
10.3.2 EIT Source Setup 181
11 REDUNDANCY SUPPORT 182
11.1 INPUT REDUNDANCY................................................................................................182
11.1.1 Configuring Service-based Input Redundancy 183
11.1.2 Configuring Port-based Input Redundancy 183
11.1.3 Alarms that cause Switching 185
11.1.4 Input Redundancy and the MMI 185
11.2 INTERNAL REDUNDANCY..........................................................................................185
11.2.1 Dual backplane configuration 186
11.2.2 Hardware Requirements 186
11.2.3 Configuring Modules for Internal Redundancy 187
11.2.4 Decoder Internal Redundancy 189
11.2.5 QAM/COFDM/IP/ASI Output Internal Redundancy 190
11.2.6 FM Radio Internal Redundancy 190
11.3 CA REDUNDANCY ...................................................................................................191
11.3.1 ECMG Redundancy 191
11.3.2 Redundancy Configuration 192
11.3.3 Manual Switching 192
11.3.4 EMMG Redundancy 193
11.4 IP OUTPUT REDUNDANCY........................................................................................193
11.4.1 Multicast Configuration 194

MC3x00 –User Manual
Page 7 / 213
11.4.2 OSPF Configuration 194
11.4.3 Defining the Source Subnet 194
11.4.4 Defining the Source IP Address 196
11.4.5 Mute on Error 197
12 CONTROL AND MONITORING 198
12.1 SYSTEM STATUS .....................................................................................................198
12.1.1 Service View 198
12.1.2 Output View 200
12.1.3 Hardware View 201
12.1.4 Active Alarms 202
12.1.5 Alarm History 203
12.1.6 Alarm Setup 204
12.1.7 Root Cause Filter 205
12.2 SNMP....................................................................................................................205
12.2.1 Configuration of SNMP Alarm Filter via the GUI 205
12.2.2 Configuration of SNMP Trap Destination Table via the GUI 205
12.2.3 Configuration of Trap Destination Table via SNMP 205
12.2.4 Interpretation of Traps 206
12.3 SOAP XML INTERFACE...........................................................................................206
13 MAINTENANCE 207
13.1 SOFTWARE UPGRADES............................................................................................207
13.2 HOT-SWAPPING ......................................................................................................207
13.2.1 Performing a Hot-Swap 207
13.2.2 Switch+MMI Module Hot-swap 207
13.2.3 Other Module Hot-swap 208
13.3 ADDING,REPLACING,OR REMOVING MODULES.........................................................208
13.4 IMPORTING AND EXPORTING CHASSIS CONFIGURATION.............................................210
13.5 RESTORING THE DEFAULT IP ADDRESS....................................................................211
14 SUPPORT AND CONTACT INFORMATION 212
A. NOTICES 213

MC3x00 –User Manual
Page 8 / 213
Table of Figures
Figure 1 –4RU chassis with power connectors, switch module and available slots.......................................................... 13
Figure 2 –1RU chassis with power connector, switch module and available slots; front and rear view.............................14
Figure 3 –Power Input for 4RU chassis with 300 and 400 Watt AC power.......................................................................15
Figure 4 –Front plate of dual 48V Power Supply in a MC3000.........................................................................................16
Figure 5 –Layout of 48V DC Power Supply Connector....................................................................................................16
Figure 6 –Power Input Connector for 1RU Chassis......................................................................................................... 16
Figure 7 –Classification label...........................................................................................................................................18
Figure 8 –CDRH identification label.................................................................................................................................18
Figure 9 –QAM Modulator...............................................................................................................................................22
Figure 10 –Two-Slot Wide Quad Decoder.......................................................................................................................24
Figure 11 –Three-Slot Wide Quad Decoder.....................................................................................................................24
Figure 12 –Web Home Page...........................................................................................................................................25
Figure 13 –Admin View...................................................................................................................................................26
Figure 14 –Admin Properties View..................................................................................................................................26
Figure 15 –Setting up Virtual LANs .................................................................................................................................27
Figure 16 –IPv6 Address in Admin Page.........................................................................................................................28
Figure 17 –Manual IPv6 Address ....................................................................................................................................29
Figure 18 –IPv6 Internal Redundancy .............................................................................................................................29
Figure 19 –IPv6 PSI Synchronization..............................................................................................................................29
Figure 20 –Setting up Virtual LANs .................................................................................................................................30
Figure 21 –Setting up Virtual LANs via Management port ...............................................................................................31
Figure 22 –Setting the Time and Date............................................................................................................................. 32
Figure 23 –Login Management Section........................................................................................................................... 32
Figure 24 –Password Configuration ................................................................................................................................32
Figure 25 –Changing the Password ................................................................................................................................33
Figure 26 –Optional Languages......................................................................................................................................33
Figure 27 –Clock reference module................................................................................................................................. 34
Figure 28 –Configuration of clock reference module........................................................................................................34
Figure 29 –Parameters of clock reference module ..........................................................................................................35
Figure 30 –MMI Clock Reference selection.....................................................................................................................36
Figure 31 –MMI Clock Reference warning.......................................................................................................................36
Figure 32 –Licensing.......................................................................................................................................................38
Figure 33 –Inputs Node................................................................................................................................................... 39
Figure 34 –Example of DVB-S/S2 Inputs......................................................................................................................... 40
Figure 35 –DVB-S/S2 Port Detailed View........................................................................................................................41
Figure 36 –Detailed PSI/SI Analysis of Input Services.....................................................................................................42
Figure 37 –PID Scrambled with Even Control Word ........................................................................................................43
Figure 38 –PID Scrambled with Odd Control Word..........................................................................................................43
Figure 39 –Selecting PID 20............................................................................................................................................44
Figure 40 –Selecting PID 550..........................................................................................................................................44
Figure 41 –Manually define Input PSI.............................................................................................................................. 45
Figure 42 –Table Analysis when an Input Service is defined...........................................................................................46
Figure 43 –Verifying manually defined Inputs.................................................................................................................. 46
Figure 44 –Defining Manual PSI...................................................................................................................................... 47
Figure 45 –Defining component for service .....................................................................................................................47
Figure 46 –Edit Language descriptor............................................................................................................................... 48
Figure 47 –Editing existing Manual PSI........................................................................................................................... 49
Figure 48 –DVB-S2 Input................................................................................................................................................ 50
Figure 49 –Edit DVB-S/S2 Port Configuration .................................................................................................................51
Figure 50 –Edit DVB-S/S2 (HW Rev. 2.0) Port Configuration..........................................................................................51
Figure 51 –DVB-S/S2 Status View..................................................................................................................................52
Figure 52 –ASI Input.......................................................................................................................................................53
Figure 53 –ASI Edit Dialog.............................................................................................................................................. 53
Figure 54 –ASI Status View.............................................................................................................................................54
Figure 55 –QAM Input..................................................................................................................................................... 55
Figure 56 –QAM Edit Dialog............................................................................................................................................ 56
Figure 57 –QAM Status View'..........................................................................................................................................56
Figure 58 –COFDM Input................................................................................................................................................58
Figure 59 –COFDM Edit Dialog.......................................................................................................................................59
Figure 60 –COFDM Status View .....................................................................................................................................59
Figure 61 –IP Input..........................................................................................................................................................61
Figure 62 –Edit IP Port.................................................................................................................................................... 62
Figure 63 –IP Input Port Status....................................................................................................................................... 63
Figure 64 –Setup of IPv6 input........................................................................................................................................ 64
Figure 65 –Edit IP Port for IGMP source filtering.............................................................................................................65
Figure 66 –IP Input Page (for Modules with FEC)............................................................................................................65
Figure 67 –IP Input Port Status (for Modules with FEC) ..................................................................................................66
Figure 68 –IP Input Seamless module Status Parameter view ........................................................................................68
Figure 69 –IP Input Seamless module Status Parameter detailed view. ..........................................................................68
Figure 70 –8VSB Input....................................................................................................................................................69
Figure 71 –8VSB Status View.........................................................................................................................................70

MC3x00 –User Manual
Page 9 / 213
Figure 72 –QAM-B Input ................................................................................................................................................. 71
Figure 73 –QAM-B Status View....................................................................................................................................... 72
Figure 74 –DVB-T2 Input ................................................................................................................................................ 73
Figure 75 –DVB-T/ Input Port Configuration.................................................................................................................... 74
Figure 76 –DVB-T Status Parameter view....................................................................................................................... 75
Figure 77 –DVB-T2 Status Parameter view..................................................................................................................... 76
Figure 78 –Conditional Access Node...............................................................................................................................77
Figure 79 –CAM Configuration within the Service Properties Dialog................................................................................ 78
Figure 80 –CAM Configuration Page...............................................................................................................................79
Figure 81 –CAM Configuration Page (for chassis with a Quad Decoder)......................................................................... 79
Figure 82 –Example of a Menu from Conax ....................................................................................................................82
Figure 83 –Example of List from CryptoWorks ................................................................................................................82
Figure 84 –Example of Enquiry....................................................................................................................................... 82
Figure 85 –Setting up the Bulk Descrambler Module....................................................................................................... 84
Figure 86 –Configuring Verimatrix Parameters................................................................................................................ 85
Figure 87 –Additional VKS Parameters........................................................................................................................... 86
Figure 88 –Creating a BISS Mode 1 Key......................................................................................................................... 87
Figure 89 –Setting up a BISS Scrambling Service........................................................................................................... 88
Figure 90 –Setting up a BISS Descrambling Service.......................................................................................................88
Figure 91 –Scrambler Module Architecture......................................................................................................................89
Figure 92 –Scramblers Overview ....................................................................................................................................90
Figure 93 –Adding an ECM Generator ............................................................................................................................91
Figure 94 –Editing ECMGs..............................................................................................................................................91
Figure 95 –Adding an ECM.............................................................................................................................................92
Figure 96 –Editing an existing ECM ................................................................................................................................93
Figure 97 –Adding an EMM Generator............................................................................................................................ 94
Figure 98 –Editing an EMM Generator............................................................................................................................95
Figure 99 –Adding an EMM/PD.......................................................................................................................................95
Figure 100 –Edit an existing EMM/PD............................................................................................................................. 96
Figure 101 –Adding an EIS .............................................................................................................................................97
Figure 102 –Edit an EIS service......................................................................................................................................98
Figure 103 –Decoders Node ........................................................................................................................................... 99
Figure 104 –Decoder Status Dialog............................................................................................................................... 101
Figure 105 –MPEG-2/4 SD/HD Quad RF Decoder Configuration.................................................................................. 104
Figure 106 –MPEG-2/4 SD/HD SDI Decoder Configuration........................................................................................... 104
Figure 107 –Illustration of the Video Aspect Ratio Conversion Parameter..................................................................... 105
Figure 108 –CC Burn-in parameter ............................................................................................................................... 109
Figure 109 –Decoders with Dolby® Digital Plus option.................................................................................................. 110
Figure 110 –Decoders with Dolby® Digital Plus option.................................................................................................. 111
Figure 111 –Manual Channel spacing........................................................................................................................... 115
Figure 112 –Adjacent RF Spacing under OIRT ............................................................................................................. 116
Figure 113 –TVMOD- PAL/SECAM Switching in decoders............................................................................................ 118
Figure 114 –Carrier offset for TV MOD.......................................................................................................................... 119
Figure 115 –Genlock feature......................................................................................................................................... 119
Figure 116 –Genlock offset feature ............................................................................................................................... 120
Figure 117 –Enable and Disable OSDM........................................................................................................................ 120
Figure 118 –Outputs View............................................................................................................................................. 122
Figure 119 –Dragging and Dropping a Service..............................................................................................................123
Figure 120 –Auto Service modes ..................................................................................................................................124
Figure 121 –Auto All Services output configuration .......................................................................................................125
Figure 122 –Stopping a selected service....................................................................................................................... 125
Figure 123 –Default Stream Properties for IP Modules..................................................................................................126
Figure 124 –Default Stream Properties for all other Modules......................................................................................... 126
Figure 125 –Service Grouping....................................................................................................................................... 127
Figure 126 –Layout of Properties Dialog for an MPTS................................................................................................... 127
Figure 127 –Layout of Properties Dialog for an SPTS ................................................................................................... 128
Figure 128 –Transport Tab for ASI Modules..................................................................................................................129
Figure 129 –Delivery Descriptors for Cable................................................................................................................... 129
Figure 130 –Delivery Descriptors for Satellite................................................................................................................130
Figure 131 –Delivery Descriptors for Terrestrial.............................................................................................................130
Figure 132 –Import TS PIDs..........................................................................................................................................130
Figure 133 –EMM Tab for IP Modules........................................................................................................................... 131
Figure 134 –Passthrough Option for EMMs in SPTS..................................................................................................... 131
Figure 135 –PSI Tab for IP Modules ............................................................................................................................. 132
Figure 136 –PSI Tab for a service encapsulated within an MPTS.................................................................................. 132
Figure 137 –EPG Tab for IP Modules............................................................................................................................ 133
Figure 138 –Service Tab for IP SPTS............................................................................................................................ 133
Figure 139 –Components Tab for IP SPTS ................................................................................................................... 135
Figure 140 –Components multiplexing .......................................................................................................................... 137
Figure 141 –Scrambling Tab for IP SPTS...................................................................................................................... 138
Figure 142 –Scrambling Tab for IP SPTS with BISS ..................................................................................................... 139
Figure 143 –Port Settings Tab for IP Modules...............................................................................................................140
Figure 144 –Forward Error Correction Panel for IP Modules ......................................................................................... 140
Figure 145 –Output Redundancy Panel for IP Modules................................................................................................. 141
Figure 146 –Enabling CBR Mode.................................................................................................................................. 142
Figure 147 –Port Settings Tab for IP output modules with IPv6..................................................................................... 142

MC3x00 –User Manual
Page 10 / 213
Figure 148 –Dragging and Dropping a Service with IPv6 Address.................................................................................143
Figure 149 –Port Settings Tab for ASI Modules............................................................................................................. 143
Figure 150 –MIP Parameters for ASI Modules ..............................................................................................................144
Figure 151 –Device Setup Node....................................................................................................................................145
Figure 152 –16QAM Annex A/C Setup.......................................................................................................................... 145
Figure 153 –16QAM Annex B Setup ............................................................................................................................. 146
Figure 154 –Port Settings Tab for COFDM Modules .....................................................................................................146
Figure 155 –DVB-S2 Output –Port Setting Configuration .............................................................................................. 147
Figure 156 –DVB-S2 Output –Linear Pre-correction...................................................................................................... 149
Figure 157 –DVB-T2 Output –Port Setting Configuration............................................................................................... 150
Figure 158 –Transport Tab for the Virtual QAM Output ................................................................................................. 151
Figure 159 –Port Settings Tab for the Virtual QAM Output ............................................................................................ 151
Figure 160 –Transparent Mode..................................................................................................................................... 152
Figure 161 –Stream Properties for Semi-transparent MPTS.......................................................................................... 152
Figure 162 –PSI Networks ............................................................................................................................................ 154
Figure 163 –Edit PSI Networks ..................................................................................................................................... 155
Figure 164 –Associate transport stream with PSI network............................................................................................. 155
Figure 165 –PSI Base Values tab (DVB Profile)............................................................................................................ 155
Figure 166 –Edit NIT Settings ....................................................................................................................................... 156
Figure 167 –Edit NIT Settings with DigitalEuorpe having HD simulcast services ........................................................... 157
Figure 168 –Edit BAT Settings...................................................................................................................................... 158
Figure 169 –TOT Settings Dialog.................................................................................................................................. 159
Figure 170 –PSI Synchronization Tab........................................................................................................................... 160
Figure 171 –Generic Descriptor Tab ............................................................................................................................. 161
Figure 172 –Setup Tab..................................................................................................................................................163
Figure 173 –PSI Domains............................................................................................................................................. 165
Figure 174 –FM Radio Page ......................................................................................................................................... 167
Figure 175 –FM Radio Settings Page............................................................................................................................ 167
Figure 176 –Editing Channel Configuration................................................................................................................... 169
Figure 177 –FM Radio Advanced Settings .................................................................................................................... 170
Figure 178 –Editing Channel Configuration (for RDS) ................................................................................................... 171
Figure 179 –Auxiliary RDS Configuration ...................................................................................................................... 172
Figure 180 –Advanced UECP Addressing Setup........................................................................................................... 172
Figure 181 –Dynamic Looping.......................................................................................................................................173
Figure 182 –Stereo override in RDS menu.................................................................................................................... 173
Figure 183 –Audio Leveling Effect................................................................................................................................. 174
Figure 184 –Setting up Audio Leveling.......................................................................................................................... 174
Figure 185 –EPG Node................................................................................................................................................. 175
Figure 186 –EPG Status Node...................................................................................................................................... 175
Figure 187 –EPG Setup................................................................................................................................................ 176
Figure 188 –EPG Sync Peer Units................................................................................................................................ 177
Figure 189 –Manually adding an EIT Source PID.......................................................................................................... 178
Figure 190 –Setting up EPG within the Outputs Node................................................................................................... 178
Figure 191 –Setting a Playout Rate............................................................................................................................... 179
Figure 192 –Setting a Playout Limit............................................................................................................................... 180
Figure 193 –Setting a Priority........................................................................................................................................180
Figure 194 –EPG Node................................................................................................................................................. 181
Figure 195 –Input Redundancy Configuration ...............................................................................................................182
Figure 196 –Configuring Service-based Input Redundancy........................................................................................... 183
Figure 197 –Configuring Port-based Input Redundancy................................................................................................ 184
Figure 198 –Redundancy Switching Triggers................................................................................................................ 185
Figure 199 –Signal Flow within a Unit with Two Backplanes.......................................................................................... 186
Figure 200 –Internal Redundancy ................................................................................................................................. 187
Figure 201 –Removing Inputs ....................................................................................................................................... 189
Figure 202 –Setting up ECMG redundancy................................................................................................................... 192
Figure 203 –Setting up EMMG redundancy................................................................................................................... 193
Figure 204 –Output Redundancy...................................................................................................................................194
Figure 205 –Edit Redundancy Options.......................................................................................................................... 195
Figure 206 –Output Redundancy Port Settings ............................................................................................................. 196
Figure 207 –Service View ............................................................................................................................................. 198
Figure 208 –Service View Options ................................................................................................................................ 199
Figure 209 –Output View............................................................................................................................................... 200
Figure 210 –Output View Options.................................................................................................................................. 201
Figure 211 –Hardware View.......................................................................................................................................... 201
Figure 212 –Active alarms............................................................................................................................................. 202
Figure 213 –Example of IP Input Module with Status LED............................................................................................. 203
Figure 214 –Alarm History.............................................................................................................................................203
Figure 215 –Registered Alarms..................................................................................................................................... 205
Figure 216 –An alarm with specific alarm description.................................................................................................... 205
Figure 217 –Five Trap Destinations and the Alarm Filter can be set in the GUI............................................................. 205
Figure 218 –A Module with its Ejector released............................................................................................................. 208
Figure 219 –Opening of Air Vents ................................................................................................................................. 209
Figure 220 –Saving Importing and Exporting Chassis Configuration .............................................................................210
Figure 221 –Hardware IP reset DIP switch.................................................................................................................... 211

MC3x00 –User Manual
Page 11 / 213
Abbreviations
ASI
Asynchronous Serial Interface
CAM
Conditional Access Module
CI
Common Interface
COFDM
Coded Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing
DDM
Dual Decoder Module
DVB
Digital Video Broadcasting
EBU
European Broadcasting Union
ECM
Entitlement Control Message
MPTS
Multiple Program Transport Stream
NTP
Network Time Protocol
QPSK
Quadrature Phase Shift Keying
SI
Service Information
SPTS
Single Program Transport Stream
VANC
Vertical Ancillary Data Space
VBI
Vertical Blanking Interval
VPS
Video Programming System

MC3x00 –User Manual
Page 12 / 213
1 Introduction
Thank you for purchasing our products. Our high-quality product range is aimed at the professional
segment of the video distribution market.
This manual describes how to install, configure, and operate your new equipment. It is written for
professional operators of video distribution systems and assumes a prerequisite level of technical
knowledge.

MC3x00 –User Manual
Page 13 / 213
2 Installation and Safety
The unit is designed to offer operators reliability and flexibility. It consists of a chassis in which a
number of modules can be installed. To cater to specific system requirements, the chassis can be
configured to host functional modules best suited for a given scenario.
ATEME products can be delivered in different chassis variations - a 1RU chassis and a 4RU chassis.
The product models MC3000 represent the 4RU chassis, while the product models MC3100
represents the 1RU chassis. Both chassis variations use the same HW insertion modules and run the
same SW platform.
2.1 The 4RU Chassis
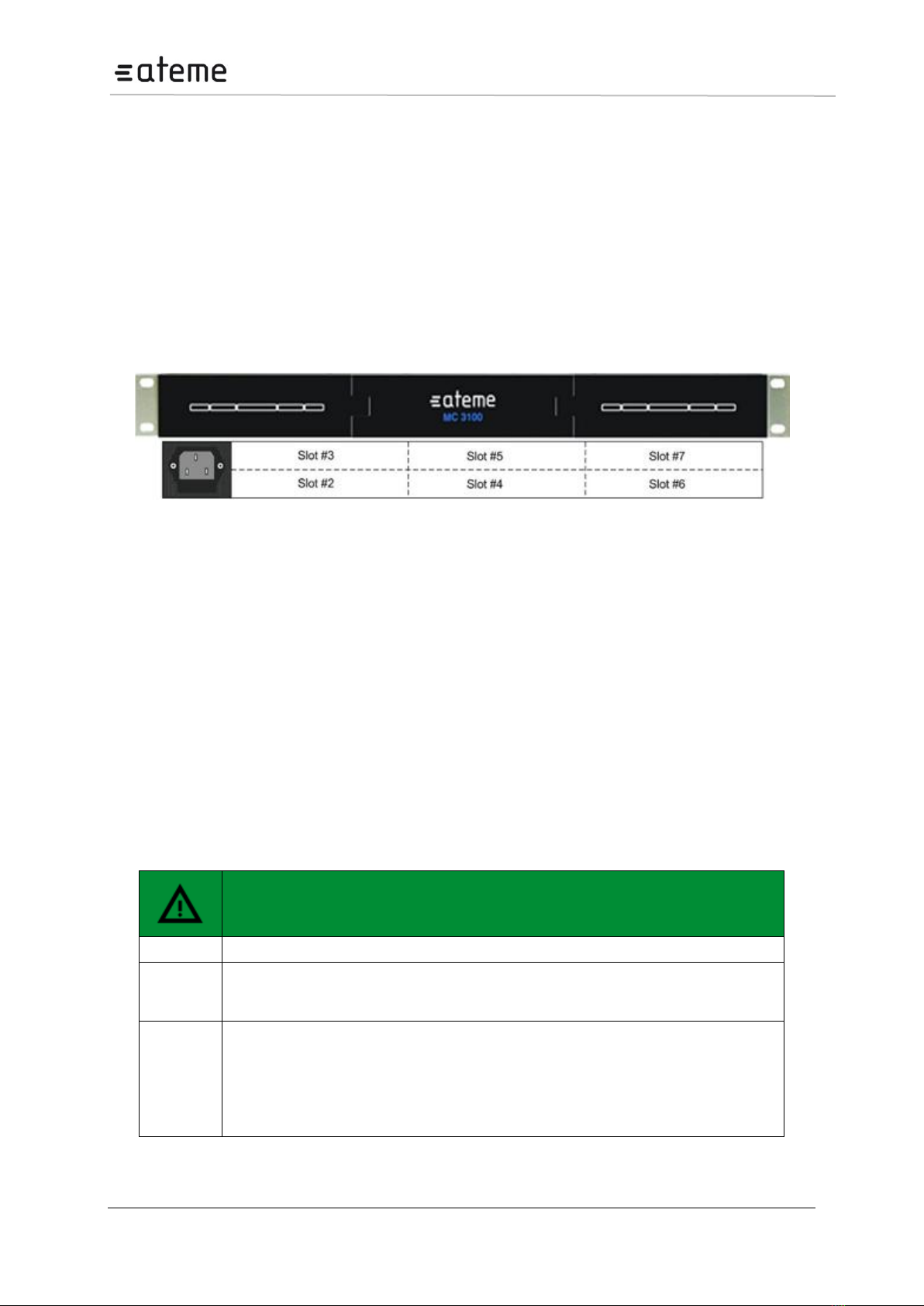
The 4RU chassis consists of a total of 18 slots all of which can host functional modules. Slot number 0
is dedicated to host the switch module and slot number 17 can only host multi-slot input modules.
Alternatively a second switch module can be placed in slot 17 for some redundancy configurations.
The remaining 16 slots are identical and can be occupied by any of the functional modules available.
A 4RU chassis including a mandatory switch module, power supply connectors, and module slots is
shown in Figure below. Power modules and fan modules are inserted from the back.
Figure 1 –4RU chassis with power connectors, switch module and available slots.
2.1.1 Ventilation
The 4RU chassis has forced air flow from front to back in the chassis, allowing for multiple units to be
stacked above each other with no space in between. However, adequate space must be provided in
front of and behind the unit for effective ventilation.
2.1.2 Replacing the power supply module
The 4RU chassis can be installed with one or two power supply modules. The modules can be
exchanged from the rear of the unit. The chassis delivered with a single power module can be updated
by acquiring additional power module.
If power is lost in one of the Power supplies, the other can feed the entire chassis. It is recommended
to connect each input power at different circuits.
MC3x00 –User Manual
Page 14 / 213
2.2 The 1RU Chassis
The 1RU chassis consists of a total of 9 slots plus a slot for the switch module. Modules can be
inserted in the front and from the back. Modules inserted in the front are not hot-swappable and can
only be serviced by factory or by authorized service facilities. However, modules inserted from the
back can be serviced in the field. The mandatory switch module is placed in slot 0 located at the front
upper right corner behind the front cover. Slot 1 is at the front below the switch module and slots 8 and
9 are at the front on the left. Slot numbers 2 to 7 are at the back as illustrated in Figure below.
Slot 1 can only support either no module, or an IP IO module or descrambler module. Slots 8 and 9
can only support descrambler modules. Slots 2 to 7 can hold any 1 or 2 slot wide module available.
Figure 2 shows the front and rear view of the 1RU chassis including a mandatory switch module,
power supply connectors, and module slots.
Figure 2 –1RU chassis with power connector, switch module and available slots; front
and rear view.
2.2.1 Ventilation
The 1RU chassis has forced air flow from left to right allowing for multiple units to be stacked above
each other with no space in between. However, adequate space must be provided on the sides for
effective ventilation.
2.2.2 Replacing the power supply module
The 1RU chassis comes with a single power module. On failure, the case should be sent to the
factory.
2.3 Safety Considerations
The unit must be connected to a grounded power connection. The power input connector is a
disconnect device. To remove the power from the device, the power cables needs to be physically
removed from the power input connector.
Mandatory Safety Instructions
1
The equipment must be installed by a qualified person.
2
For that equipment with grounding, connect the driver before connecting the power
cord. So opposite the power cord must be removed before removing the driver of the
ground.
3
The equipment must be installed in a restricted area where:
Only qualified technicians have access or who know the most important safety
measures.
Access to the area where the devices are installed will be using a tool, lock and
key, or any other safety device, and in addition the site will be controlled by an
authorized person.

MC3x00 –User Manual
Page 15 / 213
2.4 Installation
2.4.1 Power supply rating
The 4RU chassis is supplied with either a 100-240V AC 50/60 Hz power or 48V DC power. The 100-
240V AC 50/60 Hz power supply is rated for maximum 300W, 400W. The 48V DC power is rated for
maximum 400W. Figures 3, 4, 5 and 6 below shows the power supply inlets.
The 1RU chassis is supplied with a 100-240V AC 50/60 Hz power rated for maximum 200W.
2.4.2 4RU chassis with 300 and 400W AC Power
The chassis can hold two power supplies for redundancy and has independent power inlets for the two
supplies.
Figure 3 –Power Input for 4RU chassis with 300 and 400 Watt AC power

MC3x00 –User Manual
Page 16 / 213
2.4.3 4RU chassis with 400W DC (-48Volt) power supply
The chassis can hold two power supplies for redundancy and has independent power inlets for the two
supplies.
Figure 4 –Front plate of dual 48V Power Supply in a MC3000
Figure 5 –Layout of 48V DC Power Supply Connector
2.4.4 1RU chassis
The power input connector is located at the back of the unit.
Figure 6 –Power Input Connector for 1RU Chassis

MC3x00 –User Manual
Page 17 / 213
2.5 Laser Safety
The Optical SFP modules used in the MC3000 and MC3100 products are classified as class 1 laser
products according to IEC 60825-1 and are classified as class 1 laser products per CDRH, 21 CFR
1040 Laser Safety requirements.
Depending on the products configuration, the MC3000 and MC3100 products can be equipped with
multiple insertion modules containing housing for optical SFPs.
When installing SFP modules, please ensure that the module be placed in the housing present at the
front of the IP input/output module. Once inserted, the SFP module will become active.
2.5.1 FDA/CDRH Compliant SFP modules
The below list of Optical SFP modules have been selected with regards to the FDA/CDRH laser safety
requirements as the only optical modules allowed used with the ATEME products in the USA, and any
other countries and states that require compliance according to FDA/CDRH laser safety regulations.
Manufacturer
Model
wave length [nm]
Max output power1
Finisar
FTLF8519P2xCL
850 nm
-3 dBm
Finisar
FTLF8519P2xNL
850 nm
-3 dBm
Finisar
FTLF8519P2xTL
850 nm
-2.5 dBm
Finisar
FTLF1318P2xCL
1310 nm
-3 dBm
Finisar
FTLF1318P2xTL
1310 nm
-3 dBm
Finisar
FTLF1419P1xCL
1310 nm
5 dBm
Finisar
FTLF1518P1BTL
1550 nm
5 dBm
Finisar
FTLF1519P1xCL
1550 nm
5 dBm
Finisar
FTLF1519P1xNL
1550 nm
5 dBm
Finisar
FTLF1619P1xCL
1550 nm
5 dBm
Finisar
FWLF15217Dxx
1471, 1491, 1511, 1531
1551, 1571, 1591, 1611
5 dBm
Finisar
FWDM16197Dxx
1471, 1491, 1511, 1531
1551, 1571, 1591, 1611
5 dBm
Avago Technologies
AFBR-5710Z
850 nm
-3 dBm
Avago Technologies
AFBR-5715Z
850 nm
-3 dBm
Avago Technologies
AFCT-5710Z
1310 nm
-3 dBm
Avago Technologies
AFCT-5715Z
1310 nm
-3 dBm
OCP
TRXAG1SX
850 nm
-4 dBm
OCP
TRPEG1KVX-E1G
1550 nm
5 dBm
2.5.2 Warning: Radiation
Caution
Use of controls or adjustment or performance of procedures other than those
specified herein may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
1
Class 1 Laser Safety per FDA/CDRH and EN (IEC) 60825 regulations

MC3x00 –User Manual
Page 18 / 213
2.5.3 Labels
The following illustrations show the labels attached to the products, according to the standards.
A classification label is attached to the top cover of the MC3000 and MC3100 products.
Figure 7 –Classification label
A CDRH identification label according to 21 CFR 1010.3 is attached on the side of the MC3000 and
MC 3100 products.
Figure 8 –CDRH identification label

MC3x00 –User Manual
Page 19 / 213
3 Signal Connection
3.1 Connecting switch modules
Configuration, management and monitoring of you ATEME unit are done via the management port on
the switch module. The switch module will contain the database for the full configuration of the unit.
One switch module (in some configuration two switch modules) must be installed in all 1 RU and all 4
RU chassis.
Please refer to product datasheets for module identification.
3.1.1 Switch module with MMI
The switch module is equipped with one electrical connector (RJ45) for management. Automatic
sensing of 10/100/1000Mbit Ethernet connections is supported. For a 1000Mbit connection the
Ethernet cable must be a category 6 cable.
The management port should be connected to your management network. Please refer to section 4 for
configuration.
3.1.2 Switch module with MMI and IP IO
The switch module with management and two data ports is equipped with three electrical connectors
(RJ45) or one electrical connector (RJ45) and two SFP connectors. Two RJ45 electrical connectors or
two SFP connectors are for data. The last RJ45 electrical connector is for management
Automatic sensing of 10/100/1000Mbit Ethernet connections is supported on all RJ45 ports. For a
1000Mbit connection, the Ethernet cable must be a category 6 cable.
The management port should be connected to your management network and the data port to you
data network carrying the video streaming content. Please refer to section 4 for configuration.
Each port have a unique IP address and both data ports can be used at the same time as wither 2 IP
input ports, 2 IP output ports or 1 IP input and 1 IP output port.
3.2 Connecting Input Signals
Please refer to product datasheets for module identification.
3.2.1 IP Input
The IP input module is equipped with two electrical connectors (RJ45) and one SFP connector. One
RJ45 electrical connector and the SFP connector are for data. The second RJ45 electrical connector
marked “control” is not in use. It is not required to configure the IP address or connect the port to the
IP network.
Automatic sensing of 10/100/1000Mbit Ethernet connections is supported. For a 1000Mbit connection,
the Ethernet cable must be a category 6 cable.
The IP address for both the electrical (RJ45) and the optical (SFP) connectors for data is the same.
Consequently both connectors cannot be used simultaneously. These inputs are automatically
activated by IP connection. The first port activated (by establishing a link to the router) will be the
active port. To activate the other port, remove the cable from the active port.
3.2.2 ASI Input
Each ASI input module has three independent ASI inputs. The ASI connector is a 75Ω BNC
connector. The maximum input rate per connector is 212Mbit/s in burst mode.
The ASI module is equipped with an electrical connector (RJ45) marked “control” that is not in use. It
is not required to configure the IP address or connect the port to the IP network.

MC3x00 –User Manual
Page 20 / 213
3.2.3 DVB-S/S2 Input
The DVBS-S/S2 supports both DVB-S (QPSK) and DVB-S2 (DVB-S2 is a SW option). Each DVB-
S/S2 input module has 4 independent L-Band inputs. Each input is a 75Ω F that can be connected
either directly to an LNB, an L-Band distribution amplifier, or switch. The maximum input level is -
25dBm. The recommended input level is between -30dBm and -40dBm.
One ASI output port is available for monitoring. Any of the four L-Band inputs can be copied to the ASI
output without affecting the services in use. The ASI connector is a 75Ω BNC connector.
The DVB-S/S2 module is equipped with an electrical connector (RJ45) marked “control” that is not in
use. It is not required to configure the IP address or connect the port to the IP network.
3.2.4 COFDM Input
Each COFDM input module has one 75Ω F connector. The input is distributed to four tuners internally,
so each module can receive four independent frequencies. The maximum input level is -15dBm. The
recommended input level is between -30dBm and -50dBm. (An older version of this module exists with
different input levels.)
One ASI output port is available for monitoring. Any of the four COFDM inputs can be copied to the
ASI output without affecting the services in use. The ASI connector is a 75Ω BNC connector.
The COFDM module is equipped with an electrical connector (RJ45) marked “control” that is not in
use. It is not required to configure the IP address or connect the port to the IP network.
3.2.5 DVB-T/T2 Input
Each DVB-T/T2 input module has one or four 75Ω F connector. For the module having one input
connector, the input is distributed to four tuners internally, so each module can receive four
independent frequencies. For the module with 4 inputs, each input is directly connected to a tuner.
The maximum input level is -10dBm (both modules). The recommended input level is between -
20dBm and -40dBm (optimal lever will depend on modulation used).
This manual suits for next models
2
Table of contents